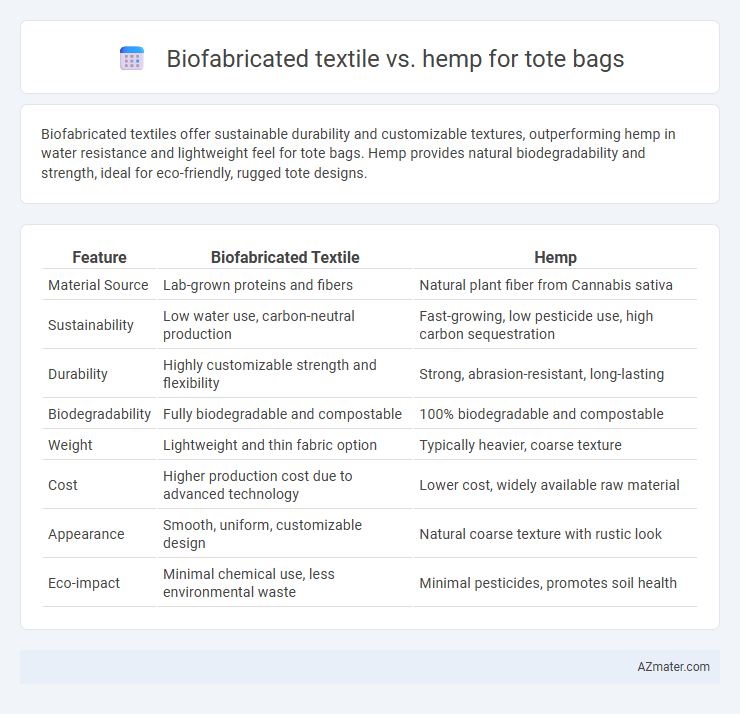
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable durability and customizable textures, outperforming hemp in water resistance and lightweight feel for tote bags. Hemp provides natural biodegradability and strength, ideal for eco-friendly, rugged tote designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown proteins and fibers | Natural plant fiber from Cannabis sativa |
| Sustainability | Low water use, carbon-neutral production | Fast-growing, low pesticide use, high carbon sequestration |
| Durability | Highly customizable strength and flexibility | Strong, abrasion-resistant, long-lasting |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable and compostable | 100% biodegradable and compostable |
| Weight | Lightweight and thin fabric option | Typically heavier, coarse texture |
| Cost | Higher production cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely available raw material |
| Appearance | Smooth, uniform, customizable design | Natural coarse texture with rustic look |
| Eco-impact | Minimal chemical use, less environmental waste | Minimal pesticides, promotes soil health |
Introduction to Biofabricated and Hemp Textiles
Biofabricated textiles are engineered materials created through biological processes, often using microorganisms or cultured cells to produce sustainable fibers with minimal environmental impact. Hemp textiles, derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, boast biodegradability, durability, and natural resistance to pests and UV light. Both materials offer innovative alternatives for tote bags, with biofabricated textiles emphasizing cutting-edge biotechnology and hemp embodying ancient agricultural resilience and eco-friendliness.
Material Sourcing: Biofabrication vs. Hemp Cultivation
Biofabricated textiles are produced through controlled microbial fermentation processes, which require less land and water compared to conventional agriculture, making sourcing highly sustainable and scalable with minimal environmental impact. Hemp cultivation involves growing the cannabis plant, requiring significant farmland but benefiting from rapid growth cycles and low pesticide use, contributing to soil health and carbon sequestration. While biofabrication offers precision and reduced resource demands, hemp cultivation provides a renewable and biodegradable fiber directly from the plant, each presenting unique ecological advantages for tote bag material sourcing.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Biofabricated textiles for tote bags demonstrate a lower environmental footprint compared to hemp by reducing water usage, land consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions during production. Hemp cultivation requires significant land and water resources, but it offers natural biodegradability and carbon sequestration benefits. Life cycle assessments reveal that biofabricated textiles, often made from microbial or plant-based processes, minimize pollution and resource depletion, contributing to more sustainable tote bag manufacturing.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Biofabricated textiles, derived from microbial or cellular processes, offer high biodegradability with minimal environmental impact due to their organic composition and ability to decompose rapidly in natural environments. Hemp fibers, known for their durability and natural resistance to pests, are also biodegradable but may take longer to break down compared to biofabricated materials, especially when treated with chemical processes. End-of-life disposal for both materials supports composting and reduces landfill waste, but biofabricated textiles provide a more controlled and eco-friendly degradation profile, enhancing sustainability in tote bag production.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Biofabricated textiles, engineered using microbial processes, exhibit impressive tensile strength and resistance to wear, often outperforming natural fibers in controlled durability tests. Hemp fibers are renowned for their high tensile strength, resistance to stretching, and longevity, making them a traditionally preferred material for durable tote bags. Comparative studies indicate biofabricated textiles offer superior environmental resistance and consistent performance, while hemp ensures robust mechanical strength and biodegradability in heavy-use scenarios.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Biofabricated textiles offer a sleek, futuristic aesthetic with customizable textures and finishes that allow designers to experiment with innovative patterns and color variations, making each tote bag unique. Hemp provides a natural, rustic look with a coarse texture and earth-toned palette, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking organic and durable materials. The design flexibility of biofabricated textiles surpasses hemp by enabling precise control over fabric properties such as weight, transparency, and elasticity, whereas hemp's traditional weave limits variation but ensures robustness and sustainability.
Production Costs and Scalability
Biofabricated textiles exhibit higher production costs due to complex biotechnological processes and specialized facilities, making initial scalability challenging compared to hemp. Hemp offers cost-efficient cultivation with rapid growth cycles and minimal resource requirements, enabling straightforward large-scale production and lower expenses for tote bag manufacturing. While biofabricated textiles promise innovative sustainability, hemp remains the more economically scalable material for eco-friendly tote bags.
Ethical and Social Implications
Biofabricated textiles offer a sustainable alternative to conventional materials by reducing reliance on agriculture and minimizing water usage, which addresses ethical concerns related to resource depletion and labor exploitation. Hemp provides strong social benefits through supporting traditional farming communities and promoting fair labor practices, but its cultivation may involve pesticide use and land competition. Evaluating both materials for tote bags highlights a trade-off between cutting-edge biotechnology's potential to alleviate environmental strain and hemp's role in sustaining rural economies and ethical farming.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Biofabricated textiles for tote bags are perceived by consumers as innovative, eco-friendly alternatives that promise reduced environmental impact and appeal to tech-savvy, sustainability-conscious audiences. Hemp, valued for its natural durability, biodegradability, and traditional ecological benefits, enjoys strong consumer trust and a well-established market presence in the eco-friendly segment. Market trends indicate growing interest in biofabricated textiles, driven by advances in material science and rising demand for cruelty-free products, while hemp maintains steady growth due to increasing awareness of its low-resource cultivation and versatility.
Future Prospects for Sustainable Tote Bags
Biofabricated textiles offer promising advancements in sustainable tote bags by utilizing lab-grown materials that reduce water use and greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional crops like hemp. Hemp remains a strong option due to its natural durability, rapid growth cycle, and carbon sequestration benefits, making it a low-impact raw material for eco-friendly bags. Future prospects integrate biofabricated textiles' innovation with hemp's renewable properties, aiming to create durable, biodegradable totes with minimal environmental footprints.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Hemp for Tote bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com