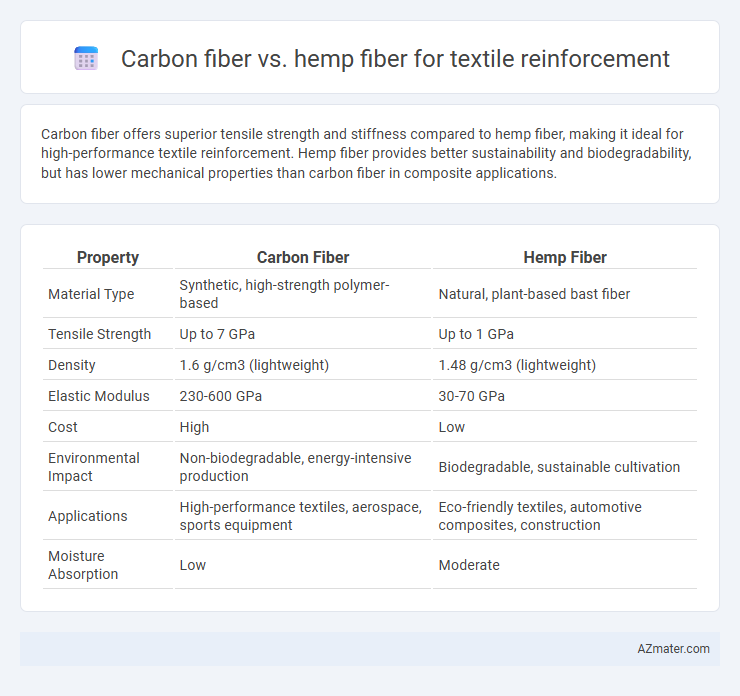
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for high-performance textile reinforcement. Hemp fiber provides better sustainability and biodegradability, but has lower mechanical properties than carbon fiber in composite applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic, high-strength polymer-based | Natural, plant-based bast fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 7 GPa | Up to 1 GPa |
| Density | 1.6 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 1.48 g/cm3 (lightweight) |
| Elastic Modulus | 230-600 GPa | 30-70 GPa |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, energy-intensive production | Biodegradable, sustainable cultivation |
| Applications | High-performance textiles, aerospace, sports equipment | Eco-friendly textiles, automotive composites, construction |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Moderate |
Introduction to Textile Reinforcement Materials
Carbon fiber and hemp fiber represent two distinct classes of textile reinforcement materials, each offering unique mechanical properties and environmental impacts. Carbon fiber is known for its exceptional tensile strength, lightweight characteristics, and high stiffness, making it ideal for advanced composite applications where performance and durability are critical. Hemp fiber, being a natural and biodegradable alternative, provides adequate reinforcement with lower environmental footprint, increased flexibility, and resistance to UV degradation, appealing to sustainable textile manufacturing and eco-friendly composite solutions.
Overview of Carbon Fiber Properties
Carbon fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, stiffness, and lightweight characteristics, making it a preferred material for high-performance textile reinforcement. Its resistance to chemical corrosion and high-temperature tolerance enhances durability in demanding applications such as aerospace and automotive industries. The high modulus-to-weight ratio of carbon fiber contributes to structural integrity without adding significant weight, outperforming natural fibers like hemp in critical engineering contexts.
Overview of Hemp Fiber Properties
Hemp fiber exhibits notable tensile strength, biodegradability, and excellent moisture absorption, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative for textile reinforcement. Its lightweight nature combined with good thermal resistance contributes to enhanced durability and comfort in composite materials. Hemp fibers also offer high acoustic damping properties and resistance to ultraviolet light, supporting their performance in various industrial applications compared to carbon fiber.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Carbon fiber offers significantly higher tensile strength, typically around 3,500 MPa, compared to hemp fiber's tensile strength, which ranges between 550 and 900 MPa. The modulus of elasticity for carbon fiber can exceed 230 GPa, providing superior stiffness, whereas hemp fibers have a modulus around 30 GPa, suitable for lightweight but less rigid applications. While carbon fiber ensures exceptional mechanical performance in demanding textile reinforcement, hemp fiber presents a sustainable alternative with moderate strength and flexibility.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio with a density around 1.6 g/cm3, making it significantly lighter and stiffer compared to hemp fiber, which typically has a density of 1.48 g/cm3 and exhibits more natural flexibility. Hemp fiber provides enhanced flexibility and impact resistance due to its cellulose-based structure, promoting improved energy absorption and bending characteristics in textile reinforcement. The choice between carbon and hemp fibers depends on the required balance between lightweight structural rigidity and adaptable material deformation in composite applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Carbon fiber offers high strength-to-weight ratio but involves energy-intensive production and limited recyclability, raising sustainability concerns. Hemp fiber is biodegradable, requires less water and pesticides, and supports carbon sequestration, making it an eco-friendly alternative for textile reinforcement. The choice between carbon and hemp fibers significantly influences the environmental footprint of composite materials used in automotive and construction industries.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability for textile reinforcement but comes at a significantly higher cost and limited availability due to complex manufacturing processes. Hemp fiber, while less strong, provides excellent cost efficiency and widespread availability as a renewable resource with easier cultivation and processing techniques. Choosing between the two depends on budget constraints and prioritization of sustainable, cost-effective materials versus high-performance, expensive composites.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Carbon fiber for textile reinforcement involves complex manufacturing processes such as polymerization, carbonization at high temperatures, and surface treatment to enhance adhesion with resin matrices, resulting in superior mechanical properties but higher production costs. Hemp fiber processing includes retting, decortication, and mechanical combing to produce coarse, natural fibers that require less energy and chemicals, making it an eco-friendly option but with lower tensile strength compared to carbon fiber. The integration of hemp fibers in textiles often demands compatibilization techniques or hybrid composites to improve bonding and durability in reinforcement applications.
Application Suitability in Textiles
Carbon fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance textile reinforcement in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment applications where durability and weight reduction are critical. Hemp fiber provides excellent biodegradability, breathability, and resistance to UV light, favoring eco-friendly textiles in fashion, interiors, and composite materials targeting sustainability. The choice between carbon fiber and hemp fiber depends on whether mechanical performance or environmental impact is prioritized in the textile reinforcement project.
Future Trends in Reinforcement Fibers
Carbon fiber continues to dominate textile reinforcement due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability, but hemp fiber is gaining traction as a sustainable alternative with lower environmental impact and biodegradability. Future trends indicate a growing emphasis on hybrid composites combining carbon and hemp fibers to optimize mechanical performance and sustainability. Advances in fiber treatment and composite manufacturing technologies are expected to enhance hemp fiber compatibility, driving broader adoption in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Hemp fiber for Textile reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com