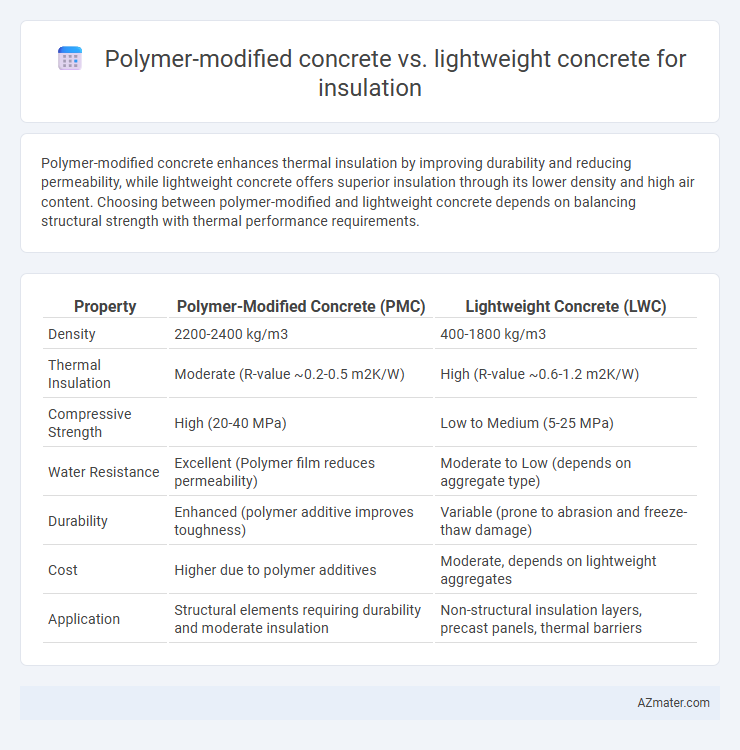
Polymer-modified concrete enhances thermal insulation by improving durability and reducing permeability, while lightweight concrete offers superior insulation through its lower density and high air content. Choosing between polymer-modified and lightweight concrete depends on balancing structural strength with thermal performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Modified Concrete (PMC) | Lightweight Concrete (LWC) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2200-2400 kg/m3 | 400-1800 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate (R-value ~0.2-0.5 m2K/W) | High (R-value ~0.6-1.2 m2K/W) |
| Compressive Strength | High (20-40 MPa) | Low to Medium (5-25 MPa) |
| Water Resistance | Excellent (Polymer film reduces permeability) | Moderate to Low (depends on aggregate type) |
| Durability | Enhanced (polymer additive improves toughness) | Variable (prone to abrasion and freeze-thaw damage) |
| Cost | Higher due to polymer additives | Moderate, depends on lightweight aggregates |
| Application | Structural elements requiring durability and moderate insulation | Non-structural insulation layers, precast panels, thermal barriers |
Introduction to Concrete Types for Insulation
Polymer-modified concrete enhances insulation properties by incorporating polymers that improve adhesion, flexibility, and water resistance, making it suitable for thermal barrier applications. Lightweight concrete uses aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice to reduce density and increase thermal insulation, offering superior energy efficiency. Both types provide distinct advantages for insulation, with polymer-modified concrete excelling in durability and lightweight concrete optimizing thermal performance.
Defining Polymer-Modified Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) is a composite material where polymers are added to traditional concrete to enhance flexibility, adhesion, and waterproofing, making it effective for insulation applications. Unlike lightweight concrete, which reduces density through lightweight aggregates to improve thermal insulation, PMC improves durability and crack resistance while maintaining structural strength. PMC's improved bond strength and reduced permeability contribute to superior insulation performance in environments requiring durable, moisture-resistant materials.
What is Lightweight Concrete?
Lightweight concrete is a type of concrete that incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, reducing its density and improving thermal insulation properties. Unlike polymer-modified concrete, which enhances durability and bonding through polymer additives, lightweight concrete primarily focuses on reducing heat transfer and overall structural weight. This makes lightweight concrete especially effective for building applications requiring enhanced insulation and energy efficiency.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits enhanced thermal insulation due to its reduced thermal conductivity and improved density control, making it effective in minimizing heat transfer in structures. Lightweight concrete inherently provides superior thermal insulation through its porous aggregate composition, which traps air and reduces heat flow. Comparing both, lightweight concrete generally offers better thermal insulation performance, but polymer modification can optimize concrete's structural integrity while maintaining moderate insulation properties.
Mechanical Strength Differences
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to lightweight concrete due to the enhanced bonding properties and reduced micro-cracking from polymer additives. Lightweight concrete, while offering superior thermal insulation and reduced density, generally has lower compressive and tensile strengths because of its porous structure and lightweight aggregates. The choice between the two depends on the required balance of insulation performance and structural load-bearing capacity in construction applications.
Durability and Longevity Assessment
Polymer-modified concrete enhances durability by improving tensile strength, reducing permeability, and resisting chemical attacks, leading to superior longevity compared to standard concrete types. Lightweight concrete offers effective thermal insulation due to its cellular structure but may exhibit lower compressive strength and increased susceptibility to shrinkage and cracking over time. In insulation-specific applications, polymer-modified concrete provides a more resilient and long-lasting solution, while lightweight concrete prioritizes thermal performance with moderate durability.
Application Areas in Construction
Polymer-modified concrete is extensively used in industrial flooring, repair works, and overlay applications due to its enhanced durability, water resistance, and adhesion properties. Lightweight concrete is preferred in building envelopes, insulating concrete forms (ICFs), and roof decks because of its superior thermal insulation and reduced structural load. Both materials optimize energy efficiency, with polymer-modified concrete improving surface protection and lightweight concrete significantly reducing heat transfer in walls and ceilings.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced durability and water resistance, increasing lifespan and reducing maintenance costs, though it typically incurs higher initial expenses compared to lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete provides superior thermal insulation properties and decreases structural load, leading to potential savings in overall construction costs. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires balancing polymer-enhanced material longevity against lightweight concrete's energy savings and structural efficiency benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer-modified concrete enhances durability and reduces maintenance by incorporating synthetic polymers, which can increase environmental footprint due to petrochemical sources and limited recyclability. Lightweight concrete, often made with natural aggregates such as expanded clay or pumice, offers superior insulation properties and lower embodied energy, contributing to improved sustainability through reduced resource consumption and thermal efficiency. Choosing lightweight concrete supports greener construction practices by minimizing carbon emissions and promoting material reuse compared to polymer-modified alternatives.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Insulation Needs
Polymer-modified concrete enhances durability and reduces permeability, making it ideal for insulation applications requiring high resistance to moisture and chemical exposure. Lightweight concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its low density and high air content, effectively reducing heat transfer in building envelopes. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing thermal insulation properties, structural strength, and environmental conditions specific to the project.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com