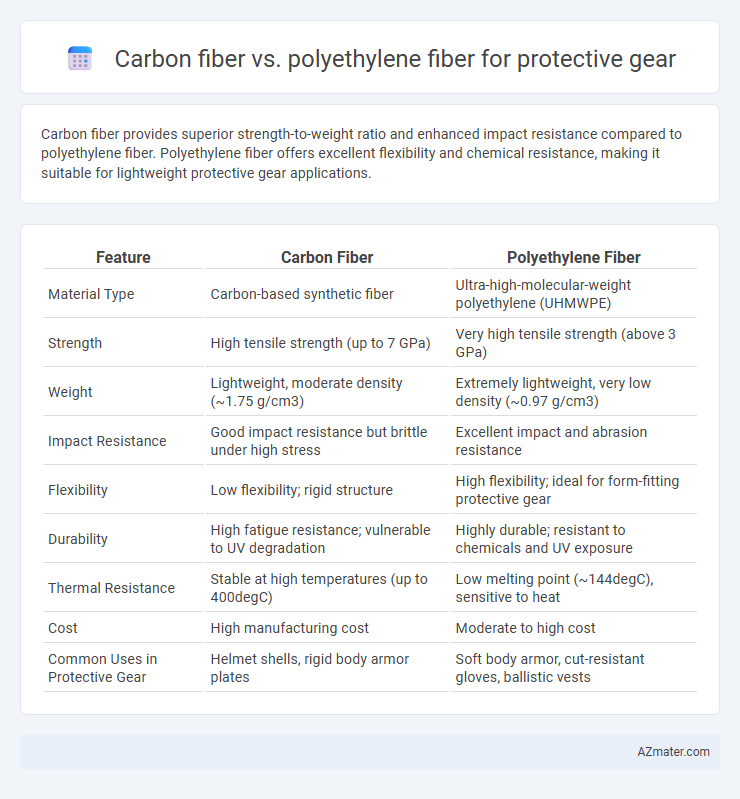
Carbon fiber provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced impact resistance compared to polyethylene fiber. Polyethylene fiber offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance, making it suitable for lightweight protective gear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based synthetic fiber | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) |
| Strength | High tensile strength (up to 7 GPa) | Very high tensile strength (above 3 GPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight, moderate density (~1.75 g/cm3) | Extremely lightweight, very low density (~0.97 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance but brittle under high stress | Excellent impact and abrasion resistance |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility; rigid structure | High flexibility; ideal for form-fitting protective gear |
| Durability | High fatigue resistance; vulnerable to UV degradation | Highly durable; resistant to chemicals and UV exposure |
| Thermal Resistance | Stable at high temperatures (up to 400degC) | Low melting point (~144degC), sensitive to heat |
| Cost | High manufacturing cost | Moderate to high cost |
| Common Uses in Protective Gear | Helmet shells, rigid body armor plates | Soft body armor, cut-resistant gloves, ballistic vests |
Introduction to Protective Gear Materials
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high tensile strength, making it ideal for impact-resistant protective gear. Polyethylene fiber, particularly ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), provides excellent cut resistance, high durability, and lighter weight compared to traditional fibers. Both materials are widely used in ballistic vests, helmets, and other protective equipment, with carbon fiber favored for structural reinforcement and polyethylene fiber for flexible protection.
Overview of Carbon Fiber Properties
Carbon fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, lightweight characteristics, and high resistance to heat and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for advanced protective gear. Its stiffness and ability to absorb impact without deformation provide superior durability and safety in helmets, body armor, and gloves. Compared to polyethylene fiber, carbon fiber offers enhanced structural integrity and thermal stability, crucial for high-performance protective applications.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber Properties
Polyethylene fiber, particularly ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, offering high tensile strength while remaining significantly lighter than carbon fiber. Its chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and excellent impact resistance make it an ideal material for protective gear designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Polyethylene fiber also provides superior flexibility and comfort compared to the more rigid carbon fiber, enhancing wearer mobility in applications such as body armor and helmets.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Carbon fiber outperforms polyethylene fiber in weight, offering a higher strength-to-weight ratio ideal for lightweight protective gear. Polyethylene fiber provides superior flexibility and impact absorption, making it better suited for gear requiring enhanced maneuverability. Selecting between carbon fiber and polyethylene fiber depends on prioritizing either minimal weight or maximum flexibility in protective equipment.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Carbon fiber offers superior impact resistance due to its high tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for protective gear requiring exceptional force absorption. Polyethylene fiber, especially Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), provides excellent durability and impact resistance with lightweight flexibility, often outperforming carbon fiber in abrasion resistance and energy dispersion. Protective equipment leveraging the advanced molecular structure of polyethylene fiber delivers enhanced durability and long-lasting performance in dynamic impact scenarios.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio but tends to be less flexible and can cause discomfort during prolonged use due to stiffness. Polyethylene fiber, such as UHMWPE, provides lightweight, high-impact resistance with superior flexibility and breathability, enhancing wearer comfort and reducing fatigue. Wearability in protective gear significantly benefits from polyethylene's ability to conform to body movements, making it preferable for extended use where comfort is critical.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability for protective gear but comes at a higher cost, often ranging from $20 to $60 per pound, limiting its widespread use. Polyethylene fiber, such as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), provides a more affordable option, typically costing $10 to $25 per pound, with high availability due to mass production in industries like maritime and ballistic protection. The cost-effectiveness and broader accessibility of polyethylene fiber make it a preferred choice for large-scale manufacturing of protective gear, especially where budget constraints are critical.
Applications in Protective Gear
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and high tensile strength, making it ideal for ballistic helmets and body armor that require maximum protection with minimal weight. Polyethylene fiber, especially ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), excels in impact resistance and flexibility, widely used in soft armor vests and cut-resistant gloves for enhanced mobility. Both materials are critical in protective gear applications, with carbon fiber favored for rigid reinforcement and polyethylene fiber prioritized for lightweight, flexible protection.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber offers high strength-to-weight ratio and durability but its production involves energy-intensive processes and generates non-recyclable waste, raising concerns about environmental impact. Polyethylene fiber, particularly Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), provides lightweight protection and can be recycled more efficiently, contributing to better sustainability. However, both materials rely on petrochemical sources, making advances in bio-based alternatives and improved recycling crucial for reducing their ecological footprint in protective gear manufacturing.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Fiber for Protection
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent impact resistance, ideal for high-performance protective gear demanding stiffness and durability. Polyethylene fiber provides exceptional cut resistance, flexibility, and lighter weight, making it suitable for protective applications requiring mobility and abrasion resistance. Selecting the best fiber depends on specific protection needs, balancing impact resistance and flexibility for optimal safety and comfort.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Polyethylene fiber for Protective gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com