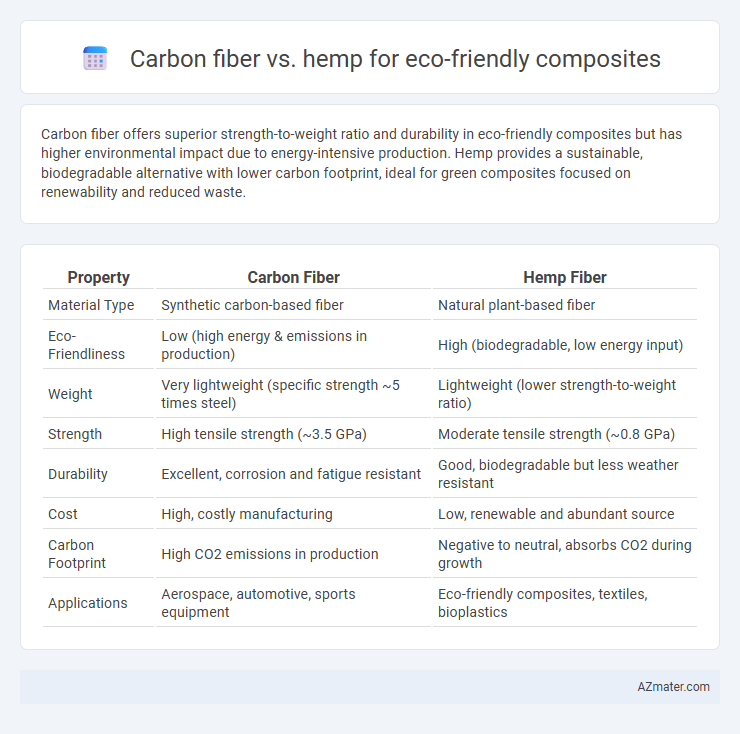
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability in eco-friendly composites but has higher environmental impact due to energy-intensive production. Hemp provides a sustainable, biodegradable alternative with lower carbon footprint, ideal for green composites focused on renewability and reduced waste.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic carbon-based fiber | Natural plant-based fiber |
| Eco-Friendliness | Low (high energy & emissions in production) | High (biodegradable, low energy input) |
| Weight | Very lightweight (specific strength ~5 times steel) | Lightweight (lower strength-to-weight ratio) |
| Strength | High tensile strength (~3.5 GPa) | Moderate tensile strength (~0.8 GPa) |
| Durability | Excellent, corrosion and fatigue resistant | Good, biodegradable but less weather resistant |
| Cost | High, costly manufacturing | Low, renewable and abundant source |
| Carbon Footprint | High CO2 emissions in production | Negative to neutral, absorbs CO2 during growth |
| Applications | Aerospace, automotive, sports equipment | Eco-friendly composites, textiles, bioplastics |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Composites
Eco-friendly composites combine sustainable materials with high-performance properties to reduce environmental impact in manufacturing. Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability but involves energy-intensive production and limited recyclability. Hemp fibers present a renewable, biodegradable alternative with lower carbon footprint and good mechanical properties, making them increasingly popular for green composite applications.
Overview of Carbon Fiber Materials
Carbon fiber is a high-strength, lightweight material composed of thin carbon strands bonded with resin, commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and sports industries for its superior tensile strength and stiffness. Its production involves energy-intensive processes and fossil-fuel-based precursors, resulting in higher environmental impacts compared to natural fibers. Despite its durability and performance advantages, carbon fiber recycling remains challenging, prompting interest in sustainable alternatives like hemp for eco-friendly composites.
Understanding Hemp Fiber Composites
Hemp fiber composites offer a sustainable alternative to carbon fiber by utilizing natural, renewable fibers with a lower environmental impact during cultivation and processing. These composites showcase high strength-to-weight ratios and biodegradability, making them ideal for eco-friendly applications in automotive and construction industries. Advances in resin compatibility and fiber treatment methods significantly improve the mechanical properties and durability of hemp-based composites, supporting their growing adoption in green manufacturing.
Comparative Material Properties
Carbon fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, stiffness, and lightweight characteristics, making it ideal for high-performance eco-friendly composites but has higher embodied energy and limited biodegradability. Hemp fiber provides moderate strength and stiffness with excellent biodegradability, natural vibration damping, and lower environmental impact due to renewable cultivation. When comparing durability, carbon fiber composites outperform hemp in mechanical performance, while hemp composites contribute significantly to sustainability and carbon sequestration benefits in eco-friendly material applications.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Carbon fiber composites exhibit high strength-to-weight ratios but entail significant environmental costs due to energy-intensive production and challenges in recycling. Hemp-based composites offer a renewable and biodegradable alternative with lower carbon footprints and soil regeneration benefits, enhancing their sustainability credentials. Life cycle assessments consistently highlight hemp composites as more eco-friendly, with reduced greenhouse gas emissions and lower toxic waste generation compared to carbon fiber.
Lifecycle Analysis: Carbon Fiber vs. Hemp
Carbon fiber composites have a higher environmental impact due to energy-intensive production and difficulty in recycling compared to hemp composites, which are biodegradable and require less energy in manufacturing. Lifecycle analysis shows hemp composites sequester carbon during growth, reducing overall emissions, while carbon fiber composites often generate significant CO2 emissions through precursor materials and curing processes. Hemp-based composites exhibit lower end-of-life environmental burdens through composting or energy recovery, making them preferable for sustainable composite applications.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Availability
Hemp-based composites offer significant cost advantages over carbon fiber due to lower raw material expenses and reduced energy-intensive processing requirements. Hemp fibers are renewable, widely available, and require less environmental impact during cultivation, providing sustainable resource availability compared to limited and costly carbon fiber precursors. The combination of affordability and abundant biomass positions hemp as a highly cost-efficient alternative for eco-friendly composite production.
Applications in Sustainable Industries
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio ideal for aerospace and automotive sectors, enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Hemp, a renewable resource with low environmental impact, is increasingly used in construction and packaging composites for biodegradable and sustainable alternatives. Both materials support sustainable industries by reducing reliance on traditional plastics and metals while promoting circular economy principles.
Challenges and Limitations
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratios but faces challenges such as high production energy consumption and limited recyclability, impacting its eco-friendliness. Hemp fibers present a renewable, biodegradable alternative with lower carbon footprints, yet suffer from variability in fiber quality and lower mechanical performance compared to carbon fiber. Both materials encounter limitations in large-scale manufacturing processes and consistent material properties for structural applications in eco-friendly composites.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Hemp-based composites exhibit significant future potential due to their biodegradability, lower carbon footprint, and renewable sourcing compared to conventional carbon fiber materials. Innovations in bio-resin matrices and fiber treatment technologies are enhancing hemp composite mechanical properties, making them increasingly viable for automotive and aerospace applications. Ongoing research into hybrid composites integrating hemp and carbon fibers aims to optimize strength-to-weight ratios and sustainability metrics, positioning hemp as a competitive eco-friendly alternative in advanced composite manufacturing.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Hemp for Eco-friendly composite
 azmater.com
azmater.com