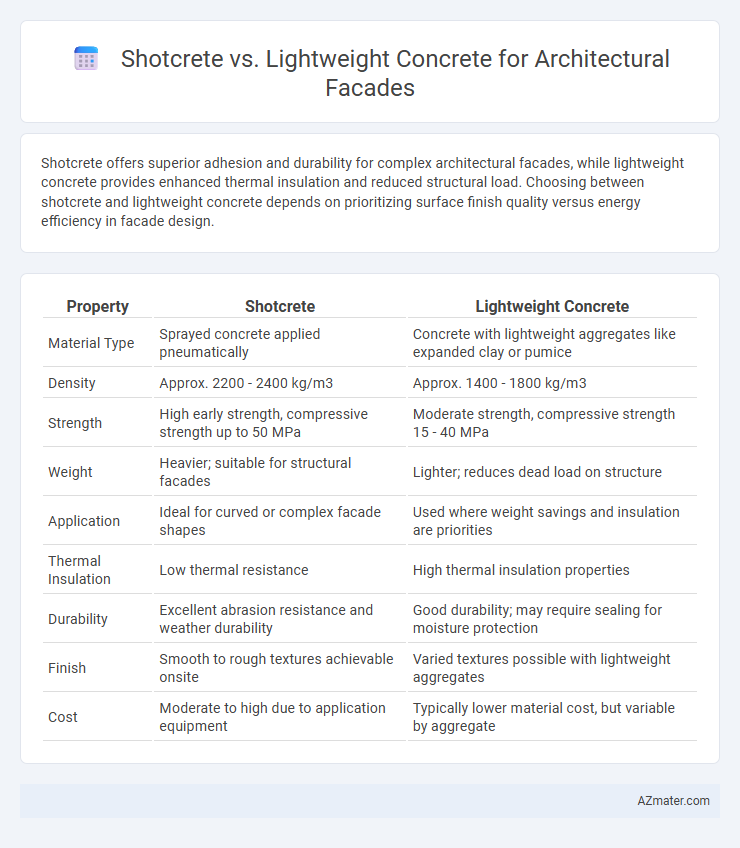
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and durability for complex architectural facades, while lightweight concrete provides enhanced thermal insulation and reduced structural load. Choosing between shotcrete and lightweight concrete depends on prioritizing surface finish quality versus energy efficiency in facade design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Shotcrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Sprayed concrete applied pneumatically | Concrete with lightweight aggregates like expanded clay or pumice |
| Density | Approx. 2200 - 2400 kg/m3 | Approx. 1400 - 1800 kg/m3 |
| Strength | High early strength, compressive strength up to 50 MPa | Moderate strength, compressive strength 15 - 40 MPa |
| Weight | Heavier; suitable for structural facades | Lighter; reduces dead load on structure |
| Application | Ideal for curved or complex facade shapes | Used where weight savings and insulation are priorities |
| Thermal Insulation | Low thermal resistance | High thermal insulation properties |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance and weather durability | Good durability; may require sealing for moisture protection |
| Finish | Smooth to rough textures achievable onsite | Varied textures possible with lightweight aggregates |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to application equipment | Typically lower material cost, but variable by aggregate |
Introduction to Shotcrete and Lightweight Concrete for Facades
Shotcrete is a sprayed concrete mix known for its high adhesion and ability to form complex shapes, making it ideal for architectural facades that demand intricate detailing and structural strength. Lightweight concrete, characterized by its reduced density using materials like expanded clay or pumice, offers enhanced thermal insulation and ease of handling for facade applications. Both materials provide distinct advantages in facade construction, balancing structural performance and aesthetic flexibility.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and density, providing high compressive strength and excellent durability for architectural facades, while lightweight concrete excels in thermal insulation and reduced structural load due to its lower density. The porosity differences influence water permeability, with shotcrete generally exhibiting lower porosity, enhancing weather resistance compared to lightweight concrete. Fire resistance varies as well; lightweight concrete typically provides better thermal insulation under fire exposure, whereas shotcrete benefits from higher structural integrity at elevated temperatures.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Shotcrete offers superior structural performance and load-bearing capacity due to its dense, high-strength application, providing excellent adhesion and reduced voids on architectural facades. Lightweight concrete, while beneficial for reducing overall structural load, typically has lower compressive strength, making it less suitable for heavy load-bearing facade elements. Engineers often select shotcrete for enhanced durability and load support in complex facade structures where structural integrity is critical.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Shotcrete offers exceptional design flexibility for architectural facades due to its ability to be sprayed onto complex shapes and contours, enabling intricate textures and seamless surfaces. Lightweight concrete provides diverse aesthetic options by incorporating various aggregates and pigments, resulting in customizable color, texture, and thermal properties ideal for modern facade designs. Both materials support innovative facade solutions, but shotcrete excels in sculptural applications while lightweight concrete emphasizes energy efficiency and versatile finishes.
Installation Process: Speed and Efficiency
Shotcrete offers rapid application through pneumatic spraying, enabling uniform layers and reduced labor time ideal for complex architectural facades. Lightweight concrete requires traditional formwork and curing stages, which extend installation duration but enhances thermal insulation and reduces structural load. The shotcrete process optimizes speed and efficiency, particularly for intricate designs, while lightweight concrete balances installation with energy performance considerations.
Cost Implications and Budget Considerations
Shotcrete offers cost advantages in architectural facades by reducing labor expenses through faster application and minimal formwork requirements, making it ideal for complex geometries. Lightweight concrete, while generally more expensive per cubic yard due to specialized aggregates and admixtures, can lower structural costs by reducing dead load and foundation requirements. Budget considerations should weigh initial material costs of lightweight concrete against overall project savings from reduced structural demands, whereas shotcrete provides immediate cost savings in labor and installation efficiency.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Benefits
Shotcrete provides superior thermal insulation due to its dense application, effectively reducing heat transfer in architectural facades, while lightweight concrete enhances acoustic insulation by absorbing sound vibrations through its porous structure. The combination of shotcrete's durability and lightweight concrete's soundproofing qualities results in energy-efficient facades with improved indoor comfort. Optimizing facade design with these materials balances insulation performance, contributing to sustainable building standards.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Shotcrete offers superior durability due to its dense application and strong adhesion, making it highly resistant to weathering and mechanical damage on architectural facades. Lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and reduces structural load but may require more frequent maintenance to address potential surface cracking and moisture infiltration. Both materials demand proper curing and sealing to enhance longevity, with shotcrete typically requiring less ongoing maintenance for exterior architectural applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Shotcrete offers superior environmental benefits due to reduced material waste and lower transportation emissions from on-site application, enhancing sustainability in architectural facades. Lightweight concrete reduces structural load, leading to smaller foundation requirements and decreased embodied carbon, supporting green building certifications like LEED and BREEAM. Both materials contribute to sustainable design, but shotcrete's application efficiency and lightweight concrete's thermal insulation properties make them ideal choices for eco-friendly facades.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Solution for Facade Projects
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and versatility, making it ideal for complex architectural facade shapes and restoration projects requiring detailed surface textures. Lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and reduced structural load, perfect for high-rise facades and energy-efficient building designs. Selecting between shotcrete and lightweight concrete depends on factors such as facade geometry, load requirements, and desired aesthetic and thermal performance.
Infographic: Shotcrete vs Lightweight Concrete for Architectural Facade
 azmater.com
azmater.com