Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and versatility for complex spillway geometries, providing high early strength and reduced rebound. Roller-compacted concrete excels in large-scale spillway construction due to its rapid placement, low cement content, and cost-effective durability.
Table of Comparison
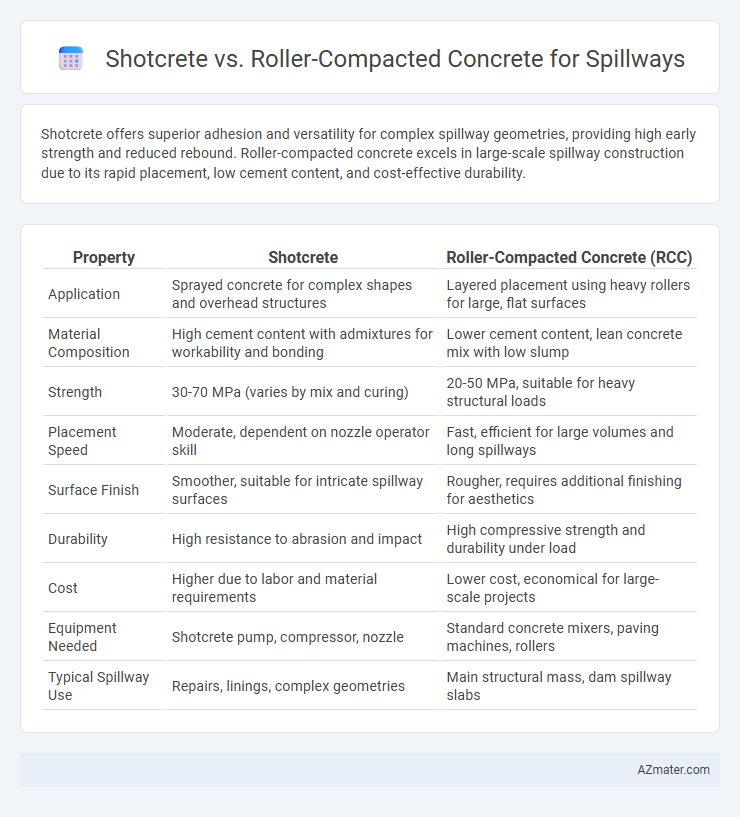
| Property | Shotcrete | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Sprayed concrete for complex shapes and overhead structures | Layered placement using heavy rollers for large, flat surfaces |
| Material Composition | High cement content with admixtures for workability and bonding | Lower cement content, lean concrete mix with low slump |
| Strength | 30-70 MPa (varies by mix and curing) | 20-50 MPa, suitable for heavy structural loads |
| Placement Speed | Moderate, dependent on nozzle operator skill | Fast, efficient for large volumes and long spillways |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, suitable for intricate spillway surfaces | Rougher, requires additional finishing for aesthetics |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and impact | High compressive strength and durability under load |
| Cost | Higher due to labor and material requirements | Lower cost, economical for large-scale projects |
| Equipment Needed | Shotcrete pump, compressor, nozzle | Standard concrete mixers, paving machines, rollers |
| Typical Spillway Use | Repairs, linings, complex geometries | Main structural mass, dam spillway slabs |
Introduction to Spillway Construction Materials
Shotcrete offers high-strength, rapid application, and superior adhesion for complex spillway surfaces, making it ideal for repair and lining projects. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides cost-effective, durable, and mechanically compacted mass suitable for large-scale spillway foundations and embankments. Selecting between shotcrete and RCC depends on factors such as structural requirements, application speed, and environmental conditions in spillway construction.
Overview of Shotcrete in Spillway Projects
Shotcrete is a versatile, pneumatically applied concrete method widely used in spillway projects for its excellent adhesion and ability to conform to complex surface geometries. Its high early strength development and low rebound rates make shotcrete ideal for spillway linings and repairs, providing durability against hydraulic and environmental stresses. Shotcrete also allows for rapid application in challenging terrains, enhancing construction efficiency and extending the service life of spillways.
Roller-Compacted Concrete: Key Features and Uses
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a high-density, low-slump concrete placed using asphalt paving equipment and compacted by rollers, offering enhanced strength and durability ideal for spillway construction. RCC's rapid placement and reduced cement content result in cost-effective construction with improved resistance to erosion and hydraulic pressures. Its key uses in spillways include structural stability under heavy water flow and the ability to form large, monolithic sections that minimize joints and leakage.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Shotcrete demonstrates high compressive strength typically ranging from 20 to 70 MPa, making it ideal for complex spillway geometries requiring strong bonding to irregular surfaces. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) achieves compressive strengths between 25 and 55 MPa, with superior durability due to its low permeability and dense matrix, enhancing resistance against freeze-thaw cycles and chemical attacks. In terms of long-term performance, RCC's uniform compaction and minimal shrinkage contribute to greater structural integrity compared to shotcrete, which may experience reduced durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Application Methods and Installation Time
Shotcrete and roller-compacted concrete (RCC) differ significantly in application methods and installation time for spillways. Shotcrete is applied pneumatically through a high-velocity hose, enabling rapid placement on vertical or overhead surfaces with minimal formwork, which accelerates installation in complex geometries. RCC employs a conveyor belt or dump truck for placement followed by compaction with rollers, allowing for large-scale, continuous paving but requiring longer curing time and more extensive site preparation.
Cost Analysis: Shotcrete vs Roller-Compacted Concrete
Shotcrete typically incurs higher labor and material costs due to its specialized application process and formwork requirements, whereas roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers cost efficiency with faster placement and reduced curing time. RCC's use of conventional earthmoving equipment and minimal formwork contributes to significant savings in both material and operational expenses, making it more suitable for large-scale spillway projects. Evaluating project scale, complexity, and available equipment is crucial to optimize cost performance between shotcrete and RCC methods.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Shotcrete for spillways requires frequent inspections and repair due to its relatively lower thickness and susceptibility to surface wear and cracking, impacting its maintenance needs. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers enhanced durability and lower permeability, which significantly reduces maintenance frequency and extends spillway longevity by resisting erosion and freeze-thaw cycles more effectively. Choosing RCC ensures longer service life and minimizes repair costs in high-stress hydraulic structures compared to shotcrete applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Shotcrete requires less water and generates minimal waste during application, enhancing its environmental sustainability for spillway construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers high durability with lower cement content and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional concrete, making it a sustainable choice for large-scale spillways. Both materials contribute to erosion control and long-term structural integrity, reducing maintenance needs and environmental disturbance.
Best Use Cases for Each Material
Shotcrete offers superior adaptability for complex spillway geometries and areas requiring precise application, making it ideal for repairs, thin overlays, and structural reinforcements. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) excels in large-scale spillway construction due to its high compressive strength, rapid placement, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for dams and extensive channel linings. Selecting between shotcrete and RCC depends on project scale, structural demands, and site accessibility to optimize durability and performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Spillway
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and flexibility, making it ideal for complex geometries and repair applications on spillways. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides high durability and rapid placement, suitable for large-scale spillway construction requiring cost efficiency. Selecting between shotcrete and RCC depends on project scale, structural requirements, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal spillway performance.
Infographic: Shotcrete vs Roller-compacted Concrete for Spillway
 azmater.com
azmater.com