Underwater concrete offers superior resistance to washout and is specifically designed for subaqueous conditions in pile foundations. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance, improving durability in dynamic loading environments commonly encountered by pile foundations.
Table of Comparison
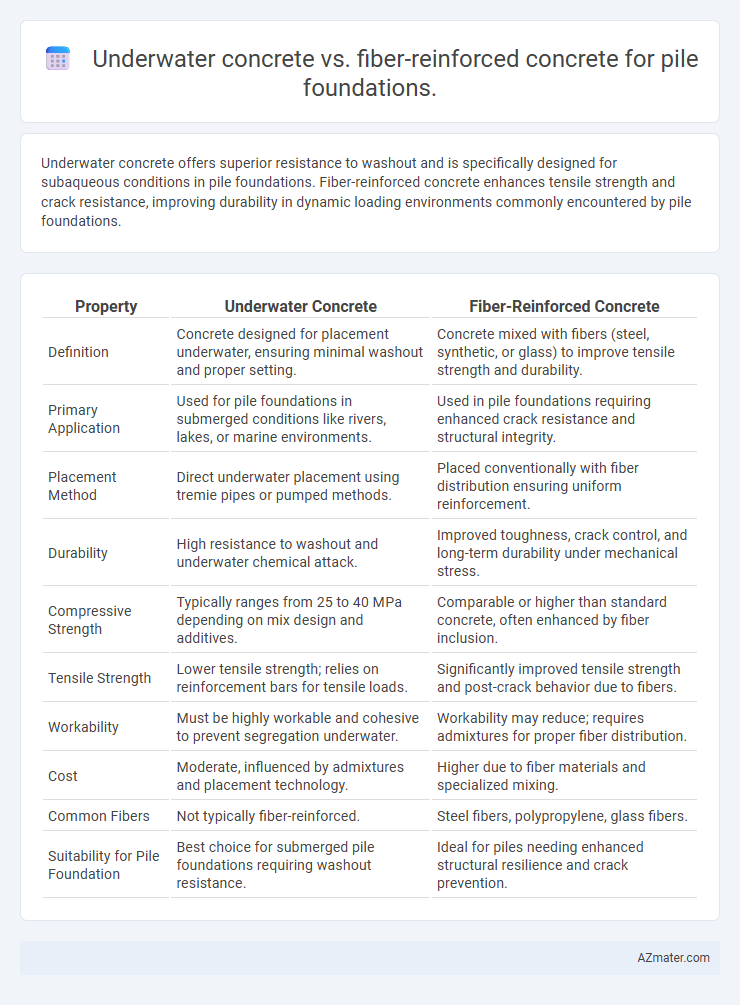
| Property | Underwater Concrete | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete designed for placement underwater, ensuring minimal washout and proper setting. | Concrete mixed with fibers (steel, synthetic, or glass) to improve tensile strength and durability. |
| Primary Application | Used for pile foundations in submerged conditions like rivers, lakes, or marine environments. | Used in pile foundations requiring enhanced crack resistance and structural integrity. |
| Placement Method | Direct underwater placement using tremie pipes or pumped methods. | Placed conventionally with fiber distribution ensuring uniform reinforcement. |
| Durability | High resistance to washout and underwater chemical attack. | Improved toughness, crack control, and long-term durability under mechanical stress. |
| Compressive Strength | Typically ranges from 25 to 40 MPa depending on mix design and additives. | Comparable or higher than standard concrete, often enhanced by fiber inclusion. |
| Tensile Strength | Lower tensile strength; relies on reinforcement bars for tensile loads. | Significantly improved tensile strength and post-crack behavior due to fibers. |
| Workability | Must be highly workable and cohesive to prevent segregation underwater. | Workability may reduce; requires admixtures for proper fiber distribution. |
| Cost | Moderate, influenced by admixtures and placement technology. | Higher due to fiber materials and specialized mixing. |
| Common Fibers | Not typically fiber-reinforced. | Steel fibers, polypropylene, glass fibers. |
| Suitability for Pile Foundation | Best choice for submerged pile foundations requiring washout resistance. | Ideal for piles needing enhanced structural resilience and crack prevention. |
Introduction to Pile Foundation Concrete Choices
Pile foundation concrete choices significantly impact structural stability and durability in marine and submerged environments. Underwater concrete is specifically formulated for placement in water, ensuring proper setting and strength development despite hydrostatic pressure and washout risks. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances crack resistance and tensile strength, improving pile durability and load-bearing capacity under dynamic and environmental stresses.
