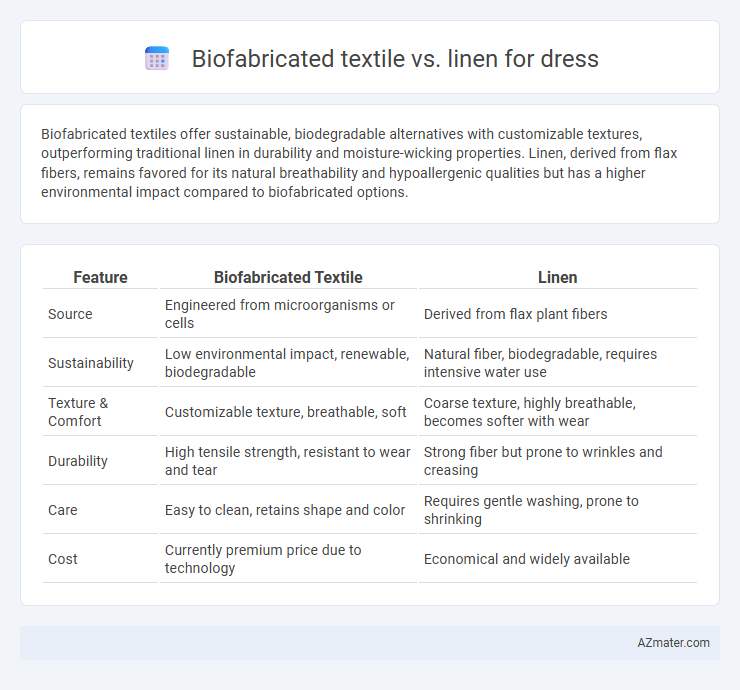
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives with customizable textures, outperforming traditional linen in durability and moisture-wicking properties. Linen, derived from flax fibers, remains favored for its natural breathability and hypoallergenic qualities but has a higher environmental impact compared to biofabricated options.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Engineered from microorganisms or cells | Derived from flax plant fibers |
| Sustainability | Low environmental impact, renewable, biodegradable | Natural fiber, biodegradable, requires intensive water use |
| Texture & Comfort | Customizable texture, breathable, soft | Coarse texture, highly breathable, becomes softer with wear |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear and tear | Strong fiber but prone to wrinkles and creasing |
| Care | Easy to clean, retains shape and color | Requires gentle washing, prone to shrinking |
| Cost | Currently premium price due to technology | Economical and widely available |
Introduction: Biofabricated Textile vs Linen for Dresses
Biofabricated textiles, created through sustainable biotechnological processes, offer innovative alternatives to traditional materials like linen for dressmaking. Linen, derived from flax fibers, is prized for its natural breathability and durability but involves resource-intensive cultivation. Comparing biofabricated textiles and linen highlights advancements in eco-friendly dress fabrics with potential benefits in environmental impact, texture, and performance.
Understanding Biofabricated Textiles
Biofabricated textiles, engineered through cellular agriculture, utilize microbial fermentation or cultured cells to produce sustainable, biodegradable fibers that reduce environmental impact compared to traditional linen derived from flax plants. These innovative materials offer enhanced customization in texture, strength, and functional properties, addressing limitations of linen such as wrinkle resistance and moisture management. Understanding biofabricated textiles involves examining their lifecycle assessments, scalability challenges, and potential to revolutionize fashion by minimizing water usage and pesticide reliance inherent in flax cultivation for linen production.
The Heritage and Value of Linen
Linen, derived from the flax plant, holds a rich heritage dating back thousands of years, celebrated for its durability, breathability, and natural luster, making it a timeless choice for dress fabrics. Its value is deeply embedded in traditional craftsmanship and eco-friendly production, which lends authenticity and sustainability to garments. While biofabricated textiles offer innovative, lab-grown alternatives with potential for customization and reduced environmental footprint, linen's proven legacy and tactile appeal continue to signify cultural sophistication and lasting quality in fashion.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biofabricated textiles use cell cultures to create sustainable fibers, drastically reducing water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional linen production, which relies heavily on water-intensive flax farming. The carbon footprint of biofabricated textiles is significantly lower, as they avoid the use of pesticides and minimize fertilizer-related emissions inherent to linen cultivation. Waste generation is also minimized in biofabrication processes through precision manufacturing, contrasting with the agricultural byproducts and soil degradation often associated with linen production.
Durability and Longevity of Materials
Biofabricated textiles offer enhanced durability and longevity compared to traditional linen, as they are engineered to resist wear, moisture, and microbial degradation. Linen, derived from flax fibers, is naturally strong and breathable but tends to weaken over time with repeated washing and exposure to sunlight. Advanced biofabricated materials maintain structural integrity longer, making them ideal for high-use clothing while also providing sustainable alternatives to conventional fabrics.
Comfort and Wearability: Biofabricated Textile vs Linen
Biofabricated textiles offer superior moisture-wicking and enhanced breathability compared to traditional linen, ensuring optimal comfort in various climates. Their engineered fiber structures provide consistent softness and stretchability, improving wearability without compromising durability. Linen, while naturally breathable and hypoallergenic, tends to wrinkle easily and may feel coarse against sensitive skin after prolonged wear.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Potential
Biofabricated textiles offer innovative aesthetic qualities with customizable textures, colors, and patterns that can be engineered to meet specific design visions, surpassing the inherent variability of traditional linen. Linen provides a timeless, natural look characterized by a subtle sheen and unique wrinkles that convey authenticity and organic beauty, valued in classic and sustainable fashion. The design potential of biofabricated materials includes enhanced durability and adaptability to complex shapes, enabling avant-garde silhouettes, whereas linen excels in breathable, lightweight elegance suited for minimalist and rustic styles.
Cost Considerations and Market Accessibility
Biofabricated textiles tend to have higher production costs compared to linen due to advanced technology and limited manufacturing scale, impacting their pricing in the fashion industry. Linen benefits from established supply chains and widespread cultivation, making it more accessible and affordable for both designers and consumers. Market accessibility favors linen as it is widely available in global textile markets, whereas biofabricated textiles are primarily available through niche brands and experimental collections.
Consumer Perceptions and Trends
Biofabricated textile appeals to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable fashion alternatives, offering innovative, cruelty-free materials with reduced environmental impact compared to traditional linen. Linen remains favored for its natural breathability, durability, and classic aesthetic, attracting consumers valuing heritage and comfort in dress fabrics. Current trends reveal a growing shift towards biofabricated textiles driven by increased awareness of climate change, while linen maintains strong loyalty among those prioritizing natural fiber authenticity and timeless style.
Future Prospects in Sustainable Dressmaking
Biofabricated textiles, made using microbial or cellular processes, offer significant future prospects for sustainable dressmaking by reducing water use, chemical waste, and carbon emissions compared to traditional linen production. While linen, derived from flax plants, remains a biodegradable and durable fabric with a relatively low environmental footprint, biofabricated textiles enable customizable properties and scalability with minimal land use. Advancements in biofabrication technology could revolutionize sustainable fashion by creating clothing materials that combine ecological benefits with innovative design flexibility.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Linen for Dress
 azmater.com
azmater.com