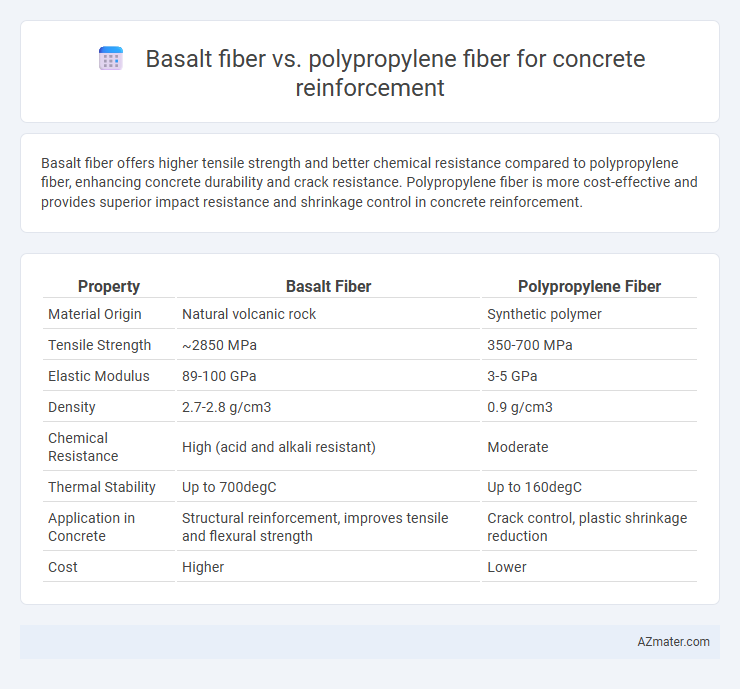
Basalt fiber offers higher tensile strength and better chemical resistance compared to polypropylene fiber, enhancing concrete durability and crack resistance. Polypropylene fiber is more cost-effective and provides superior impact resistance and shrinkage control in concrete reinforcement.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Natural volcanic rock | Synthetic polymer |
| Tensile Strength | ~2850 MPa | 350-700 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 89-100 GPa | 3-5 GPa |
| Density | 2.7-2.8 g/cm3 | 0.9 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Resistance | High (acid and alkali resistant) | Moderate |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 700degC | Up to 160degC |
| Application in Concrete | Structural reinforcement, improves tensile and flexural strength | Crack control, plastic shrinkage reduction |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Fiber Reinforced Concrete
Fiber reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances structural performance by incorporating discrete fibers such as basalt fiber and polypropylene fiber, which improve tensile strength, ductility, and crack resistance. Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic rocks, offers superior mechanical properties, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance compared to polypropylene fiber, which is a synthetic polymer known for its chemical inertness and cost-effectiveness. Selection between basalt and polypropylene fibers depends on factors like reinforcement efficiency, environmental exposure, and economic considerations in concrete applications.
Overview of Basalt Fiber
Basalt fiber is a high-performance material derived from volcanic basalt rock, known for its excellent tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability, making it highly suitable for concrete reinforcement. Unlike polypropylene fiber, basalt fiber enhances structural durability and crack resistance without compromising the workability of the concrete mix. Its eco-friendly production and superior mechanical properties position basalt fiber as a durable and sustainable alternative in reinforced concrete applications.
Overview of Polypropylene Fiber
Polypropylene fiber is a synthetic polymer widely used in concrete reinforcement due to its excellent chemical resistance, low cost, and ability to control plastic shrinkage cracking. These fibers enhance concrete toughness and impact resistance without compromising workability, making them ideal for applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant reinforcement. Compared to basalt fiber, polypropylene fiber offers superior flexibility and ease of mixing, though it has lower tensile strength and modulus of elasticity.
Material Properties: Basalt vs Polypropylene
Basalt fiber offers superior tensile strength and higher modulus of elasticity compared to polypropylene fiber, making it more effective for load-bearing concrete reinforcement. Its excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance enhance durability in harsh environments, unlike polypropylene fiber which has lower melting points and is less resistant to chemical attack. Basalt fiber's higher density and stiffness contribute to improved crack control and structural integrity in reinforced concrete applications.
Mechanical Performance in Concrete
Basalt fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and elastic modulus compared to polypropylene fiber, enhancing concrete's load-bearing capacity and crack resistance. The higher stiffness of basalt fibers improves concrete durability under mechanical stress, while polypropylene fibers primarily aid in controlling plastic shrinkage and impact resistance. Concrete reinforced with basalt fibers demonstrates improved flexural strength and toughness, making it more suitable for structural applications requiring enhanced mechanical performance.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Basalt fiber exhibits superior durability and environmental resistance compared to polypropylene fiber when used for concrete reinforcement, maintaining strength and structural integrity under high temperatures, UV exposure, and chemical attacks. Polypropylene fibers, while effective in controlling plastic shrinkage cracks, degrade faster under prolonged UV radiation and chemical exposure, leading to reduced long-term performance. Basalt fiber's natural resistance to alkali environments and moisture makes it a preferred choice in harsh conditions, enhancing the longevity and sustainability of reinforced concrete structures.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Basalt fiber offers higher tensile strength and durability compared to polypropylene fiber, but it generally comes at a higher initial cost, which may impact project budgets. Polypropylene fiber is widely available and more cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for large-scale concrete reinforcement projects with budget constraints. The global supply chain for polypropylene fibers is well-established, ensuring consistent availability, whereas basalt fibers, sourced from volcanic rock, can face variability in supply depending on regional mining and processing capabilities.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Basalt fiber for concrete reinforcement offers superior sustainability due to its natural origin from volcanic rock, resulting in lower carbon emissions during production compared to synthetic polypropylene fiber. Basalt fiber is fully recyclable and non-toxic, promoting a reduced environmental footprint, while polypropylene fibers are derived from petrochemicals and contribute to microplastic pollution. The enhanced durability and corrosion resistance of basalt fiber extend concrete structure lifespan, minimizing resource consumption and waste generation over time.
Applications and Recommended Uses
Basalt fiber offers superior strength and durability compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for high-performance concrete applications such as bridges, tunnels, and industrial flooring where enhanced crack resistance and longevity are critical. Polypropylene fiber excels in lightweight concrete and non-structural projects like slabs, pavements, and shotcrete due to its cost-effectiveness and resistance to shrinkage and plastic cracking. For applications requiring chemical resistance and fire resistance, basalt fiber is preferred, whereas polypropylene fiber is suitable for improving workability and controlling plastic shrinkage in mass concrete pours.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Concrete Reinforcement
Basalt fiber offers superior tensile strength, durability, and chemical resistance compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for high-performance concrete applications requiring enhanced structural integrity. Polypropylene fiber is cost-effective, improves crack resistance, and provides excellent workability, suitable for general-purpose concrete reinforcement and controlling plastic shrinkage. Selecting between basalt and polypropylene fibers depends on project-specific requirements such as load-bearing capacity, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal concrete performance.
Infographic: Basalt fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Concrete reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com