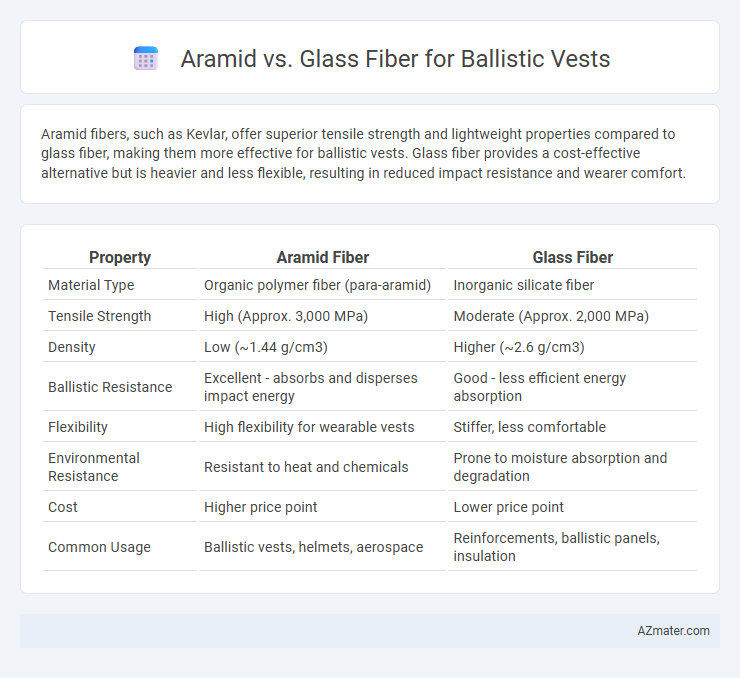
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior tensile strength and lightweight properties compared to glass fiber, making them more effective for ballistic vests. Glass fiber provides a cost-effective alternative but is heavier and less flexible, resulting in reduced impact resistance and wearer comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Organic polymer fiber (para-aramid) | Inorganic silicate fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (Approx. 3,000 MPa) | Moderate (Approx. 2,000 MPa) |
| Density | Low (~1.44 g/cm3) | Higher (~2.6 g/cm3) |
| Ballistic Resistance | Excellent - absorbs and disperses impact energy | Good - less efficient energy absorption |
| Flexibility | High flexibility for wearable vests | Stiffer, less comfortable |
| Environmental Resistance | Resistant to heat and chemicals | Prone to moisture absorption and degradation |
| Cost | Higher price point | Lower price point |
| Common Usage | Ballistic vests, helmets, aerospace | Reinforcements, ballistic panels, insulation |
Introduction to Ballistic Vest Materials
Aramid and glass fiber are two critical materials used in the construction of ballistic vests, with aramid fibers like Kevlar offering superior tensile strength and energy absorption properties ideal for personal armor. Glass fiber, while more cost-effective and providing decent impact resistance, generally lacks the lightweight and flexibility advantages essential for high-performance ballistic protection. Understanding the material composition is vital as aramid fibers deliver enhanced durability and multi-hit capability, making them the preferred choice in advanced ballistic applications.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, widely used in ballistic vests, offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high tensile strength, making it ideal for impact resistance and bulletproof applications. This synthetic fiber is inherently heat-resistant and chemically stable, ensuring durability under extreme conditions while maintaining flexibility for wearer comfort. Compared to glass fiber, aramid delivers superior energy absorption and lighter weight, enhancing mobility and overall protection in ballistic gear.
Overview of Glass Fiber
Glass fiber, composed of fine glass strands woven into a fabric, offers high tensile strength and lightweight properties, making it a viable material for ballistic vests. Its excellent resistance to heat and corrosion enhances durability under harsh conditions, although it generally provides lower impact resistance compared to aramid fibers. Cost-effectiveness and ease of production contribute to its use in protective gear where moderate ballistic performance is acceptable.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior tensile strength and higher energy absorption compared to glass fibers, making them more effective for ballistic protection. Glass fibers are denser and less flexible, leading to heavier and less comfortable vests despite their cost advantages. The low elongation at break and excellent thermal resistance of aramid enhance durability and performance under ballistic impact.
Ballistic Performance and Protection Levels
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior ballistic performance compared to glass fibers due to their high tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities, making them the preferred choice in high-risk ballistic vests. Glass fiber provides adequate protection at lower threat levels but lacks the flexibility and multi-hit resistance of aramid, limiting its use in advanced ballistic applications. Ballistic vests incorporating aramid materials typically achieve higher protection levels under NIJ standards, effectively stopping rifle rounds and multiple impacts while maintaining wearability.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior durability and impact resistance compared to glass fiber, maintaining structural integrity under repeated ballistic impacts. Glass fiber provides good mechanical strength but tends to degrade more quickly when exposed to moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations, reducing its environmental resistance. The inherent chemical stability and heat resistance of aramid fibers make them more suitable for long-term use in ballistic vests subjected to harsh environmental conditions.
Weight and Comfort Factors
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are renowned for their high strength-to-weight ratio, making ballistic vests lighter and more comfortable for extended wear compared to glass fiber options. Glass fiber vests typically weigh more due to the material's higher density and rigidity, which can reduce flexibility and overall comfort. The superior flexibility and lower weight of aramid fibers enhance mobility and reduce fatigue, critical factors for users requiring long-term ballistic protection.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, generally have higher production costs than glass fibers due to complex manufacturing processes and specialized raw materials, impacting the overall expense of ballistic vests. Glass fiber offers a more cost-effective alternative with wider availability, especially in regions where aramid supply chains are limited or disrupted. Budget-conscious procurement often leans toward glass fiber composites for ballistic protection when cost and material accessibility are critical factors.
Suitability for Different Applications
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior tensile strength and flexibility, making them ideal for high-performance ballistic vests used by military and law enforcement personnel requiring lightweight, durable protection against high-velocity projectiles. Glass fiber, while more cost-effective and resistant to environmental factors, provides heavier and less flexible protection suited for lower-threat applications like vehicle reinforcements or industrial safety gear. The choice between aramid and glass fiber depends on the specific ballistic threat level, weight constraints, and environmental conditions of the intended application.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Material
Aramid fibers provide superior tensile strength, high impact resistance, and lightweight properties essential for effective ballistic vests, outperforming glass fiber in flexibility and durability. Glass fiber offers cost advantages and good compressive strength but lacks the same level of multi-hit resistance and comfort. Selecting aramid over glass fiber results in enhanced protection and maneuverability for high-threat environments.
Infographic: Aramid vs Glass Fiber for Ballistic Vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com