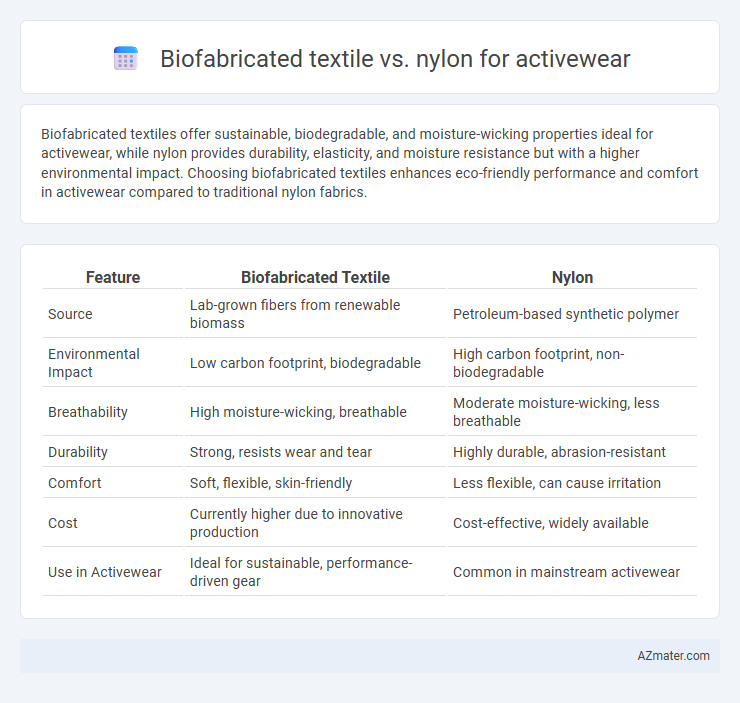
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable, and moisture-wicking properties ideal for activewear, while nylon provides durability, elasticity, and moisture resistance but with a higher environmental impact. Choosing biofabricated textiles enhances eco-friendly performance and comfort in activewear compared to traditional nylon fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown fibers from renewable biomass | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Breathability | High moisture-wicking, breathable | Moderate moisture-wicking, less breathable |
| Durability | Strong, resists wear and tear | Highly durable, abrasion-resistant |
| Comfort | Soft, flexible, skin-friendly | Less flexible, can cause irritation |
| Cost | Currently higher due to innovative production | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Use in Activewear | Ideal for sustainable, performance-driven gear | Common in mainstream activewear |
Introduction to Biofabricated Textiles and Nylon in Activewear
Biofabricated textiles, created through sustainable biotechnological processes using microorganisms or plant-based materials, are emerging as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional nylon in activewear, offering enhanced breathability and biodegradability. Nylon, a synthetic polymer derived from petrochemicals, has long been favored in activewear for its durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties, but raises environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradability and energy-intensive production. The shift towards biofabricated textiles aims to reduce the carbon footprint and plastic waste associated with nylon while maintaining performance standards essential for athletic wear.
Material Composition and Production Processes
Biofabricated textiles are created using cultured cells or microorganisms, often producing proteins like collagen or spider silk through sustainable fermentation processes, resulting in biodegradable and renewable activewear materials. Nylon, a synthetic polymer derived from petrochemicals via energy-intensive processes, offers high durability and elasticity but contributes to environmental pollution and microplastic release. The contrast in material composition highlights biofabricated textiles as eco-friendly alternatives to nylon's fossil fuel dependency and chemical synthesis methods.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Biofabricated textiles offer a sustainable alternative to nylon in activewear by significantly reducing carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels during production. These innovative materials are often biodegradable, minimizing microplastic pollution that nylon fibers contribute to in marine environments. Choosing biofabricated textiles supports circular economy principles and lessens the environmental footprint associated with synthetic fiber manufacturing.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Biofabricated textiles outperform nylon in activewear by offering superior moisture-wicking properties and enhanced breathability, promoting optimal body temperature regulation during intense workouts. These innovative materials exhibit increased stretch recovery and abrasion resistance, ensuring long-lasting durability under repetitive motion and friction typical in active sports. Furthermore, biofabricated textiles maintain structural integrity and shape retention better than conventional nylon, contributing to sustained performance and extended garment life.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Biofabricated textiles offer superior moisture management by utilizing advanced biomaterials that efficiently wick sweat and promote rapid evaporation, enhancing comfort during intense physical activity. Unlike traditional nylon, biofabricated fabrics provide improved breathability due to their porous, natural fiber structures that facilitate better air circulation and temperature regulation. These qualities make biofabricated textiles an innovative choice for activewear, combining sustainability with functional performance.
Comfort and Skin Sensitivity
Biofabricated textiles for activewear offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional nylon, enhancing overall comfort during intense physical activity. These innovative materials are hypoallergenic and reduce the risk of skin irritation or allergic reactions commonly associated with synthetic fibers like nylon. Advances in biofabrication technology contribute to softer textures and improved elasticity, making biofabricated textiles gentle on sensitive skin while maintaining durability and performance.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Potential
Biofabricated textiles offer exceptional design flexibility and aesthetic potential due to their ability to be engineered at the molecular level, enabling customization in texture, pattern, and color beyond traditional materials. Nylon, while durable and lightweight, has limitations in surface variation and customization, often requiring additional treatments to achieve diverse aesthetics. The innovation in biofabricated materials supports sustainable activewear designs with unique visual and tactile qualities that enhance both performance and style.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Biofabricated textiles offer promising sustainability benefits but currently face higher production costs compared to nylon, impacting cost efficiency in activewear manufacturing. Nylon remains more cost-effective due to established global supply chains and economies of scale, ensuring widespread market availability and consistent pricing. The growing investment in biofabricated materials may lower costs over time, yet nylon dominates activewear markets today due to its affordability and accessibility.
Consumer Perceptions and Adoption Trends
Biofabricated textiles for activewear are gaining traction due to their eco-friendly appeal and innovative production methods, resonating with environmentally conscious consumers who seek sustainable alternatives to traditional nylon. Studies show a growing consumer shift towards biofabricated materials, driven by increasing awareness of nylon's environmental impact, including pollution and non-biodegradability. Market adoption trends highlight early adopters in premium and niche activewear brands, with a projected rise in mainstream acceptance as biofabrication technology advances and costs decrease.
Future Prospects in Activewear Innovation
Biofabricated textile offers groundbreaking sustainability and enhanced biodegradability compared to traditional nylon, positioning it as a key innovation for future activewear. Advancements in biofabrication technology enable the production of high-performance materials with adaptive breathability, moisture-wicking, and durability tailored for athletic demands. Increasing consumer preference for eco-friendly products drives the integration of biofabricated textiles, promising a transformative impact on activewear design and environmental footprint.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Nylon for Activewear
 azmater.com
azmater.com