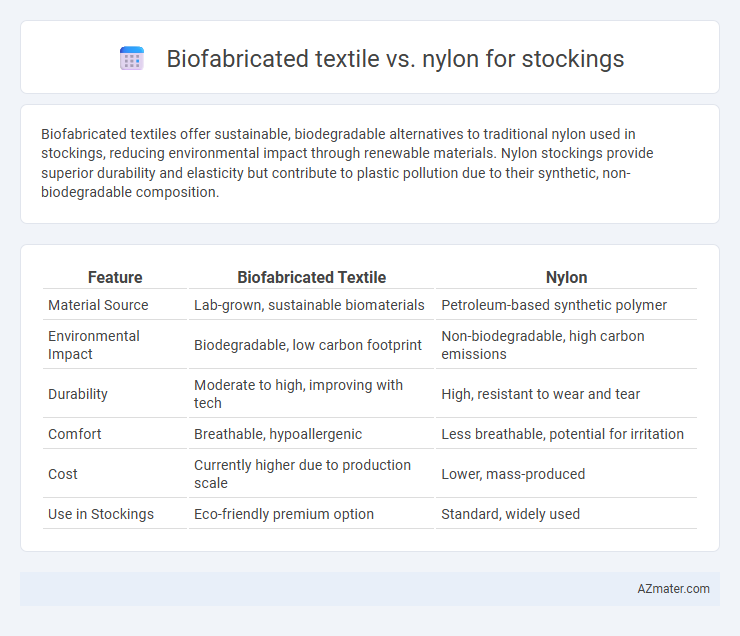
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives to traditional nylon used in stockings, reducing environmental impact through renewable materials. Nylon stockings provide superior durability and elasticity but contribute to plastic pollution due to their synthetic, non-biodegradable composition.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown, sustainable biomaterials | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon emissions |
| Durability | Moderate to high, improving with tech | High, resistant to wear and tear |
| Comfort | Breathable, hypoallergenic | Less breathable, potential for irritation |
| Cost | Currently higher due to production scale | Lower, mass-produced |
| Use in Stockings | Eco-friendly premium option | Standard, widely used |
Introduction to Stocking Materials
Stocking materials traditionally rely on nylon, a synthetic polymer known for its durability, elasticity, and smooth texture. Biofabricated textiles offer an innovative alternative by utilizing sustainable, lab-grown fibers derived from natural proteins or cellulose, reducing environmental impact. These new materials aim to maintain the comfort and resilience of nylon while enhancing biodegradability and reducing reliance on petrochemicals.
What is Biofabricated Textile?
Biofabricated textile is an innovative material produced through sustainable processes using living organisms like bacteria, yeast, or fungi to create fibers that mimic natural fabrics without relying on petroleum-based sources. Unlike nylon, which is a synthetic polymer derived from petrochemicals, biofabricated textiles offer enhanced biodegradability, reduced carbon footprint, and lower environmental impact during production. This emerging technology addresses the ecological concerns of traditional nylon stockings by providing durable, eco-friendly alternatives that blend performance with sustainability.
How Nylon Revolutionized Stocking Production
Nylon revolutionized stocking production by introducing a synthetic fiber that combines exceptional strength, elasticity, and affordability, allowing mass production of durable and comfortable stockings. Unlike traditional silk stockings, nylon stockings offered better resistance to runs and tears, significantly extending product lifespan and accessibility for consumers. Biofabricated textiles are emerging as sustainable alternatives, aiming to match or exceed nylon's performance while reducing environmental impact through biodegradable and renewable materials.
Sustainability: Biofabricated Textile vs Nylon
Biofabricated textiles offer a sustainable alternative to nylon for stockings by significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing carbon emissions during production. Unlike nylon, which is derived from petrochemicals and contributes to microplastic pollution, biofabricated materials utilize renewable resources and biodegradable components. This shift towards biofabrication promotes circular fashion, reducing environmental impact and supporting resource-efficient textile manufacturing.
Performance and Comfort Comparison
Biofabricated textiles demonstrate enhanced breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional nylon, resulting in superior comfort for stockings. Performance-wise, biofabricated materials often exhibit greater elasticity and durability, reducing wear and tear over time. In contrast, nylon stockings tend to retain heat and may cause discomfort due to lower moisture permeability and less adaptive stretch.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Biofabricated textiles for stockings significantly reduce environmental footprint through lower greenhouse gas emissions and minimized water usage compared to conventional nylon. Nylon production relies heavily on petrochemicals, contributing to high carbon emissions and non-biodegradable waste accumulation. Life cycle assessments reveal biofabricated materials offer enhanced biodegradability and renewable resource utilization, positioning them as sustainable alternatives in hosiery manufacturing.
Cost and Scalability Considerations
Biofabricated textiles offer a sustainable alternative to nylon for stockings, with cost structures currently higher due to nascent production technologies and limited manufacturing scale. Nylon benefits from established global supply chains and economies of scale, enabling lower unit costs and mass production capabilities. Scaling biofabricated textiles requires significant investment in bioreactor infrastructure, but advancements in synthetic biology could reduce costs and enhance scalability over time.
Market Trends in Stocking Materials
Biofabricated textiles for stockings are gaining traction due to their sustainability and biodegradability, aligning with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly fashion materials. Nylon remains dominant in the stocking market owing to its durability, elasticity, and affordability but faces increasing scrutiny for environmental concerns such as non-biodegradability and microplastic pollution. Market trends indicate a shift towards biofabricated alternatives driven by regulatory pressure, advancements in biotechnology, and rising awareness of plastic waste impact on ecosystems.
Consumer Preferences and Perceptions
Consumers increasingly prefer biofabricated textiles for stockings due to their eco-friendly attributes, superior breathability, and sustainability compared to traditional nylon. Market studies reveal a growing perception of biofabricated materials as safer, hypoallergenic, and more comfortable, aligning with rising demand for ethical fashion. Price sensitivity and durability concerns remain challenges, but positive consumer sentiment drives innovation and adoption in sustainable hosiery.
Future Prospects: Biofabricated vs Nylon Stockings
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable alternatives to traditional nylon stockings by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing environmental impact through biodegradable materials. Innovations in biofabrication enable enhanced comfort, breathability, and customizable textures compared to conventional nylon, positioning them as a future-forward choice for eco-conscious consumers. Advancements in scalability and cost-efficiency will drive wider adoption of biofabricated stockings, potentially transforming the hosiery market by aligning with global sustainability goals.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Nylon for Stocking
 azmater.com
azmater.com