Carbon fiber offers superior thermal insulation and durability compared to acrylic for blanketing applications. Its lightweight, high strength, and resistance to heat make it ideal for advanced thermal management systems.
Table of Comparison
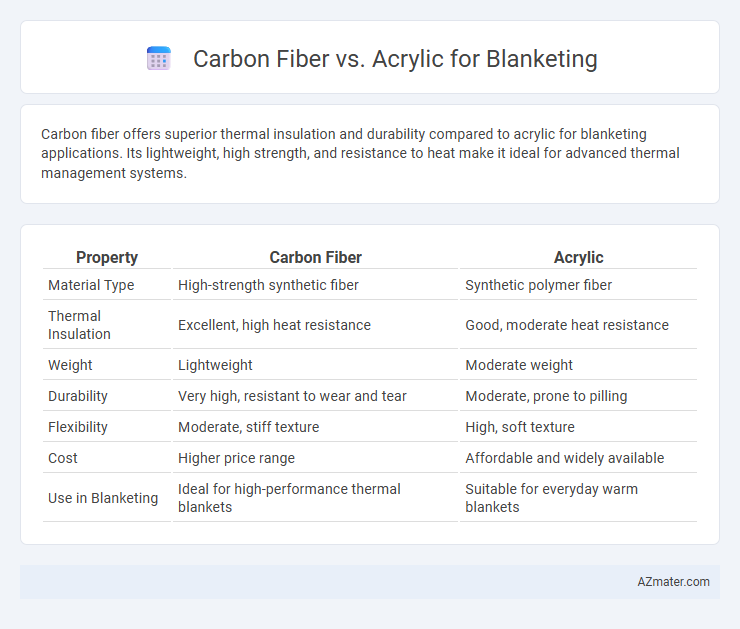
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-strength synthetic fiber | Synthetic polymer fiber |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, high heat resistance | Good, moderate heat resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight | Moderate weight |
| Durability | Very high, resistant to wear and tear | Moderate, prone to pilling |
| Flexibility | Moderate, stiff texture | High, soft texture |
| Cost | Higher price range | Affordable and widely available |
| Use in Blanketing | Ideal for high-performance thermal blankets | Suitable for everyday warm blankets |
Introduction to Blanketing Materials
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal insulation properties compared to acrylic, making it ideal for high-performance blanketing applications. Acrylic provides good flexibility and cost-effectiveness but lacks the durability and heat resistance found in carbon fiber materials. Selecting between carbon fiber and acrylic depends on requirements like temperature resistance, mechanical durability, and budget constraints in blanketing solutions.
Overview of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance blanketing applications where durability and temperature regulation are critical. Its low density combined with high tensile strength provides enhanced protection without adding significant weight, outperforming acrylic in resistance to heat and mechanical stress. Carbon fiber's advanced fiber matrix structure contributes to increased longevity and efficiency in insulating materials compared to traditional acrylic options.
Overview of Acrylic
Acrylic blankets are lightweight, soft, and provide excellent insulation with moisture-resistant properties, making them ideal for cold and damp environments. They offer durability and colorfastness, maintaining their appearance after repeated washing and exposure to sunlight. Compared to carbon fiber, acrylic is more affordable and widely used in household and outdoor textiles due to its comfort and easy care.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Carbon fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and rigidity compared to acrylic, making it ideal for applications requiring superior mechanical durability. The tensile strength of carbon fiber can exceed 3,500 MPa, whereas acrylic typically ranges around 70 MPa, highlighting a substantial difference in load-bearing capacity. Carbon fiber's superior stiffness and fatigue resistance enhance its performance for blanketing materials subjected to mechanical stress.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Carbon fiber blankets offer superior weight advantages, typically weighing 30-50% less than acrylic counterparts, enhancing portability and ease of handling. Flexibility in carbon fiber materials is enhanced due to their high tensile strength, allowing for tighter conforming wraps without compromising structural integrity. Acrylic blankets, while heavier and less flexible, provide greater cushioning and thermal insulation, making them suitable for static applications where weight and flexibility are less critical.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Carbon fiber offers superior thermal insulation performance compared to acrylic, with a higher thermal resistance and better heat retention properties. Its low thermal conductivity enables efficient heat management, making it ideal for high-performance blanketing applications where temperature control is critical. Acrylic, while lightweight and cost-effective, provides moderate insulation but falls short in environments requiring advanced thermal protection.
Durability and Lifespan
Carbon fiber blankets exhibit superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to acrylic blankets, owing to their high tensile strength and resistance to wear and environmental degradation. Acrylic blankets tend to degrade faster under UV exposure and frequent use, leading to reduced durability over time. Therefore, carbon fiber is the preferred choice for applications requiring long-lasting, resilient blanketing solutions.
Cost Analysis
Carbon fiber blankets typically cost significantly more than acrylic blankets due to expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes, often priced between $50 to $150 per square foot compared to acrylic's $5 to $20. Despite the higher upfront investment, carbon fiber offers superior durability, lightweight properties, and thermal resistance, which can reduce long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Cost analysis must balance initial expenditure against performance benefits, with acrylic serving as a budget-friendly option for less demanding applications.
Environmental Impact
Carbon fiber offers superior durability and lightweight properties, resulting in longer-lasting blankets that reduce material waste over time. Acrylic blankets, often derived from synthetic polymers, have higher energy consumption during production and contribute to microplastic pollution upon washing. Choosing carbon fiber materials can reduce environmental footprint by lowering resource usage and enhancing recyclability compared to acrylic alternatives.
Best Applications for Each Material
Carbon fiber excels in high-performance insulation applications requiring superior strength-to-weight ratios and thermal stability, such as in aerospace, automotive, and advanced industrial settings. Acrylic blankets are best suited for general-purpose insulation and protective coverings in construction, home furnishings, and outdoor use due to their affordability, UV resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Selecting between carbon fiber and acrylic depends on specific needs for durability, heat resistance, and environmental exposure.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Acrylic for Blanketing
 azmater.com
azmater.com