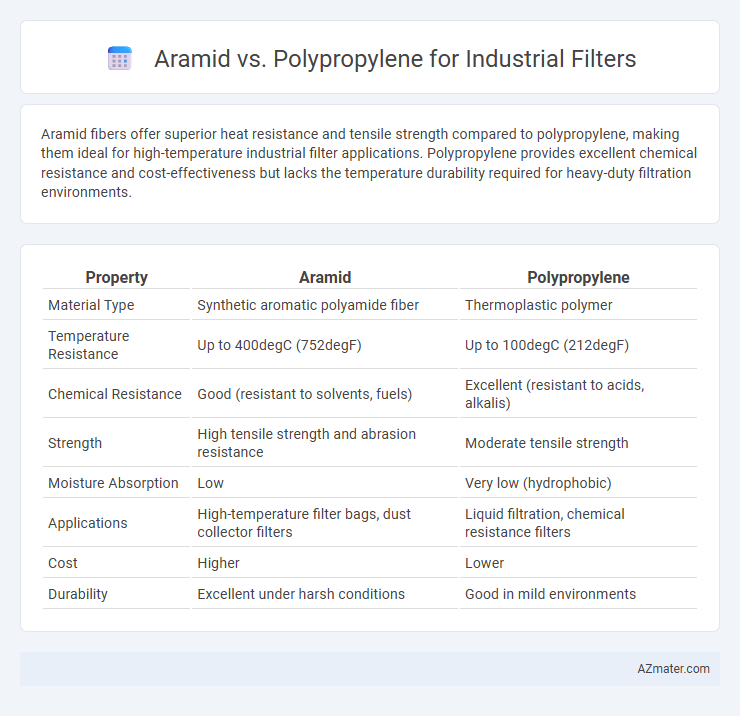
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and tensile strength compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial filter applications. Polypropylene provides excellent chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness but lacks the temperature durability required for heavy-duty filtration environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fiber | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 400degC (752degF) | Up to 100degC (212degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (resistant to solvents, fuels) | Excellent (resistant to acids, alkalis) |
| Strength | High tensile strength and abrasion resistance | Moderate tensile strength |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Very low (hydrophobic) |
| Applications | High-temperature filter bags, dust collector filters | Liquid filtration, chemical resistance filters |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Durability | Excellent under harsh conditions | Good in mild environments |
Introduction to Industrial Filter Materials
Aramid fibers offer exceptional strength and thermal resistance, making them ideal for industrial filters exposed to high temperatures and harsh chemical environments. Polypropylene provides excellent chemical resistance and moisture repellency, suitable for applications requiring lightweight and cost-effective filter media. Selecting between aramid and polypropylene depends on factors like operational temperature, chemical exposure, and filtration efficiency requirements.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, are widely used in industrial filter media to provide durability and chemical stability in harsh environments. These fibers exhibit high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and thermal stability up to 400degC, making them ideal for filtration applications involving high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. Compared to polypropylene, aramid fibers offer superior mechanical properties and longer service life, especially in heavy-duty industrial filters.
Overview of Polypropylene Fibers
Polypropylene fibers are widely used in industrial filters due to their excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and cost-effectiveness. These thermoplastic polymers offer high tensile strength and durability, making them suitable for filtering applications in harsh environments involving acids, bases, and organic solvents. Compared to aramid fibers, polypropylene provides enhanced resistance to corrosion and contamination, while maintaining lightweight and flexible properties essential for efficient filtration processes.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to polypropylene in industrial filter applications, offering higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance. Aramid's molecular structure provides excellent durability under high stress and temperature conditions, making it ideal for demanding filtration environments. Polypropylene, while more cost-effective, has lower tensile strength and is less resistant to mechanical wear, limiting its use in high-performance industrial filters.
Thermal Resistance and Performance
Aramid fibers exhibit superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 500degF (260degC), making them ideal for high-temperature industrial filter applications. Polypropylene offers lower thermal stability, degrading around 180degF (82degC), which limits its use in environments with extreme heat but provides excellent chemical resistance and cost efficiency. The performance of aramid filters under thermal stress outperforms polypropylene by sustaining filtration efficiency and media durability in harsh industrial conditions.
Chemical Compatibility and Durability
Aramid fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and solvents compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for harsh industrial filtration environments. Polypropylene offers good resistance to bases and certain acids but degrades quickly in the presence of strong oxidizers and aromatic hydrocarbons. In terms of durability, aramid provides higher tensile strength and thermal stability, ensuring longer service life under extreme conditions, while polypropylene is valued for its low cost and moderate strength in less demanding applications.
Filtration Efficiency and Particle Retention
Aramid fibers exhibit superior filtration efficiency and particle retention compared to polypropylene due to their high tensile strength and thermal stability, making them ideal for demanding industrial filter environments. Polypropylene filters offer cost-effective and chemical-resistant options but generally have lower filtration precision and particle capture capabilities. The choice between aramid and polypropylene significantly impacts filter performance in applications requiring fine particulate control and durability.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Aramid fibers offer high tensile strength and excellent heat resistance, making them suitable for demanding industrial filter applications but come at a higher upfront cost. Polypropylene filters provide a more affordable solution with good chemical resistance and adequate durability for less intensive environments, resulting in lower initial investment and replacement expenses. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, polypropylene is ideal for budget-sensitive projects, while aramid delivers longer service life and reduced maintenance frequency, potentially lowering total cost of ownership in heavy-duty contexts.
Common Industrial Applications
Aramid fibers are widely used in industrial filters for high-temperature applications such as automotive, chemical processing, and heavy machinery due to their exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength. Polypropylene filters are preferred in water treatment, food processing, and pharmaceutical industries where chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness are critical. Both materials offer unique advantages, with aramid excelling in durability under harsh conditions and polypropylene providing efficient filtration in less demanding environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Filter Material
Aramid fibers offer superior thermal resistance, chemical stability, and mechanical strength, making them ideal for demanding industrial filtration applications involving high temperatures and aggressive chemicals. Polypropylene filters provide cost-effective solutions with excellent chemical resistance and hydrophobic properties, suited for less extreme environments and applications requiring moisture resistance. Selecting the optimal filter material depends on the specific industrial conditions, target contaminants, and operational temperature, with aramid favored for heavy-duty filtration and polypropylene for economical, chemical-resistant filtration needs.
Infographic: Aramid vs Polypropylene for Industrial Filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com