Overview of Underwater Concrete
Underwater concrete is specially formulated for placement in submerged conditions, ensuring proper setting and strength development despite water exposure. It incorporates anti-washout admixtures and maintains a cohesive mix to resist dispersion during underwater placement, crucial for pile foundation stability. This concrete type provides excellent durability and impermeability, making it suitable for marine and infrastructure projects requiring reliable underwater construction.
Overview of Fiber-reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances the structural performance of pile foundations by incorporating discrete fibers that improve tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability under harsh environmental conditions. Compared to traditional underwater concrete, FRC offers superior resistance to dynamic and cyclic loading, reducing maintenance costs and extending the service life of marine infrastructure. The integration of steel, glass, or synthetic fibers optimizes mechanical properties, making FRC a preferred choice for pile foundations exposed to underwater conditions.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Underwater concrete exhibits high flowability and anti-washout properties essential for submerged pile foundations, ensuring cohesive placement and reduced segregation. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability in pile foundations, improving structural integrity under dynamic loads. Both materials offer distinct advantages: underwater concrete prioritizes pumpability and cohesion in wet environments, while fiber-reinforced concrete optimizes mechanical performance and long-term resilience.
Workability and Placement Techniques
Underwater concrete is specifically designed for underwater placement with anti-washout admixtures enhancing workability and preventing segregation during subaqueous pours, while fiber-reinforced concrete relies on the distribution of fibers to improve structural integrity post-placement but demands meticulous mixing to maintain uniform fiber dispersion. Placement techniques for underwater concrete often involve tremie pipes or pumped placement to minimize washout and maintain consistency, whereas fiber-reinforced concrete is typically placed using conventional methods, requiring careful vibration or compaction to avoid fiber clumping and ensure homogeneity. Both types require precise control of mix design parameters to optimize workability and achieve desired pile foundation performance under challenging site conditions.
Durability in Aggressive Environments
Underwater concrete exhibits enhanced durability in aggressive environments due to its high-density mix design and chemical admixtures that reduce permeability and resist sulfate attack, making it ideal for submerged pile foundations. Fiber-reinforced concrete improves crack resistance and toughness by distributing tensile stresses, which helps mitigate chloride ion penetration and corrosion in aggressive soils but may require supplementary treatments for extended durability. Selecting underwater concrete ensures long-term structural integrity under hydrostatic pressure, while fiber reinforcement enhances durability in dynamic load conditions, particularly in saline or chemically aggressive sites.
Structural Performance and Load-bearing Capacity
Underwater concrete exhibits superior durability and resistance to washout, ensuring consistent structural integrity in submerged pile foundations, while fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack control, significantly improving load-bearing capacity. The integration of synthetic or steel fibers in concrete mixes effectively distributes stress and reduces brittleness, resulting in higher energy absorption and improved fatigue resistance under cyclic loads. Comparative studies reveal fiber-reinforced concrete piles demonstrate increased flexural strength and service life, whereas underwater concrete is optimized for placement stability and long-term underwater performance.
Cost Considerations and Budget Implications
Underwater concrete typically demands specialized admixtures and placement techniques, leading to higher initial material and labor costs compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, which incorporates synthetic or steel fibers to enhance durability without significantly increasing expenses. Fiber-reinforced concrete reduces long-term maintenance costs due to improved crack resistance and toughness, potentially offering better budget efficiency over the lifecycle of pile foundations. Cost considerations must balance the upfront investment of underwater concrete's complex application against fiber-reinforced concrete's enhanced performance and reduced repair needs.
Suitability for Deep Water and Marine Applications
Underwater concrete demonstrates superior resistance to washout and maintains workability in deep water conditions, making it highly suitable for marine pile foundations subjected to strong currents and high hydrostatic pressures. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack control but may require additional admixtures to ensure proper setting underwater, potentially limiting its direct application in deep marine environments without specialized mixes. Projects in deep water often favor underwater concrete formulations optimized for cohesion and placement, while fiber reinforcement is more commonly integrated in marine applications where structural performance under tensile stresses is critical.
Recommendations for Optimal Pile Foundation Selection
Underwater concrete requires a mix design with high workability and anti-washout properties to ensure proper setting and durability in submerged conditions, making it ideal for pile foundations in marine or groundwater-rich environments. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength, crack resistance, and durability, proving beneficial for pile foundations subjected to dynamic loads or seismic activity. Optimal pile foundation selection depends on site-specific factors like water presence, load conditions, and environmental exposure, recommending underwater concrete for submerged applications and fiber-reinforced concrete for enhanced structural performance under stress.
Infographic: Underwater concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Pile foundation
 azmater.com
azmater.com