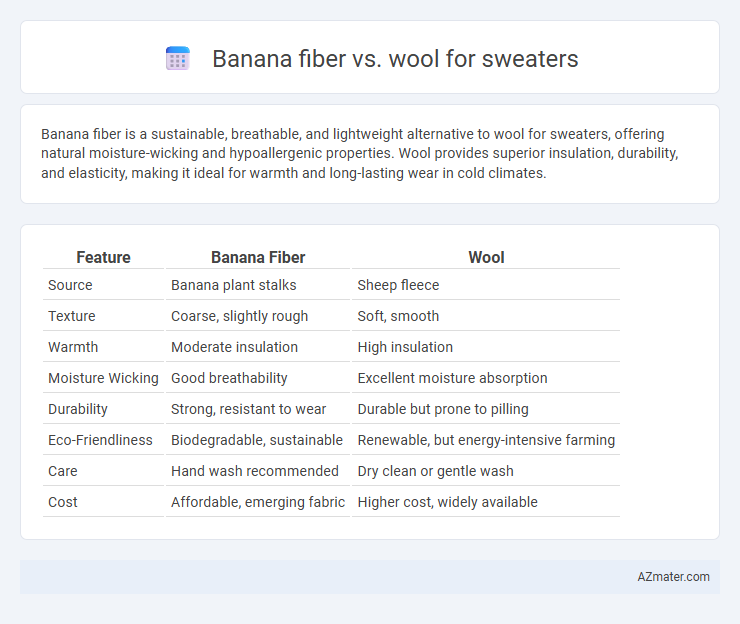
Banana fiber is a sustainable, breathable, and lightweight alternative to wool for sweaters, offering natural moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic properties. Wool provides superior insulation, durability, and elasticity, making it ideal for warmth and long-lasting wear in cold climates.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Banana Fiber | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Banana plant stalks | Sheep fleece |
| Texture | Coarse, slightly rough | Soft, smooth |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation | High insulation |
| Moisture Wicking | Good breathability | Excellent moisture absorption |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to wear | Durable but prone to pilling |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable | Renewable, but energy-intensive farming |
| Care | Hand wash recommended | Dry clean or gentle wash |
| Cost | Affordable, emerging fabric | Higher cost, widely available |
Introduction: Comparing Banana Fiber and Wool for Sweaters
Banana fiber, derived from the pseudostem of banana plants, offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional wool in sweater production. Wool, known for its natural insulation and moisture-wicking properties, remains a classic choice for warmth and durability. Exploring the differences in texture, environmental impact, and thermal performance reveals how banana fiber compares to wool in creating comfortable and sustainable sweaters.
Material Origins: Banana Fiber vs. Wool
Banana fiber, derived from the stalks of banana plants, offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional wool sourced from sheep fleece. Banana fiber's natural cellulose composition provides lightweight breathability and biodegradability, whereas wool is rich in keratin protein, imparting superior warmth and moisture-wicking properties. Understanding the material origins highlights banana fiber's plant-based renewable qualities versus wool's animal-derived resilience and insulation benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Banana fiber offers a highly sustainable alternative to wool for sweaters due to its biodegradable nature and low water consumption during cultivation, significantly reducing environmental impact. In contrast, wool production involves intensive water use, methane emissions from sheep, and land degradation, contributing to a larger carbon footprint. Choosing banana fiber supports eco-friendly fashion by utilizing agricultural waste and minimizing resource depletion.
Texture and Comfort for Wearers
Banana fiber sweaters offer a unique, lightweight texture that is breathable and moisture-wicking, making them ideal for warm climates and sensitive skin. Wool sweaters provide superior insulation with a soft, plush texture that retains heat effectively, making them perfect for cold weather wearers seeking warmth and comfort. While banana fiber tends to be coarser, it softens with wear, whereas wool's natural elasticity enhances durability and tactile comfort over time.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Banana fiber offers excellent breathability and moisture-wicking properties but provides less warmth and insulation compared to wool. Wool fibers trap air efficiently, creating superior thermal insulation ideal for cold weather sweaters. For optimal warmth and insulation, wool remains the preferred material, while banana fiber suits lightweight, breathable garments.
Durability and Lifespan of Sweaters
Banana fiber sweaters offer high durability due to the strong cellulose fibers derived from banana plant stalks, making them resistant to wear and tear over time. Wool sweaters provide excellent longevity with natural elasticity and resilience, maintaining shape and warmth through multiple uses and washes. Compared to wool, banana fiber's durability is enhanced by its resistance to moisture and pests, contributing to a longer lifespan in humid or variable climates.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Banana fiber sweaters require gentle hand washing with mild detergent and air drying to maintain their natural texture and prevent shrinkage, while wool sweaters demand careful laundering with specialized wool detergents and careful drying flat to avoid stretching or felting. Banana fiber's moisture-wicking properties allow for easier odor control, reducing frequent washes compared to wool, which often needs more regular cleaning to manage its absorbency. Proper storage for both fibers involves keeping them in breathable garment bags to protect against moths and maintain fiber integrity.
Allergies and Skin Sensitivities
Banana fiber offers a hypoallergenic alternative to wool, making it ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies, as it is naturally smooth and free from lanolin, a common irritant in wool. Wool, while warm and breathable, can cause itching or allergic reactions in some people due to its coarse texture and lanolin content. Choosing banana fiber sweaters reduces the risk of skin irritation, particularly for those prone to eczema or contact dermatitis.
Style and Aesthetic Differences
Banana fiber sweaters offer a unique, matte finish with a natural, rustic aesthetic that appeals to eco-conscious fashion enthusiasts seeking sustainable alternatives. Wool sweaters provide a classic, rich texture with a soft, lofty appearance that enhances traditional and sophisticated style choices. The coarse, textured look of banana fiber contrasts with the smooth, resilient fibers of wool, making each fabric suited for distinct fashion statements and seasonal wear.
Cost and Market Availability
Banana fiber sweaters are generally more affordable due to lower raw material costs and simpler production processes compared to wool, which involves higher expenses for animal husbandry and processing. Wool remains widely available in mainstream markets, leveraging a well-established supply chain, whereas banana fiber products are more niche and less commonly found in retail outlets. The market for wool sweaters is larger and more mature, while banana fiber items appeal to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives.
Infographic: Banana fiber vs Wool for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com