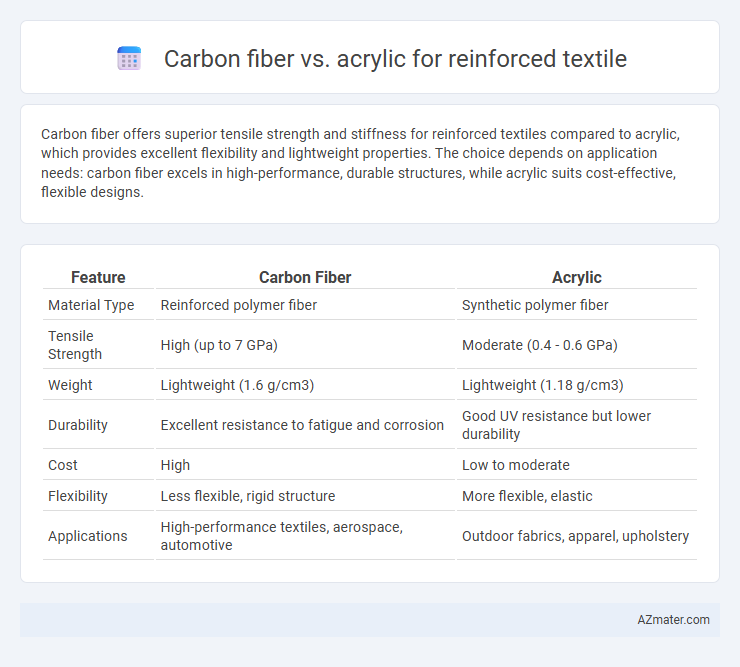
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness for reinforced textiles compared to acrylic, which provides excellent flexibility and lightweight properties. The choice depends on application needs: carbon fiber excels in high-performance, durable structures, while acrylic suits cost-effective, flexible designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Fiber | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Reinforced polymer fiber | Synthetic polymer fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 7 GPa) | Moderate (0.4 - 0.6 GPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight (1.6 g/cm3) | Lightweight (1.18 g/cm3) |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to fatigue and corrosion | Good UV resistance but lower durability |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, rigid structure | More flexible, elastic |
| Applications | High-performance textiles, aerospace, automotive | Outdoor fabrics, apparel, upholstery |
Introduction to Reinforced Textiles
Reinforced textiles combine high-performance fibers with a polymer matrix to enhance strength and durability in applications such as aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment. Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for structural reinforcement where high load capacity is required. Acrylic fibers provide excellent impact resistance and flexibility, suitable for reinforcement in textiles needing moderate strength with enhanced toughness and UV resistance.
Key Properties of Carbon Fiber in Textiles
Carbon fiber in reinforced textiles offers exceptional tensile strength, lightweight durability, and high stiffness, making it ideal for applications requiring structural integrity and flexibility. Its superior resistance to chemical corrosion, thermal stability, and fatigue enhances the longevity of composite materials compared to acrylic fibers. These properties enable carbon fiber textiles to outperform acrylic in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment manufacturing, where performance and reliability are critical.
Key Properties of Acrylic in Textiles
Acrylic fibers in reinforced textiles offer excellent lightweight characteristics combined with high resistance to UV radiation and weathering, making them ideal for outdoor applications. Their inherent softness and flexibility contribute to enhanced comfort and durability, while also providing good insulation and resistance to chemicals and moisture. Acrylic's ability to retain color vibrancy over time adds aesthetic value alongside its mechanical strength in reinforced textile composites.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to acrylic, making it ideal for reinforced textiles requiring high performance and load-bearing capabilities. Its exceptional durability includes excellent resistance to fatigue, environmental degradation, and long-term wear, outperforming acrylic in demanding applications. Acrylic reinforced textiles, while lightweight and cost-effective, lack the sustained mechanical strength and resilience under stress that carbon fiber provides.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio with a significantly lower density of approximately 1.6 g/cm3 compared to acrylic's density around 1.18 g/cm3 when used in reinforced textiles, making carbon fiber textiles lighter yet structurally more robust. Acrylic fibers provide greater flexibility and elasticity, enabling better drapability and stretchability, while carbon fiber textiles are stiffer and more rigid, ideal for applications requiring high tensile strength and minimal deformation. The choice between carbon fiber and acrylic depends on prioritizing lightweight strength or flexible resilience in textile reinforcement.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Fiber vs Acrylic
Carbon fiber composites typically cost between $15 to $30 per pound, driven by their high-strength-to-weight ratio and extensive manufacturing processes. Acrylic fibers, by contrast, are significantly more affordable, averaging around $3 to $5 per pound, making them a cost-efficient choice for reinforced textiles with moderate performance requirements. The higher initial expense of carbon fiber is often justified in applications demanding superior durability and performance, while acrylic remains viable for budget-conscious projects with less stringent mechanical demands.
Applications in Modern Textile Engineering
Carbon fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for advanced applications in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment textiles. Acrylic fibers provide excellent color retention and UV resistance, commonly used in outdoor fabrics, upholstery, and protective clothing. Modern textile engineering leverages carbon fiber for structural reinforcement, while acrylic enhances durability and weather resistance in composite materials.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Carbon fiber offers superior durability and strength compared to acrylic, resulting in longer-lasting reinforced textiles that reduce the frequency of replacement and waste. Acrylic production relies heavily on fossil fuels and emits significant greenhouse gases, while carbon fiber manufacturing, though energy-intensive, can incorporate recycling processes to minimize carbon footprint. Sustainable practices favor carbon fiber reinforced textiles for their potential to lower environmental impact through extended lifecycle and recyclability.
Performance in Extreme Conditions
Carbon fiber reinforced textiles exhibit superior performance in extreme conditions due to their exceptional tensile strength, thermal stability up to 600degC, and resistance to chemical corrosion. Acrylic reinforced textiles, while lighter and more flexible, degrade significantly under UV exposure and have lower resistance to high temperatures, typically withstanding only up to 150degC. The enhanced durability and stiffness of carbon fiber composites make them the preferred choice for aerospace and military applications where performance under harsh environments is critical.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance reinforced textiles requiring lightweight durability and resistance to deformation. Acrylic fibers provide excellent UV resistance and moisture-wicking properties, suitable for applications emphasizing comfort and weather resistance. Selecting between carbon fiber and acrylic depends on whether structural strength or environmental resilience is the priority in your reinforced textile project.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Acrylic for Reinforced textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com