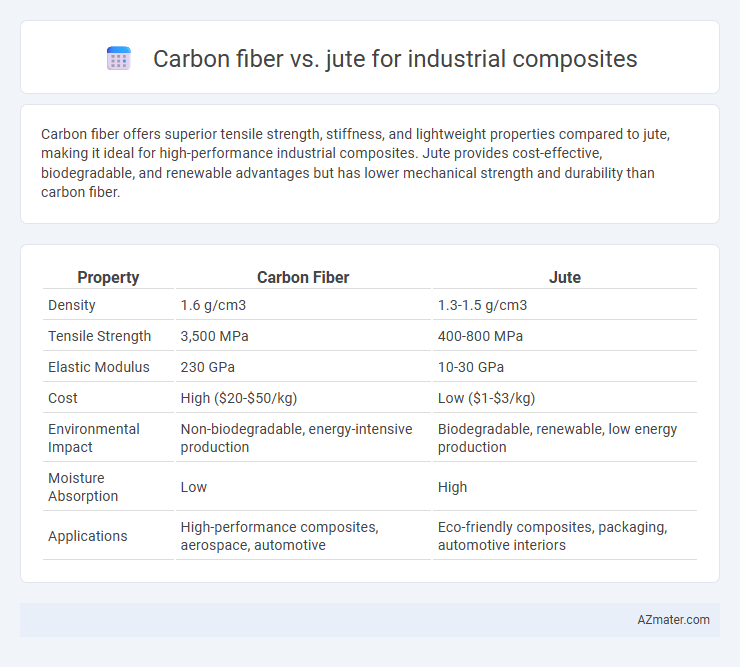
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties compared to jute, making it ideal for high-performance industrial composites. Jute provides cost-effective, biodegradable, and renewable advantages but has lower mechanical strength and durability than carbon fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Jute |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.6 g/cm3 | 1.3-1.5 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 3,500 MPa | 400-800 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 230 GPa | 10-30 GPa |
| Cost | High ($20-$50/kg) | Low ($1-$3/kg) |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production | Biodegradable, renewable, low energy production |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High |
| Applications | High-performance composites, aerospace, automotive | Eco-friendly composites, packaging, automotive interiors |
Introduction to Carbon Fiber and Jute in Industrial Composites
Carbon fiber is a high-strength, lightweight material composed of thin strands of carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline structure, widely used in industrial composites for its exceptional tensile strength and stiffness. Jute, a natural fiber derived from the jute plant, offers biodegradability, low cost, and moderate mechanical properties, making it an eco-friendly alternative in composite manufacturing. The choice between carbon fiber and jute in industrial composites depends on balancing performance requirements, cost efficiency, and environmental impact for diverse applications.
Material Properties Comparison: Carbon Fiber vs Jute
Carbon fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength of up to 7,000 MPa and a low density around 1.6 g/cm3, making it ideal for high-performance industrial composites requiring stiffness and durability. Jute fibers provide moderate tensile strength averaging 400-800 MPa and a density near 1.3 g/cm3, offering biodegradability and cost-effectiveness for sustainable composite applications. While carbon fiber outperforms jute in mechanical properties and thermal stability, jute is favored in industries prioritizing environmental impact and material renewability.
Mechanical Strength and Performance
Carbon fiber offers superior mechanical strength with a tensile strength of approximately 3,500 MPa and a modulus of elasticity around 230 GPa, making it ideal for high-performance industrial composites requiring lightweight and durable materials. Jute fibers, with tensile strength values typically ranging from 200 to 600 MPa and a modulus of about 20 GPa, provide moderate strength but excel in cost-effectiveness and biodegradability for sustainable composite applications. The performance of carbon fiber composites significantly outperforms jute-based composites in terms of stiffness, impact resistance, and fatigue life, though jute composites maintain advantages in ecological impact and vibration damping.
Weight and Density Factors
Carbon fiber composites typically exhibit a density of around 1.6 g/cm3, making them significantly lighter than traditional metals while providing exceptional strength-to-weight ratios for industrial applications. Jute composites have a lower density, approximately 1.3 g/cm3, which translates to lighter weight but with reduced mechanical properties compared to carbon fiber. The choice between carbon fiber and jute for industrial composites heavily depends on the required balance between weight savings and structural performance, with carbon fiber favored for high-strength, lightweight needs and jute preferred for environmentally friendly, cost-effective solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber offers high strength-to-weight ratio and durability but involves energy-intensive manufacturing and produces non-biodegradable waste, raising environmental concerns. Jute, a natural fiber, provides renewable, biodegradable reinforcement with lower carbon footprint and energy consumption during processing, making it a more sustainable choice for industrial composites. Industrial applications increasingly favor jute composites for eco-friendly products aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining adequate mechanical properties.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Fiber vs Jute
Carbon fiber composites typically incur higher production costs due to expensive raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes, making them less cost-effective for large-scale industrial applications. Jute, as a natural fiber, offers a significantly lower material and processing cost, providing an economical alternative for composites while delivering sufficient strength and lightweight characteristics. Cost analysis reveals jute composites can reduce overall expenses by up to 50-70% compared to carbon fiber composites in industrial uses.
Manufacturing and Processing Techniques
Carbon fiber manufacturing involves energy-intensive processes like polyacrylonitrile (PAN) precursor stabilization, carbonization at temperatures exceeding 1,000degC, and surface treatment to enhance resin adhesion, resulting in high strength-to-weight ratio composites ideal for aerospace and automotive industries. Jute processing relies on retting to extract fibers, followed by drying, carding, and weaving, offering biodegradable, low-cost reinforcement with compatibility for bio-based resins, suitable for sustainable industrial composites. Advanced composite fabrication techniques such as resin transfer molding (RTM) are adapted for carbon fiber to optimize fiber alignment and mechanical properties, while jute composites often employ compression molding and extrusion methods optimized to handle the natural fiber's moisture sensitivity and lower thermal stability.
Application Areas: Industrial Use Cases
Carbon fiber composites dominate aerospace, automotive, and high-performance sporting goods due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for load-bearing structural components and precision engineering parts. Jute composites find extensive use in automotive interiors, packaging, and construction panels, valued for their sustainability, low cost, and biodegradability. Industrial applications leverage carbon fiber for critical structural integrity where high mechanical performance is essential, while jute composites serve eco-friendly roles in non-structural or semi-structural applications requiring moderate strength and environmental benefits.
Durability, Maintenance, and Lifespan
Carbon fiber composites offer superior durability with high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications, while jute composites, though less durable, provide adequate mechanical properties for lighter usage and are more susceptible to environmental degradation. Maintenance requirements for carbon fiber are minimal due to its resistance to wear and chemical exposure, whereas jute requires regular inspection and treatment to prevent moisture damage and fungal growth. The lifespan of carbon fiber composites can exceed 20 years under industrial conditions, contrasting with jute composites, which typically last 5 to 10 years depending on exposure and maintenance practices.
Future Trends and Innovations in Composite Materials
Carbon fiber continues to dominate industrial composite applications due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and thermal resistance, but jute fiber gains momentum as a sustainable and cost-effective alternative driven by eco-conscious manufacturing trends. Innovations in hybrid composites combining carbon and natural fibers like jute are enhancing mechanical properties while reducing environmental impact, promoting circular economy principles. Advances in bio-resin systems and nanotechnology integration further push the performance boundaries of jute-based composites, supporting wider adoption in automotive, construction, and aerospace industries.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Jute for Industrial composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com