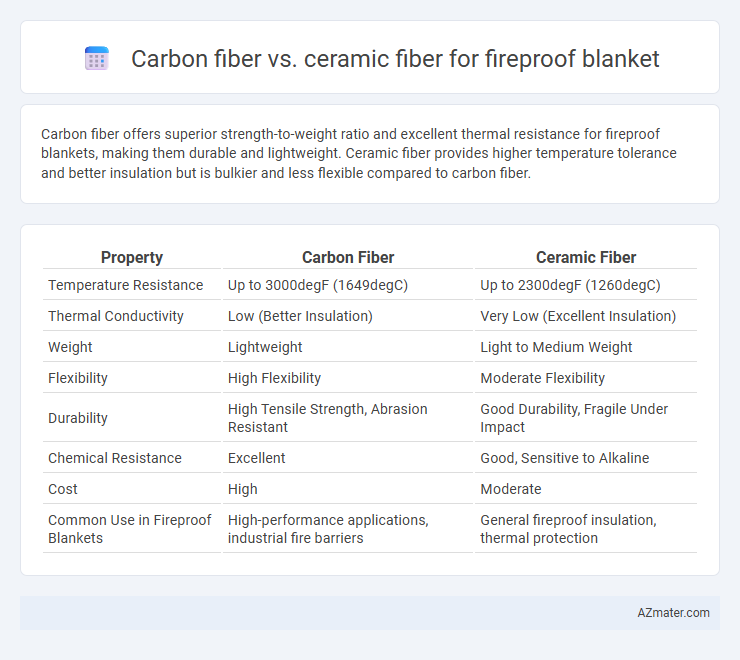
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal resistance for fireproof blankets, making them durable and lightweight. Ceramic fiber provides higher temperature tolerance and better insulation but is bulkier and less flexible compared to carbon fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Ceramic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 3000degF (1649degC) | Up to 2300degF (1260degC) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (Better Insulation) | Very Low (Excellent Insulation) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to Medium Weight |
| Flexibility | High Flexibility | Moderate Flexibility |
| Durability | High Tensile Strength, Abrasion Resistant | Good Durability, Fragile Under Impact |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good, Sensitive to Alkaline |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Common Use in Fireproof Blankets | High-performance applications, industrial fire barriers | General fireproof insulation, thermal protection |
Introduction to Fireproof Blankets
Fireproof blankets primarily use carbon fiber or ceramic fiber for heat resistance and insulation. Carbon fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for firefighters and industrial safety. Ceramic fiber provides superior heat retention with exceptional resistance to thermal shock, suitable for high-temperature applications like furnaces and kilns.
What is Carbon Fiber?
Carbon fiber is a high-strength material composed of thin, strong crystalline filaments of carbon, known for its excellent heat resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for fireproof blankets. It offers superior thermal conductivity and durability compared to ceramic fiber, allowing for enhanced protection against extreme temperatures and rapid heat dissipation. Carbon fiber fireproof blankets are commonly used in industrial applications requiring both heat shielding and mechanical strength.
What is Ceramic Fiber?
Ceramic fiber is an inorganic, refractory material composed primarily of alumina and silica, known for its high-temperature resistance and excellent thermal insulation properties. It withstands temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC) and is widely used in fireproof blankets to provide effective protection against heat and flames. Compared to carbon fiber, ceramic fiber offers superior heat insulation but is less flexible and less durable under mechanical stress.
Key Properties of Carbon Fiber Blankets
Carbon fiber blankets exhibit exceptional thermal stability withstanding temperatures up to 1,500degC, making them ideal for high-temperature fireproof applications. Their low density and high tensile strength provide superior durability and flexibility compared to ceramic fiber blankets, which tend to be more brittle. Carbon fiber's low thermal conductivity ensures efficient insulation while maintaining resistance to chemical corrosion and mechanical wear.
Key Properties of Ceramic Fiber Blankets
Ceramic fiber blankets exhibit exceptional thermal stability with operating temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC), making them ideal for high-temperature insulation and fireproof applications. Their low thermal conductivity and excellent chemical inertness provide superior resistance to thermal shock and corrosion compared to carbon fiber alternatives. These blankets also offer lightweight flexibility and high tensile strength, ensuring durability and ease of installation in fireproofing and furnace lining environments.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Carbon fiber fireproof blankets exhibit superior heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 3000degF (1649degC), making them ideal for extreme industrial applications. Ceramic fiber blankets typically resist temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC), offering excellent insulation but lower tolerance to direct high-heat exposure compared to carbon fiber. The dense molecular structure of carbon fiber enhances its thermal stability and durability under prolonged high-temperature conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Carbon fiber fireproof blankets exhibit superior durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear, making them ideal for repeated use in extreme fire conditions. Ceramic fiber blankets offer excellent thermal stability and can withstand prolonged exposure to high temperatures without significant degradation, ensuring long-term fire protection. While ceramic fibers excel in temperature resistance, carbon fibers provide enhanced mechanical toughness, making them complementary materials depending on specific fireproofing requirements.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
Carbon fiber fireproof blankets offer superior heat resistance and mechanical strength but may release harmful particulates when damaged or exposed to extreme conditions. Ceramic fiber blankets provide excellent thermal insulation and are generally inert, minimizing toxic gas emissions during fire exposure. Safety protocols should consider the potential release of fibers and proper handling to reduce respiratory hazards associated with both materials.
Typical Applications: Carbon vs Ceramic Fiber
Carbon fiber fireproof blankets excel in high-temperature industrial applications such as furnace insulation, welding protection, and aerospace fire barriers due to their superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. Ceramic fiber blankets are typically used in refractory linings, kilns, and furnace door seals, offering exceptional resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion. Both materials provide fire protection, but carbon fiber is preferred for flexibility and structural support, while ceramic fiber is ideal for extreme heat environments requiring prolonged thermal insulation.
Choosing the Right Fireproof Blanket Material
Choosing the right fireproof blanket material involves comparing carbon fiber and ceramic fiber based on heat resistance and durability. Carbon fiber offers superior strength and excellent thermal performance up to 3700degF, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Ceramic fiber provides exceptional insulation and can withstand temperatures up to 2300degF, offering a lightweight and cost-effective solution for moderate fireproofing needs.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Ceramic fiber for Fireproof blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com