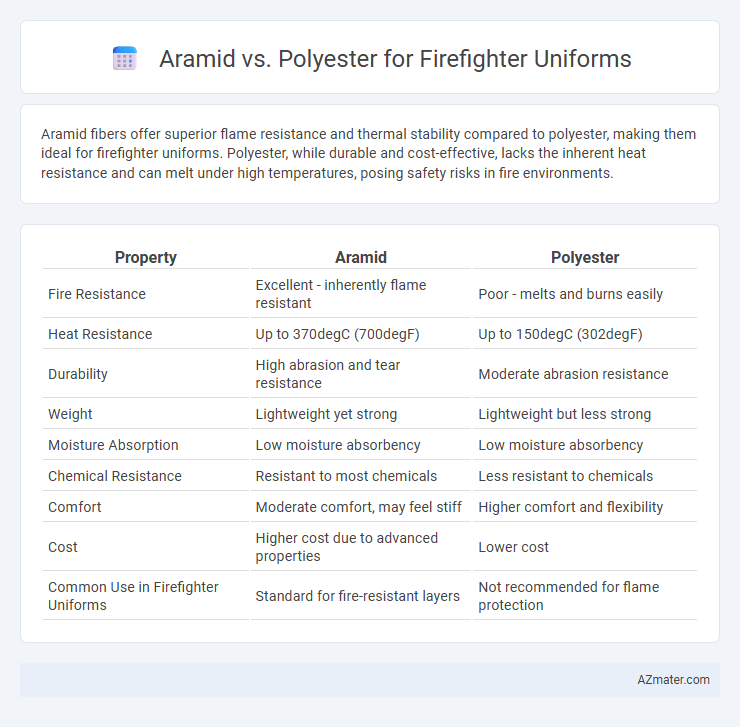
Aramid fibers offer superior flame resistance and thermal stability compared to polyester, making them ideal for firefighter uniforms. Polyester, while durable and cost-effective, lacks the inherent heat resistance and can melt under high temperatures, posing safety risks in fire environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Fire Resistance | Excellent - inherently flame resistant | Poor - melts and burns easily |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 370degC (700degF) | Up to 150degC (302degF) |
| Durability | High abrasion and tear resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance |
| Weight | Lightweight yet strong | Lightweight but less strong |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorbency | Low moisture absorbency |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most chemicals | Less resistant to chemicals |
| Comfort | Moderate comfort, may feel stiff | Higher comfort and flexibility |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced properties | Lower cost |
| Common Use in Firefighter Uniforms | Standard for fire-resistant layers | Not recommended for flame protection |
Introduction to Firefighter Uniform Materials
Firefighter uniforms primarily utilize aramid and polyester fibers, each offering distinct advantages in thermal protection and durability. Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, provide superior heat resistance and flame retardancy, making them essential for high-risk firefighting environments. Polyester, while less heat-resistant, offers enhanced strength and moisture-wicking properties, contributing to comfort and durability during extended operations.
What is Aramid?
Aramid fibers are high-performance synthetic fibers known for their exceptional heat resistance, strength, and durability, making them ideal for firefighter uniforms. Unlike polyester, aramid materials such as Nomex and Kevlar provide superior flame retardant properties and maintain integrity at extreme temperatures. These characteristics help protect firefighters from burns and injuries during high-risk fire incidents.
What is Polyester?
Polyester is a synthetic polymer widely used in firefighter uniforms for its lightweight and moisture-wicking properties. Unlike aramid fibers, polyester has a lower inherent flame resistance and requires chemical treatments to meet safety standards. Its durability and affordability make it a common blend with aramid materials to enhance comfort without compromising protection.
Heat and Flame Resistance Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, exhibit superior heat and flame resistance compared to polyester, maintaining integrity and thermal protection even under extreme temperatures above 370degC (700degF). Polyester tends to melt and ignite, increasing burn risk, whereas aramid fabrics char and insulate, preventing heat transfer to the skin. Firefighter uniforms made with aramid blends provide enhanced durability and safety for prolonged exposure to high-heat environments during firefighting operations.
Durability and Wear Performance
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, exhibit superior durability and wear performance in firefighter uniforms due to their inherent heat resistance and strong molecular structure, which safeguards against flames and mechanical abrasion. Polyester, while offering better moisture management and comfort, tends to degrade faster under high temperatures and prolonged exposure to flames, limiting its durability in extreme firefighting conditions. The combination of aramid's high thermal stability and resistance to wear makes it the preferred choice for protective gear designed to withstand rigorous firefighting environments.
Comfort and Breathability Factors
Aramid fibers, known for inherent flame resistance, offer superior thermal protection but can feel heavier and less breathable than polyester blends, which enhance comfort through moisture-wicking properties. Polyester contributes to lighter, more breathable uniforms by allowing better air circulation and quicker drying, essential for maintaining firefighter comfort during prolonged heat exposure. Optimizing firefighter uniforms often involves combining aramid's flame resistance with polyester's comfort to balance safety and breathability effectively.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Aramid fibers, commonly used in firefighter uniforms, offer superior heat resistance and durability while maintaining a lightweight profile, typically ranging from 4 to 6 ounces per square yard. Polyester fabrics, although more flexible and comfortable due to their softer texture, tend to be heavier and less heat resistant, often weighing closer to 6 to 8 ounces per square yard. The enhanced flexibility of polyester can improve mobility, but aramid's combination of light weight and high thermal stability makes it the preferred choice for critical protective gear.
Cost and Availability
Aramid fibers, known for superior heat and flame resistance, typically cost more than polyester, impacting budget considerations for firefighter uniforms. Polyester is more widely available and less expensive but lacks the inherent flame-retardant properties of aramid, often requiring chemical treatments to meet safety standards. Choosing between aramid and polyester involves balancing higher upfront material costs against performance and compliance with fire safety regulations.
Safety Standards and Compliance
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, meet NFPA 1971 standards for firefighter turnout gear, offering superior flame resistance, thermal protection, and durability under extreme conditions. Polyester fabrics typically lack inherent flame resistance and must be treated chemically to approach compliance, which may degrade after repeated laundering. Firefighter uniforms made from aramid blends ensure consistent compliance with OSHA and NFPA safety regulations, providing enhanced protection against flash fires and radiant heat exposure.
Choosing the Best Material for Firefighter Uniforms
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, offer superior heat resistance, flame retardancy, and durability compared to polyester, making them the preferred choice for firefighter uniforms where maximum protection is critical. Polyester, while lighter and more cost-effective, lacks inherent flame-resistant properties and can melt under high temperatures, posing significant risks in firefighting scenarios. Selecting aramid-based materials ensures enhanced safety, compliance with NFPA 1971 standards, and longer garment lifespan in extreme fire environments.
Infographic: Aramid vs Polyester for Firefighter Uniform
 azmater.com
azmater.com