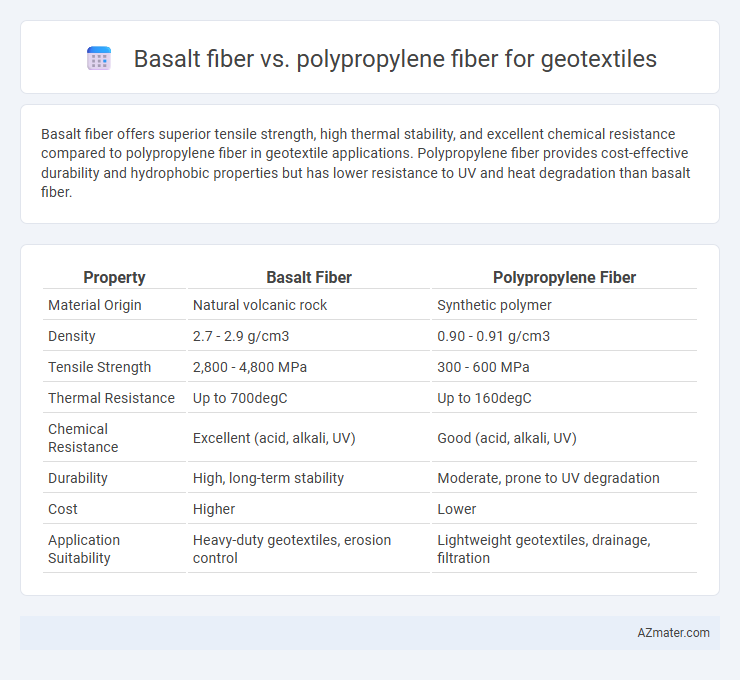
Basalt fiber offers superior tensile strength, high thermal stability, and excellent chemical resistance compared to polypropylene fiber in geotextile applications. Polypropylene fiber provides cost-effective durability and hydrophobic properties but has lower resistance to UV and heat degradation than basalt fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Natural volcanic rock | Synthetic polymer |
| Density | 2.7 - 2.9 g/cm3 | 0.90 - 0.91 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 2,800 - 4,800 MPa | 300 - 600 MPa |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 700degC | Up to 160degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acid, alkali, UV) | Good (acid, alkali, UV) |
| Durability | High, long-term stability | Moderate, prone to UV degradation |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Application Suitability | Heavy-duty geotextiles, erosion control | Lightweight geotextiles, drainage, filtration |
Introduction to Geotextile Reinforcement
Basalt fiber and polypropylene fiber are two prominent materials used in geotextile reinforcement for soil stabilization and erosion control. Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic rock, offers superior tensile strength, thermal resistance, and durability compared to polypropylene fiber, which is a synthetic polymer known for its chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness. Selecting between basalt and polypropylene fibers depends on project-specific requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and long-term performance in geotechnical applications.
Overview of Basalt Fiber Properties
Basalt fiber exhibits high tensile strength, excellent chemical and thermal resistance, and superior durability compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for geotextile reinforcement in aggressive environments. Its natural volcanic rock origin provides inherent fire resistance and eco-friendly attributes, while offering enhanced UV stability for prolonged outdoor applications. Basalt fibers demonstrate better mechanical performance and environmental resilience, positioning them as a sustainable alternative to synthetic polypropylene fibers in geotextile materials.
Overview of Polypropylene Fiber Properties
Polypropylene fiber is widely used in geotextile applications due to its robust chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and excellent tensile strength, which ensures durability in various soil stabilization projects. Its hydrophobic properties prevent water absorption, enhancing dimensional stability and resistance to microbial degradation compared to basalt fiber. The cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing polypropylene fiber contribute to its extensive use in erosion control, reinforcement, and filtration within geotechnical engineering.
Mechanical Performance Comparison
Basalt fiber exhibits superior mechanical performance compared to polypropylene fiber for geotextile applications, offering higher tensile strength and better resistance to UV degradation and chemical exposure. Its modulus of elasticity is significantly greater, enhancing structural reinforcement and durability under heavy loads and dynamic stresses. Polypropylene fiber, while cost-effective and lightweight, typically shows lower durability and tensile strength, making basalt fiber more suitable for long-term geotechnical projects requiring enhanced mechanical stability.
Durability and Chemical Resistance
Basalt fiber offers superior durability compared to polypropylene fiber in geotextile applications due to its high tensile strength and resistance to UV radiation, heat, and abrasion. Its exceptional chemical inertness ensures resistance against acids, alkalis, and salts, making it ideal for harsh environmental conditions. Polypropylene fiber, while cost-effective and chemically resistant to many substances, tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and higher temperatures, limiting its long-term durability in geotextile use.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Basalt fiber geotextiles exhibit superior environmental benefits due to their natural basalt rock origin, promoting biodegradability and reduced carbon footprint compared to polypropylene fibers derived from non-renewable petroleum. The production of basalt fibers emits fewer greenhouse gases and avoids toxic chemical use, supporting sustainable infrastructure development. Polypropylene fibers, while durable, persist in ecosystems causing microplastic pollution, challenging long-term environmental sustainability in geotextile applications.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Basalt fiber geotextiles generally have higher initial costs compared to polypropylene fibers due to their production complexity and raw material sourcing. Polypropylene fibers benefit from widespread availability and established manufacturing processes, resulting in lower prices and easier procurement globally. Cost efficiency in large-scale geotextile projects favors polypropylene fibers, while basalt fiber offers superior durability and environmental resistance, impacting long-term value.
Installation and Application Techniques
Basalt fiber geotextiles offer superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, making them ideal for harsh environments and demanding installation conditions, while polypropylene fibers excel in flexibility and ease of handling during deployment. Basalt fibers require precise cutting and anchoring techniques to prevent fiber damage and ensure long-term stability, whereas polypropylene fibers can be rinsed and repositioned with simpler fastening methods. In erosion control and soil stabilization, basalt fiber geotextiles provide enhanced durability, whereas polypropylene fibers are preferred for lightweight, cost-effective applications with faster installation times.
Case Studies and Real-World Performance
Case studies comparing basalt fiber and polypropylene fiber in geotextile applications reveal basalt fiber's superior durability and resistance to high temperatures, chemical degradation, and UV exposure, leading to longer service life in harsh environments. Real-world performance data from infrastructure projects demonstrate basalt fiber geotextiles maintain structural integrity under heavy loads and aggressive soil conditions better than polypropylene fibers, which tend to degrade faster. Field tests in coastal and industrial sites confirm basalt fiber's enhanced tensile strength and environmental sustainability, making it a preferred choice for demanding geotechnical uses.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Geotextiles
Basalt fiber offers superior durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for reinforced geotextiles in demanding environmental conditions. Polypropylene fiber provides cost-effective, lightweight solutions with excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, suitable for general drainage and soil stabilization applications. Selecting the right fiber depends on project-specific requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Basalt fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Geotextile
 azmater.com
azmater.com