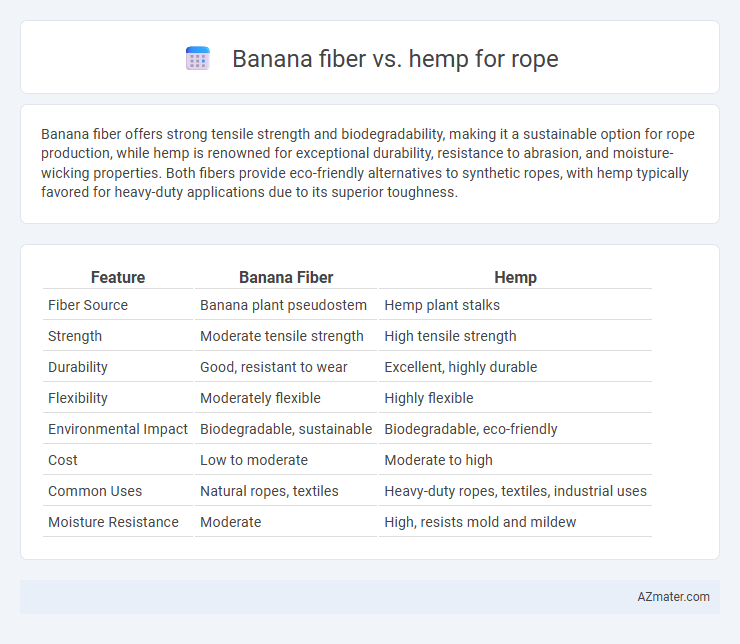
Banana fiber offers strong tensile strength and biodegradability, making it a sustainable option for rope production, while hemp is renowned for exceptional durability, resistance to abrasion, and moisture-wicking properties. Both fibers provide eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic ropes, with hemp typically favored for heavy-duty applications due to its superior toughness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Banana Fiber | Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Source | Banana plant pseudostem | Hemp plant stalks |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Durability | Good, resistant to wear | Excellent, highly durable |
| Flexibility | Moderately flexible | Highly flexible |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable | Biodegradable, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Common Uses | Natural ropes, textiles | Heavy-duty ropes, textiles, industrial uses |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate | High, resists mold and mildew |
Introduction to Natural Fiber Ropes
Natural fiber ropes commonly utilize banana fiber and hemp due to their strength and sustainability, each offering unique advantages. Banana fiber provides excellent flexibility and a smooth texture, making it ideal for lighter, decorative ropes, while hemp stands out for its superior durability, resistance to abrasion, and historical use in heavy-duty applications like maritime rigging. The environmental benefits of both fibers include biodegradability and low-impact cultivation, positioning them as eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic ropes.
Overview of Banana Fiber and Its Properties
Banana fiber, extracted from the pseudostem of the banana plant, is known for its high tensile strength and flexibility, making it a durable option for rope manufacturing. This natural fiber exhibits excellent resistance to moisture, biodegradability, and is lightweight compared to hemp, which typically has coarser texture and higher lignin content. Its eco-friendly nature and renewable sourcing contribute to sustainable production, positioning banana fiber as a versatile and environmentally conscious alternative to traditional hemp fibers in rope applications.
Key Characteristics of Hemp Fiber
Hemp fiber is highly durable, naturally resistant to rot and UV damage, and offers exceptional tensile strength, making it ideal for rope production. Its long, strong bast fibers provide superior abrasion resistance and minimal elongation compared to banana fiber. These key characteristics enable hemp ropes to maintain integrity under heavy load and harsh environmental conditions, outperforming banana fiber ropes in longevity and performance.
Strength Comparison: Banana Fiber vs Hemp
Hemp fibers exhibit higher tensile strength than banana fibers, typically ranging between 550 to 900 MPa, making hemp ropes exceptionally durable and resistant to breaking under strain. Banana fiber offers moderate tensile strength, approximately 500 to 600 MPa, providing adequate durability but less robustness compared to hemp. The superior molecular structure of hemp fibers contributes to their enhanced strength, making hemp the preferred choice for heavy-duty rope applications requiring maximum load-bearing capacity and longevity.
Durability and Longevity in Rope Applications
Hemp rope exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to banana fiber due to its higher tensile strength and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture and UV exposure. Banana fiber tends to degrade faster under constant stress and harsh weather, making hemp a preferred choice for heavy-duty and long-term rope applications. The natural lignin content in hemp fibers enhances its structural integrity, resulting in ropes that maintain performance over extended periods.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Banana fiber and hemp are both environmentally sustainable options for rope production, with hemp exhibiting a lower water footprint and faster growth cycle, typically maturing in 3-4 months compared to banana fiber's 9-12 months. Hemp cultivation requires minimal pesticides and enhances soil health through its phytoremediation properties, while banana fiber utilizes agricultural waste, reducing biomass but demanding more energy-intensive processing. Both fibers are biodegradable and renewable; however, hemp's widespread agricultural compatibility and higher tensile strength offer superior durability and eco-efficiency in sustainable rope manufacturing.
Processing Methods: Banana Fiber vs Hemp Fiber
Banana fiber is extracted through a decortication process that separates the fibers from the pseudostem, followed by retting to soften and clean them, resulting in a coarse texture ideal for rope making. Hemp fiber undergoes a retting process that breaks down the pectin binding the fibers, followed by breaking and scutching to produce long, strong, and smooth fibers well-suited for durable ropes. The processing of hemp typically yields fibers with higher tensile strength and uniformity compared to banana fiber, influencing the rope's durability and performance.
Cost and Availability of Both Fibers
Banana fiber is generally more cost-effective than hemp due to its abundant availability in tropical regions and lower processing expenses. Hemp fibers, while stronger and more durable, often come with higher prices attributed to stricter cultivation regulations and limited growing areas. Availability of banana fiber is seasonal but widespread in countries like India and the Philippines, whereas hemp is predominantly produced in Europe and North America, influencing supply consistency and overall cost for rope manufacturing.
Common Uses for Banana Fiber and Hemp Rope
Banana fiber is commonly used for making eco-friendly ropes, mats, and handicrafts due to its high tensile strength and flexibility. Hemp rope is widely preferred in industrial applications, marine environments, and gardening because of its durability, resistance to UV light, and natural antimicrobial properties. Both fibers serve sustainable alternatives but cater to different needs: banana fiber excels in lightweight and biodegradable products, while hemp provides robust and long-lasting rope solutions.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Banana Fiber and Hemp for Rope
Banana fiber offers exceptional softness and flexibility, making it suitable for lightweight and eco-friendly rope applications, while hemp provides superior strength, durability, and resistance to wear, ideal for heavy-duty tasks. Both fibers are biodegradable and sustainable, but hemp's long tradition in rope making and higher tensile strength often make it the preferred choice for industrial and marine uses. Selecting between banana fiber and hemp depends on the specific rope requirements, balancing factors such as strength, texture, environmental impact, and intended usage.
Infographic: Banana fiber vs Hemp for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com