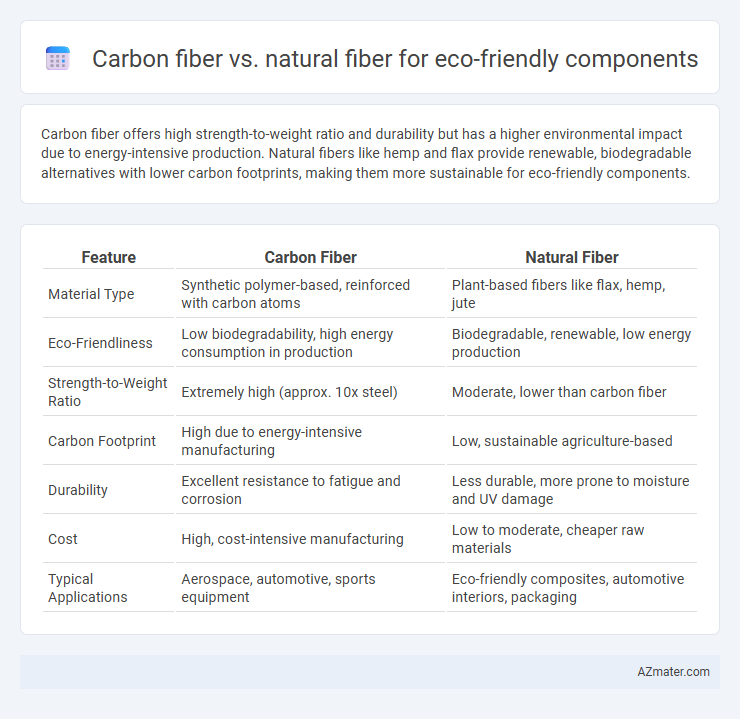
Carbon fiber offers high strength-to-weight ratio and durability but has a higher environmental impact due to energy-intensive production. Natural fibers like hemp and flax provide renewable, biodegradable alternatives with lower carbon footprints, making them more sustainable for eco-friendly components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer-based, reinforced with carbon atoms | Plant-based fibers like flax, hemp, jute |
| Eco-Friendliness | Low biodegradability, high energy consumption in production | Biodegradable, renewable, low energy production |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Extremely high (approx. 10x steel) | Moderate, lower than carbon fiber |
| Carbon Footprint | High due to energy-intensive manufacturing | Low, sustainable agriculture-based |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to fatigue and corrosion | Less durable, more prone to moisture and UV damage |
| Cost | High, cost-intensive manufacturing | Low to moderate, cheaper raw materials |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, automotive, sports equipment | Eco-friendly composites, automotive interiors, packaging |
Understanding Carbon Fiber and Natural Fiber
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability, making it a preferred material in high-performance applications, while its production process involves significant energy consumption and emits carbon dioxide, impacting its eco-friendliness. Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute provide renewable, biodegradable alternatives with lower environmental footprints due to minimal processing and carbon sequestration during growth. Understanding the lifecycle impacts and mechanical properties of both materials is crucial for selecting sustainable components that balance performance with ecological responsibility.
Production Processes and Environmental Impact
Carbon fiber production requires energy-intensive processes involving petroleum-based precursors and high-temperature carbonization, resulting in significant carbon emissions and limited recyclability. Natural fiber production involves renewable plant-based materials such as flax, hemp, or jute, grown with lower energy inputs and carbon footprints, offering better biodegradability and soil health benefits. While carbon fibers provide superior mechanical strength, natural fibers present a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly components due to their lower environmental impact during cultivation and end-of-life disposal.
Material Properties Comparison
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio, high stiffness, and excellent fatigue resistance, making it ideal for lightweight, high-performance eco-friendly components. Natural fibers, such as flax or hemp, provide biodegradability, lower environmental impact, and good specific mechanical properties but generally lack the rigidity and durability of carbon fiber. The choice depends on balancing lightweight strength with sustainability considerations and end-of-life recyclability.
Carbon Footprint Analysis
Carbon fiber exhibits a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive manufacturing processes involving precursor production and high-temperature carbonization, whereas natural fibers like hemp or flax have significantly lower emissions stemming from their renewable growth and minimal processing requirements. Life cycle assessments reveal that natural fibers contribute less to greenhouse gas emissions, making them more advantageous for eco-friendly components focused on sustainability. Despite carbon fiber's superior strength-to-weight ratio, its environmental impact demands consideration in applications prioritizing carbon footprint reduction.
Renewable Resources and Sustainability
Natural fibers like hemp, flax, and jute offer superior sustainability due to their renewable origins, biodegradability, and lower carbon footprint compared to carbon fibers derived from fossil fuels. Carbon fiber production involves high energy consumption and non-renewable petrochemical sources, making it less eco-friendly despite its strength-to-weight ratio advantages. Incorporating natural fiber composites in eco-friendly components enhances renewable resource use and reduces environmental impact in sustainable manufacturing.
Durability and Life Cycle Assessments
Carbon fiber exhibits exceptional durability and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for long-lasting eco-friendly components, although its energy-intensive production can impact its life cycle assessment (LCA). Natural fibers such as hemp, flax, and jute offer biodegradability and lower embodied energy, resulting in more favorable LCAs, despite generally lower mechanical strength and shorter lifespan compared to carbon fiber. Evaluating durability alongside full life cycle assessments highlights natural fibers as sustainable alternatives, while carbon fiber supports high-performance applications requiring extended service life.
End-of-Life Disposal and Recycling
Carbon fiber offers high strength and lightweight properties but poses significant challenges in end-of-life disposal due to its resistance to biodegradation and limited recycling options, often ending in landfills or energy-intensive processes. Natural fibers, such as hemp or flax, are biodegradable and can be composted or recycled more sustainably, significantly reducing environmental impact at disposal. Choosing natural fiber composites enhances eco-friendly component lifecycle management by promoting circularity and reducing reliance on non-renewable recycling technologies.
Applications in Eco-friendly Components
Carbon fiber and natural fiber both serve critical roles in eco-friendly components, with carbon fiber favored for high-strength applications such as lightweight automotive parts and aerospace structures due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability. Natural fibers like hemp, flax, and jute are increasingly used in biodegradable composites for consumer goods, automotive interiors, and construction materials because of their renewability, low environmental impact, and ability to sequester carbon. Industries prioritize natural fibers for sustainability and carbon footprint reduction, while carbon fiber remains essential where performance and long-term durability are critical.
Cost Efficiency and Market Trends
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio but incurs higher manufacturing costs compared to natural fibers, impacting overall cost efficiency in eco-friendly components. Natural fibers such as hemp and flax are gaining traction due to lower raw material costs, biodegradability, and growing consumer demand for sustainable alternatives in automotive and construction markets. Market trends show increasing investment in hybrid composites combining carbon and natural fibers to enhance performance while maintaining eco-friendly credentials and cost-effectiveness.
Future Innovations in Sustainable Materials
Future innovations in eco-friendly components emphasize hybrid composites that combine carbon fiber's exceptional strength and lightweight properties with the biodegradability and renewability of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or jute. Advances in bio-based carbon fiber production and enhanced recycling methods for natural fiber composites aim to reduce environmental impact while maintaining high performance. Emerging technologies in nanocellulose reinforcement and green resin systems further support the development of sustainable, durable materials for automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Natural fiber for Eco-friendly component
 azmater.com
azmater.com