Smart concrete enhances sidewalk durability by integrating self-healing properties and sensors for real-time damage detection. Pervious concrete improves sidewalk drainage and reduces runoff by allowing water to permeate through its porous structure.
Table of Comparison
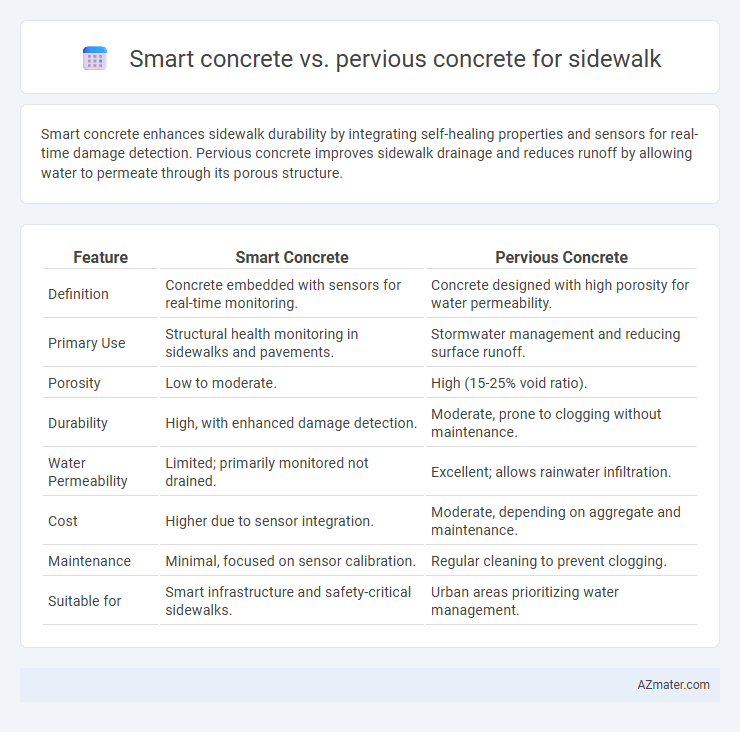
| Feature | Smart Concrete | Pervious Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete embedded with sensors for real-time monitoring. | Concrete designed with high porosity for water permeability. |
| Primary Use | Structural health monitoring in sidewalks and pavements. | Stormwater management and reducing surface runoff. |
| Porosity | Low to moderate. | High (15-25% void ratio). |
| Durability | High, with enhanced damage detection. | Moderate, prone to clogging without maintenance. |
| Water Permeability | Limited; primarily monitored not drained. | Excellent; allows rainwater infiltration. |
| Cost | Higher due to sensor integration. | Moderate, depending on aggregate and maintenance. |
| Maintenance | Minimal, focused on sensor calibration. | Regular cleaning to prevent clogging. |
| Suitable for | Smart infrastructure and safety-critical sidewalks. | Urban areas prioritizing water management. |
Introduction to Smart Concrete and Pervious Concrete
Smart concrete incorporates embedded sensors and self-healing materials to monitor structural health and repair micro-cracks autonomously, enhancing durability and lifespan in sidewalk applications. Pervious concrete features a porous matrix that facilitates rapid water drainage, significantly reducing surface runoff and promoting groundwater recharge in urban pedestrian areas. Both materials address different sustainability and maintenance challenges, with smart concrete prioritizing structural integrity and pervious concrete optimizing water management.
Key Differences Between Smart Concrete and Pervious Concrete
Smart concrete incorporates sensors and embedded technology to monitor structural health and environmental conditions, enhancing durability and safety in sidewalks. Pervious concrete prioritizes permeability, allowing water to pass through, reducing runoff and promoting groundwater recharge, making it ideal for sustainable urban drainage. The key difference lies in smart concrete's focus on real-time data and structural monitoring, whereas pervious concrete emphasizes water management and environmental benefits.
Composition and Materials Used
Smart concrete for sidewalks incorporates advanced materials like carbon nanotubes, fibers, and conductive polymers to enhance properties such as self-sensing and durability. Pervious concrete consists of coarse aggregates, cement, water, and little to no fine aggregates, creating a porous structure that facilitates water drainage. The key difference lies in smart concrete's engineered additives designed for performance enhancement versus pervious concrete's focus on permeability through its specific aggregate composition.
Structural Performance and Durability
Smart concrete utilizes embedded sensors and self-healing properties to monitor stress and repair micro-cracks, enhancing structural performance and extending durability in sidewalks. Pervious concrete facilitates water drainage through its porous structure, reducing hydrostatic pressure and surface wear, but it generally exhibits lower compressive strength and requires more frequent maintenance under heavy load conditions. For sidewalks, smart concrete offers superior long-term resilience and load-bearing capacity, while pervious concrete prioritizes stormwater management at the expense of structural robustness.
Water Permeability and Drainage Capabilities
Smart concrete incorporates sensors and self-healing properties that enhance structural durability but offers limited water permeability compared to pervious concrete. Pervious concrete is specifically designed with high porosity, allowing rapid water infiltration to significantly improve drainage and reduce surface runoff on sidewalks. The superior water permeability of pervious concrete makes it more effective for managing stormwater and preventing pooling in pedestrian areas.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart concrete incorporates self-healing properties and sensors to monitor structural health, reducing maintenance frequency and material waste, thereby enhancing sustainability. Pervious concrete improves stormwater management by allowing water infiltration, reducing runoff and groundwater pollution, which supports urban water cycle restoration. Both materials contribute to environmental impact reduction but target different sustainability aspects: durability and resource efficiency for smart concrete versus ecological water management for pervious concrete.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Smart concrete for sidewalks generally involves higher initial costs due to embedded sensors and advanced materials, whereas pervious concrete offers moderate upfront expenses with its porous, water-permeable design. Long-term economic benefits of smart concrete include reduced maintenance through real-time damage detection, while pervious concrete helps lower stormwater management costs by minimizing runoff. Decision-making should weigh the higher capital investment of smart concrete against the sustainability and drainage advantages of pervious concrete for budget-sensitive infrastructure projects.
Installation Process and Maintenance Requirements
Smart concrete integrates sensors within its matrix during installation, allowing real-time monitoring of structural health and environmental conditions, which requires precise embedding techniques and skilled labor. Pervious concrete involves specialized mixing and careful placement to maintain its porous structure, enabling efficient stormwater drainage with relatively simple installation but demands routine cleaning to prevent clogging. Maintenance for smart concrete focuses on sensor calibration and data management, whereas pervious concrete requires regular vacuuming or power washing to sustain permeability and prevent surface deterioration.
Best Applications for Sidewalk Projects
Smart concrete integrates sensors to monitor structural health and environmental conditions, making it ideal for high-traffic urban sidewalks requiring real-time maintenance data. Pervious concrete enhances water drainage, significantly reducing surface runoff and preventing puddles, which is beneficial in sidewalks located in areas prone to heavy rainfall or flooding. Selecting between smart and pervious concrete depends on project priorities: smart concrete suits technologically advanced urban settings, while pervious concrete excels in sustainable, environmentally sensitive sidewalks.
Future Trends in Sidewalk Construction Technologies
Smart concrete integrates sensors and self-healing properties, advancing sidewalk durability and real-time monitoring, while pervious concrete enhances stormwater management by allowing water infiltration, reducing runoff and urban flooding. Future trends highlight combining these technologies with IoT-enabled systems for predictive maintenance and environmentally sustainable urban infrastructure. Innovations aim to optimize longevity, safety, and ecological impact in modern sidewalk construction.
Infographic: Smart concrete vs Pervious concrete for Sidewalk
 azmater.com
azmater.com