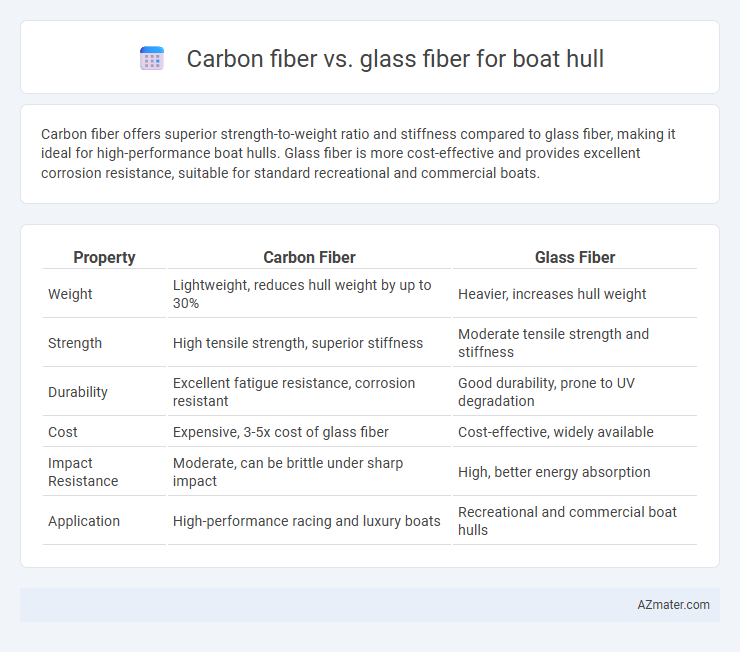
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls. Glass fiber is more cost-effective and provides excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for standard recreational and commercial boats.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces hull weight by up to 30% | Heavier, increases hull weight |
| Strength | High tensile strength, superior stiffness | Moderate tensile strength and stiffness |
| Durability | Excellent fatigue resistance, corrosion resistant | Good durability, prone to UV degradation |
| Cost | Expensive, 3-5x cost of glass fiber | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, can be brittle under sharp impact | High, better energy absorption |
| Application | High-performance racing and luxury boats | Recreational and commercial boat hulls |
Introduction to Boat Hull Materials
Boat hull materials primarily include carbon fiber and glass fiber, each offering distinct advantages in marine construction. Carbon fiber provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, resulting in lighter and faster boats with enhanced durability. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective choice with excellent corrosion resistance and ease of repair, making it ideal for a wide range of recreational and commercial vessels.
Overview of Carbon Fiber and Glass Fiber
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls where durability and lightweight construction are critical. Glass fiber, while heavier and less stiff than carbon fiber, provides excellent corrosion resistance, affordability, and ease of repair, making it a popular choice for recreational and commercial boat hulls. The selection between carbon fiber and glass fiber depends on performance requirements, cost considerations, and desired hull properties.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for high-performance boat hulls that require maximum rigidity and impact resistance. Glass fiber provides excellent durability and flexibility, with better resistance to fatigue and water absorption, making it more cost-effective for general marine applications. While carbon fiber excels in tensile strength and stiffness, glass fiber tends to outperform in long-term resistance against cracking and environmental wear.
Weight Differences and Impact on Performance
Carbon fiber boat hulls weigh approximately 30-50% less than glass fiber hulls, significantly reducing overall vessel weight. The reduced weight of carbon fiber enhances acceleration, top speed, and fuel efficiency, improving performance in both recreational and competitive boating. Glass fiber hulls, while heavier, offer greater flexibility and lower cost but compromise on weight-sensitive performance metrics.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Fiber vs Glass Fiber
Carbon fiber boat hulls typically cost between $20 and $30 per pound, significantly higher than glass fiber's $3 to $7 per pound range, making glass fiber the more budget-friendly choice for most boat builders. Despite the higher upfront material expense, carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratios and durability, potentially lowering long-term maintenance and fuel costs. Glass fiber remains popular due to its affordability and adequate performance for many recreational and commercial vessels.
Resistance to Corrosion and Weathering
Carbon fiber offers superior resistance to corrosion and weathering compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for marine environments where exposure to saltwater and UV rays is constant. The dense molecular structure of carbon fiber prevents water absorption and chemical degradation, extending the lifespan of boat hulls significantly. Glass fiber, while more cost-effective, tends to absorb water over time and is more prone to surface degradation from UV exposure, requiring regular maintenance to preserve hull integrity.
Ease of Manufacturing and Repairs
Carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and strength but requires precise fabrication techniques, often necessitating specialized tools and controlled environments, making the manufacturing process more complex compared to glass fiber. Glass fiber is more user-friendly for boat hull construction due to its pliability, lower cost, and simpler layup process, which facilitates easier repairs and patching even for novices. Repairing carbon fiber hulls demands advanced skills and materials, as the resin systems and fiber orientation must be carefully matched to restore structural integrity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber boat hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, leading to lighter vessels and improved fuel efficiency, which reduces carbon emissions over the vessel's lifetime. However, the production of carbon fiber involves high energy consumption and emits significant greenhouse gases, and its recycling options remain limited compared to glass fiber. Glass fiber, while heavier and less fuel-efficient, is more widely recyclable and has a less energy-intensive manufacturing process, making it a somewhat more sustainable option in terms of environmental impact.
Application Suitability for Different Boat Types
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance racing sailboats and lightweight powerboats that demand speed and agility. Glass fiber provides excellent durability and cost-effectiveness, well-suited for recreational boats, fishing vessels, and cruisers where impact resistance and affordability are prioritized. The choice depends on specific vessel requirements: carbon fiber enhances speed and maneuverability, while glass fiber ensures robustness and budget-friendly construction.
Final Recommendations and Use Cases
Carbon fiber boat hulls offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced stiffness, making them ideal for high-performance racing boats and luxury yachts requiring maximum speed and durability. Glass fiber hulls provide cost-effective durability with excellent corrosion resistance, suited for recreational vessels and commercial boats where budget and maintenance are key factors. Choosing between carbon and glass fiber depends on the balance between performance demands, budget constraints, and specific operational conditions.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Glass fiber for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com