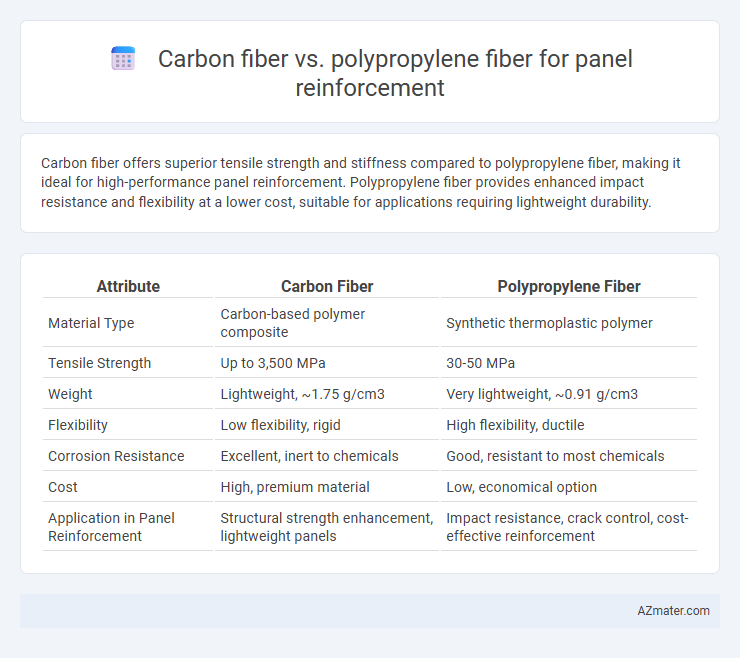
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for high-performance panel reinforcement. Polypropylene fiber provides enhanced impact resistance and flexibility at a lower cost, suitable for applications requiring lightweight durability.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Carbon Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based polymer composite | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3,500 MPa | 30-50 MPa |
| Weight | Lightweight, ~1.75 g/cm3 | Very lightweight, ~0.91 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility, rigid | High flexibility, ductile |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, inert to chemicals | Good, resistant to most chemicals |
| Cost | High, premium material | Low, economical option |
| Application in Panel Reinforcement | Structural strength enhancement, lightweight panels | Impact resistance, crack control, cost-effective reinforcement |
Introduction to Panel Reinforcement Fibers
Carbon fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance panel reinforcement that demands durability and lightweight properties. Polypropylene fiber provides excellent impact resistance and crack control at a lower cost, enhancing the toughness and longevity of concrete panels. Both fibers improve structural integrity, but the choice depends on specific performance requirements and budget constraints.
Composition and Properties of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber consists of thin strands of carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline formation, which gives it exceptional tensile strength and stiffness compared to polypropylene fiber, composed of polymer chains with lower density and flexibility. The high modulus of elasticity and low thermal expansion of carbon fiber make it ideal for panel reinforcement, offering superior durability under mechanical stress and environmental exposure. Carbon fiber's composition provides enhanced resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and UV degradation, outperforming polypropylene fibers in long-term structural applications.
Overview of Polypropylene Fiber Characteristics
Polypropylene fiber offers excellent chemical resistance, low density, and high impact toughness, making it a cost-effective reinforcement option for concrete panels. Its hydrophobic nature reduces moisture absorption, enhancing durability and minimizing microcracking under freeze-thaw cycles. While it lacks the tensile strength of carbon fiber, polypropylene fiber effectively controls shrinkage and improves impact resistance in panel reinforcement applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength, often exceeding 3,500 MPa, compared to polypropylene fiber's typical range of 300-600 MPa, making it ideal for high-performance panel reinforcement. In terms of durability, carbon fiber offers superior resistance to fatigue, chemical degradation, and environmental factors such as UV exposure and moisture, ensuring long-term structural integrity. Polypropylene fiber, while more economical and resistant to impact and corrosion, generally provides lower mechanical strength and less stiffness, limiting its application in panels that require advanced load-bearing capacity.
Weight and Density Differences
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to polypropylene fiber, making it an ideal choice for lightweight panel reinforcement. Carbon fiber density typically ranges around 1.6 g/cm3, significantly higher than polypropylene fiber, which has a density of approximately 0.9 g/cm3. This density difference contributes to carbon fiber panels being both lighter and stronger, enhancing structural performance without adding excessive weight.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Carbon fiber offers superior resistance to environmental factors such as UV radiation, moisture, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for long-term durability in panel reinforcement. Polypropylene fiber provides moderate resistance with good moisture tolerance but tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and harsh chemicals. Choosing carbon fiber ensures enhanced structural integrity and longevity in demanding environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Fiber vs Polypropylene
Carbon fiber panels exhibit significantly higher material costs, averaging $20 to $30 per pound compared to polypropylene's $1 to $3 per pound, impacting upfront investment. Despite the premium, carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance expenses. Polypropylene reinforcement provides a cost-effective solution for moderate performance needs, but may incur higher lifecycle costs due to lower resistance to fatigue and environmental degradation.
Installation and Workability in Panels
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity but requires specialized tools and skilled labor for installation, making the process more complex and time-consuming compared to polypropylene fiber. Polypropylene fiber is highly workable, easily mixed into concrete panels without special equipment, and improves crack resistance and durability while allowing faster installation. The choice between these fibers depends on balancing performance requirements with installation efficiency and labor costs.
Common Applications in Construction and Industry
Carbon fiber panels are widely used in high-performance construction applications such as bridge retrofitting, seismic strengthening, and protective cladding due to their superior tensile strength, stiffness, and corrosion resistance. Polypropylene fiber reinforced panels find common use in industrial flooring, concrete slab reinforcement, and shotcrete applications where impact resistance, crack control, and cost-efficiency are critical. Both fibers enhance panel durability, but carbon fiber suits structural reinforcement demanding high strength-to-weight ratios, while polypropylene fibers excel in improving toughness and resilience in less structurally critical environments.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Panel Reinforcement
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance panel reinforcement where durability and load-bearing capacity are critical. Polypropylene fiber provides excellent impact resistance and crack control at a lower cost, suitable for non-structural or lightweight panel applications. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints for optimal panel performance.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Panel reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com