Aramid fibers offer exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-strength thread applications requiring durability and safety. Silk, while providing natural elasticity and smoothness, lacks the superior strength and thermal stability of aramid, limiting its use in extreme stress environments.
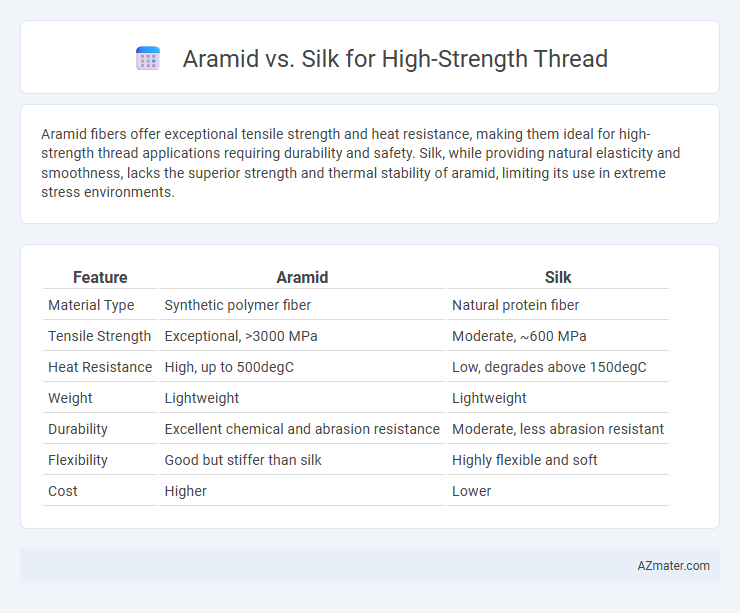
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid | Silk |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer fiber | Natural protein fiber |
| Tensile Strength | Exceptional, >3000 MPa | Moderate, ~600 MPa |
| Heat Resistance | High, up to 500degC | Low, degrades above 150degC |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Durability | Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance | Moderate, less abrasion resistant |
| Flexibility | Good but stiffer than silk | Highly flexible and soft |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to High-Strength Threads
High-strength threads like aramid and silk are essential in applications requiring exceptional durability and resistance to abrasion. Aramid fibers, known for their heat resistance and tensile strength, are widely used in industrial, aerospace, and military textiles, outperforming many natural materials. Silk threads, though natural, exhibit impressive tensile strength and flexibility, making them valuable in specialized applications such as surgical sutures and luxury textiles where both strength and softness are required.
What are Aramid Threads?
Aramid threads are synthetic fibers known for exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, often used in aerospace, military, and industrial applications. These threads possess high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and chemicals, outperforming natural fibers like silk in demanding environments. Unlike silk, aramid threads maintain structural integrity under extreme stress and elevated temperatures, making them ideal for safety gear, bulletproof vests, and high-performance composites.
What are Silk Threads?
Silk threads are natural fibers derived from the cocoons of the silkworm, renowned for their tensile strength and smooth texture. They offer exceptional elasticity and resilience, making them suitable for delicate yet durable sewing and embroidery projects. Compared to synthetic alternatives like aramid threads, silk provides a biodegradable and comfortable option, though it typically has lower heat resistance and abrasion strength.
Key Properties of Aramid Threads
Aramid threads exhibit exceptional tensile strength, heat resistance up to 500degC, and excellent chemical stability, making them ideal for high-strength applications like aerospace and military use. Unlike silk, aramid offers superior abrasion resistance and low flammability, ensuring durability in extreme environments. These properties position aramid as a preferred material for protective gear, composites, and industrial thread solutions.
Key Properties of Silk Threads
Silk threads exhibit remarkable tensile strength combined with exceptional elasticity and natural resilience, making them suitable for applications requiring both durability and flexibility. Their smooth surface ensures minimal friction, enhancing performance in delicate or high-precision textile uses. Unlike aramid threads, silk offers superior moisture absorption and biodegradability, appealing to eco-conscious industries prioritizing sustainable high-strength materials.
Aramid vs Silk: Strength and Durability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer significantly higher tensile strength and superior durability compared to silk, making them ideal for high-strength thread applications requiring resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure. Silk, while naturally strong for a natural fiber and providing excellent flexibility and smoothness, lacks the same level of tensile strength and long-term durability under extreme conditions that aramid fibers achieve. The molecular structure of aramid imparts exceptional resistance to stretching and wear, positioning it as the preferred choice over silk in industrial and safety-critical sewing tasks.
Heat and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit superior heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 450degC, whereas silk begins to degrade around 200degC, limiting its use in high-temperature applications. Chemically, aramid threads resist a wide range of solvents, fuels, and alkalis, making them ideal for industrial and protective gear, while silk fibers are prone to damage from acids and prolonged exposure to moisture. The enhanced thermal stability and chemical resistance of aramid threads make them more suitable for demanding environments compared to silk.
Flexibility and Handling Differences
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for high-strength thread applications requiring durability. Silk fibers provide superior flexibility and smoother handling, allowing for easier manipulation and finer stitching in delicate or intricate work. While aramid threads excel in performance under stress, silk threads are preferred when flexibility and ease of use are critical factors.
Common Applications: Aramid vs Silk
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are commonly used in high-strength thread applications including aerospace components, body armor, and industrial sewing due to their exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance. Silk threads, while not as strong as aramid, find frequent use in delicate applications like embroidery, luxury garment stitching, and medical sutures where flexibility and smooth texture are essential. Choosing between aramid and silk for high-strength thread depends on the balance between required durability, heat resistance, and aesthetic or tactile qualities.
Choosing the Best Thread: Aramid or Silk?
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, outperform silk in high-strength thread applications requiring durability and safety under extreme conditions. Silk threads offer natural elasticity and smoothness, making them suitable for delicate fabrics but less ideal for heavy-duty use compared to aramid's superior abrasion resistance. When selecting the best thread, consider aramid for industrial, automotive, or protective gear projects where maximum strength and thermal stability are critical, while silk remains preferable for luxury textiles demanding softness and fine detail.
Infographic: Aramid vs Silk for High-strength Thread
 azmater.com
azmater.com