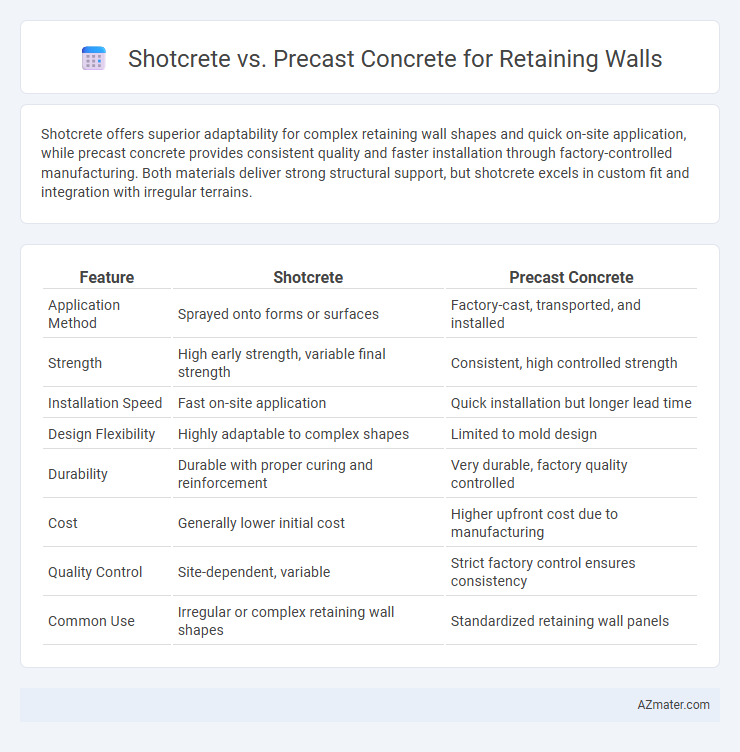
Shotcrete offers superior adaptability for complex retaining wall shapes and quick on-site application, while precast concrete provides consistent quality and faster installation through factory-controlled manufacturing. Both materials deliver strong structural support, but shotcrete excels in custom fit and integration with irregular terrains.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shotcrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Sprayed onto forms or surfaces | Factory-cast, transported, and installed |
| Strength | High early strength, variable final strength | Consistent, high controlled strength |
| Installation Speed | Fast on-site application | Quick installation but longer lead time |
| Design Flexibility | Highly adaptable to complex shapes | Limited to mold design |
| Durability | Durable with proper curing and reinforcement | Very durable, factory quality controlled |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost due to manufacturing |
| Quality Control | Site-dependent, variable | Strict factory control ensures consistency |
| Common Use | Irregular or complex retaining wall shapes | Standardized retaining wall panels |
Introduction to Retaining Wall Construction Methods
Retaining wall construction methods include shotcrete and precast concrete, both offering distinct advantages for structural support and soil stabilization. Shotcrete involves spraying concrete onto surfaces, allowing flexible application on irregular shapes and quick setting times ideal for complex site conditions. Precast concrete consists of factory-made panels or blocks that provide uniform quality, faster installation, and enhanced durability for standardized wall designs.
What is Shotcrete?
Shotcrete is a method of applying concrete through a high-pressure hose, allowing it to be sprayed directly onto surfaces such as retaining walls. This technique offers superior adhesion and is ideal for complex shapes or curved surfaces where traditional formwork is challenging. Shotcrete provides rapid setting times and enhanced durability, making it a preferred choice for retaining wall construction in rugged or uneven terrains.
Overview of Precast Concrete
Precast concrete for retaining walls is manufactured in controlled factory environments, ensuring consistent quality and strength typically ranging from 4,000 to 6,000 psi. It offers rapid installation times since panels or blocks are produced off-site and quickly assembled on location, minimizing construction delays. The durability and uniformity of precast concrete enhance structural reliability, making it resistant to weathering and reducing long-term maintenance costs.
Key Differences Between Shotcrete and Precast Concrete
Shotcrete and precast concrete differ primarily in their application methods; shotcrete is sprayed directly onto a surface using high-pressure equipment, allowing for continuous, monolithic wall formation, while precast concrete components are manufactured off-site and then transported for assembly. Shotcrete offers flexibility for complex shapes and irregular sites, whereas precast concrete provides uniform quality and faster installation due to factory-controlled conditions. The choice influences factors like structural integrity, curing time, and labor costs, with shotcrete enabling quicker adjustments on-site and precast ensuring consistent, repeatable dimensions.
Structural Strength Comparison
Shotcrete offers superior bonding strength and adaptability to complex shapes, creating a monolithic structure with fewer joints that enhances load distribution in retaining walls. Precast concrete provides consistent quality and controlled curing conditions, resulting in high compressive strength and uniform structural performance. While shotcrete excels in creating continuous, customized forms, precast concrete ensures reliable structural integrity through precise manufacturing standards.
Installation Speed and Process
Shotcrete offers faster installation for retaining walls due to its sprayed application directly onto surfaces, eliminating the need for formwork and enabling rapid curing. Precast concrete involves manufacturing wall panels off-site under controlled conditions, followed by transportation and on-site assembly, which can extend installation time but enhances quality control. Choosing shotcrete reduces labor and formwork time, while precast emphasizes precision and minimal curing delays.
Cost Analysis: Shotcrete vs Precast Concrete
Shotcrete offers cost advantages through reduced labor and faster application, making it ideal for complex or irregular retaining walls, while precast concrete typically demands higher upfront costs due to mold fabrication and transportation but provides consistent quality and shorter onsite assembly times. Project-specific factors such as wall size, shape complexity, site accessibility, and labor rates significantly influence the overall cost difference between shotcrete and precast concrete solutions. Detailed cost analysis should consider material expenses, equipment requirements, curing time, and long-term maintenance to determine the most economical option for retaining wall construction.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Shotcrete offers superior durability for retaining walls due to its dense, monolithic application that resists cracking and water infiltration more effectively than precast concrete. Maintenance requirements for shotcrete walls are generally lower, as its continuous surface reduces joint-related weaknesses where moisture and vegetation can cause damage. Precast concrete walls may require more frequent inspection and repair at joints to prevent deterioration from environmental exposure.
Common Applications for Each Method
Shotcrete is commonly used for complex or irregularly shaped retaining walls where rapid application and excellent adhesion to surfaces are required, such as in slope stabilization and tunnel linings. Precast concrete is preferred for standardized, modular retaining walls in residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects where quality control and faster installation are priorities. Both methods serve distinct roles within civil engineering depending on project design, site conditions, and construction timelines.
Selecting the Best Option for Your Project
Shotcrete offers superior flexibility and adaptability for complex retaining wall shapes and uneven terrain, making it ideal for customized project requirements. Precast concrete provides consistent quality, faster installation, and enhanced durability, which can reduce labor costs and project timelines. Selecting the best option depends on site conditions, budget constraints, and desired structural complexity.
Infographic: Shotcrete vs Precast Concrete for Retaining Wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com