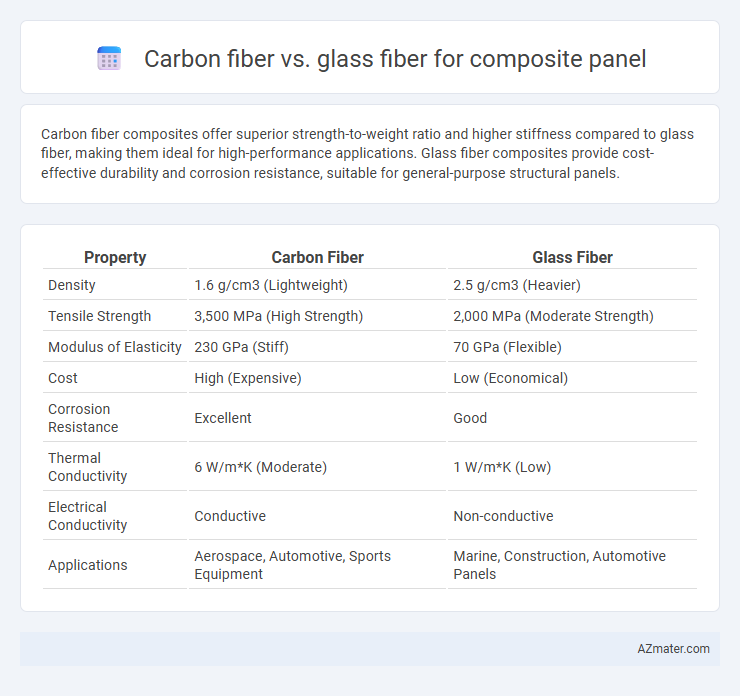
Carbon fiber composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratio and higher stiffness compared to glass fiber, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Glass fiber composites provide cost-effective durability and corrosion resistance, suitable for general-purpose structural panels.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.6 g/cm3 (Lightweight) | 2.5 g/cm3 (Heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | 3,500 MPa (High Strength) | 2,000 MPa (Moderate Strength) |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 230 GPa (Stiff) | 70 GPa (Flexible) |
| Cost | High (Expensive) | Low (Economical) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Conductivity | 6 W/m*K (Moderate) | 1 W/m*K (Low) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Conductive | Non-conductive |
| Applications | Aerospace, Automotive, Sports Equipment | Marine, Construction, Automotive Panels |
Introduction to Composite Panels
Composite panels consist of a matrix material reinforced with fibers to enhance strength and durability, with carbon fiber and glass fiber being the most common reinforcements. Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace and automotive industries. Glass fiber provides cost-effective durability and corrosion resistance, widely used in construction and marine panels where weight is less critical.
Understanding Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance composite panels in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries. Its high tensile strength comes from tightly woven carbon strands bonded with epoxy resin, providing enhanced durability and resistance to fatigue. Carbon fiber composites also exhibit better thermal stability and corrosion resistance, though they tend to be more expensive and less impact-resistant than glass fiber alternatives.
Exploring Glass Fiber
Glass fiber, known for its excellent tensile strength and cost-effectiveness, is widely used in composite panels for applications requiring lightweight durability. Its high resistance to corrosion, impact, and moisture makes it ideal for marine, automotive, and construction industries. Compared to carbon fiber, glass fiber offers greater flexibility in manufacturing processes and superior insulation properties, enhancing its versatility in composite material design.
Key Material Properties Compared
Carbon fiber composite panels offer significantly higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to glass fiber, making them ideal for high-performance applications requiring superior load-bearing capacity. Glass fiber panels provide better impact resistance and are more cost-effective, with lower density contributing to lightweight yet durable solutions. Both materials exhibit excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue performance, but carbon fiber's superior modulus and strength-to-weight ratio typically justify its higher price in advanced engineering uses.
Strength and Weight Considerations
Carbon fiber composites exhibit superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to glass fiber, offering higher tensile strength and stiffness while maintaining significantly lower weight. Glass fiber composites provide adequate strength at a lower cost but result in panels that are heavier and less rigid than those made with carbon fiber. For applications demanding maximum strength and minimal weight, carbon fiber panels are preferred despite their higher price point.
Durability and Longevity
Carbon fiber composite panels exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to glass fiber panels due to their high tensile strength and resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and environmental degradation. Glass fiber panels, while cost-effective, tend to absorb moisture over time, leading to potential structural weakening and reduced lifespan. The advanced molecular structure of carbon fiber enhances its ability to maintain integrity under cyclic loading and extreme conditions, making it ideal for long-term applications.
Cost Comparison: Carbon Fiber vs Glass Fiber
Carbon fiber composite panels generally cost significantly more than glass fiber panels due to the higher price of raw carbon fiber materials and the complex manufacturing process involved. Glass fiber composite panels offer a more cost-effective solution with lower material costs and simpler production methods, making them ideal for budget-sensitive applications. The cost difference can be substantial, with carbon fiber panels often priced two to three times higher than comparable glass fiber options.
Common Applications in Industry
Carbon fiber composite panels are extensively used in aerospace, automotive, and high-performance sports equipment due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness. Glass fiber composite panels find common applications in marine, construction, and wind energy sectors, valued for their cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and electrical insulation properties. Both materials serve critical roles in industrial applications where mechanical performance and environmental durability are essential.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber composites offer superior strength-to-weight ratios but involve high energy consumption and significant carbon emissions during production, making their environmental footprint considerable. Glass fiber composites, while generally less durable and heavier, require less energy to manufacture and are often more recyclable, contributing to better sustainability profiles. Lifecycle assessments indicate that glass fiber composites present a lower overall environmental impact, although advances in carbon fiber recycling technologies are gradually improving their sustainability.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance applications like aerospace and automotive industries. Glass fiber, while less expensive and more flexible, provides excellent impact resistance and chemical stability suitable for construction and marine uses. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors such as budget, mechanical properties, durability, and specific performance requirements of the composite panel.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Glass fiber for Composite panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com