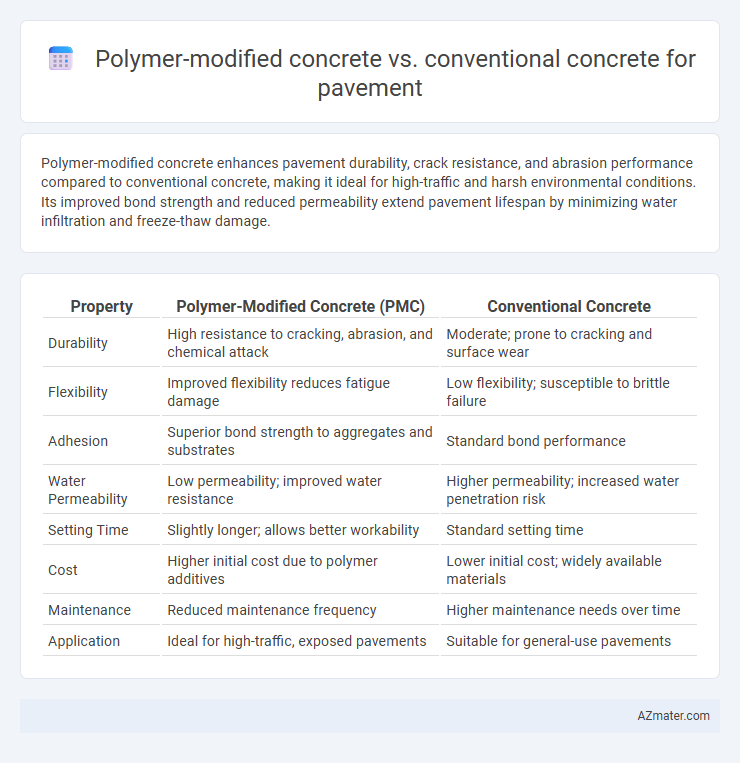
Polymer-modified concrete enhances pavement durability, crack resistance, and abrasion performance compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for high-traffic and harsh environmental conditions. Its improved bond strength and reduced permeability extend pavement lifespan by minimizing water infiltration and freeze-thaw damage.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Modified Concrete (PMC) | Conventional Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to cracking, abrasion, and chemical attack | Moderate; prone to cracking and surface wear |
| Flexibility | Improved flexibility reduces fatigue damage | Low flexibility; susceptible to brittle failure |
| Adhesion | Superior bond strength to aggregates and substrates | Standard bond performance |
| Water Permeability | Low permeability; improved water resistance | Higher permeability; increased water penetration risk |
| Setting Time | Slightly longer; allows better workability | Standard setting time |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to polymer additives | Lower initial cost; widely available materials |
| Maintenance | Reduced maintenance frequency | Higher maintenance needs over time |
| Application | Ideal for high-traffic, exposed pavements | Suitable for general-use pavements |
Introduction to Concrete Pavement Technologies
Polymer-modified concrete enhances pavement durability and resistance compared to conventional concrete by incorporating polymers that improve bonding and flexibility. Conventional concrete pavement, widely used for its cost-effectiveness and compressive strength, can suffer from cracking and reduced longevity under heavy traffic loads. Advances in polymer-modified concrete technologies enable longer service life and reduced maintenance, making it a preferred choice for modern infrastructure projects.
Overview of Conventional Concrete for Pavement
Conventional concrete for pavement primarily consists of cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures, providing high compressive strength and durability under heavy traffic loads. It features excellent rigidity and resistance to deformation, making it suitable for highways and airport runways but is more prone to cracking due to shrinkage and thermal stresses. The mixture's workability and curing process critically impact the pavement's long-term performance and maintenance requirements.
Fundamentals of Polymer-Modified Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) incorporates polymers such as styrene-butadiene rubber or epoxy into the cement matrix to enhance adhesion, flexibility, and durability compared to conventional concrete. This modification improves resistance to cracking, abrasion, and chemical attack, making PMC ideal for high-stress pavement applications. The fundamental chemistry involves polymers forming a continuous film within the concrete pores, reducing permeability and increasing tensile strength.
Key Differences between Polymer-Modified and Conventional Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) incorporates polymers that enhance properties such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemical attacks compared to conventional concrete, which relies solely on cement, aggregates, and water. PMC exhibits improved tensile strength and reduced permeability, making it more suitable for pavements exposed to heavy traffic and harsh environmental conditions. Conventional concrete tends to have higher susceptibility to cracking and wear under freeze-thaw cycles, whereas polymer modifications significantly extend the service life of pavement structures.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength than conventional concrete, with compressive strength improvements ranging from 20% to 40%, enhancing load-bearing capacity for pavement applications. Its enhanced durability is attributed to reduced permeability and improved resistance to abrasion, chemical attack, and freeze-thaw cycles, resulting in extended pavement lifespan. Studies also show polymer modifiers reduce shrinkage and cracking, which minimizes maintenance needs and contributes to long-term structural integrity.
Resistance to Environmental and Chemical Attacks
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits superior resistance to environmental and chemical attacks compared to conventional concrete, making it particularly suitable for pavement applications exposed to harsh conditions. The incorporation of polymers enhances the concrete's impermeability, reducing water penetration and improving resilience against freeze-thaw cycles, de-icing salts, and acidic substances. This increased durability significantly extends the lifespan of pavements subjected to aggressive chemical exposures and fluctuating weather environments.
Workability and Setting Time: A Comparative Analysis
Polymer-modified concrete significantly improves workability by enhancing the mix's cohesiveness and reducing segregation, which facilitates easier placement and finishing compared to conventional concrete. The setting time of polymer-modified concrete is generally longer, allowing for extended handling and finishing times, while conventional concrete sets faster but may require rapid execution to avoid issues like early stiffening or plastic shrinkage. This comparative advantage in workability and controlled setting time makes polymer-modified concrete preferable for complex pavement applications requiring precision and durability.
Cost Implications and Life-Cycle Assessment
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) for pavement exhibits higher initial costs compared to conventional concrete due to the expense of polymers and specialized mixing processes; however, its enhanced durability and resistance to cracking reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Life-cycle assessment (LCA) reveals that PMC's extended service life and lower repair frequency result in reduced environmental impact and overall cost over time. Conventional concrete, while cheaper upfront, often incurs higher life-cycle costs due to frequent repairs and shorter pavement lifespan.
Applications and Case Studies in Pavement Engineering
Polymer-modified concrete demonstrates superior durability, resistance to chemical attack, and enhanced bond strength compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for high-traffic pavement applications and heavy-duty industrial floors. Case studies from urban infrastructure projects reveal that polymer-modified concrete extends pavement service life by up to 50%, reducing maintenance costs and improving skid resistance under varying climatic conditions. The use of polymers in concrete mixtures has been validated in airport runways and highway overlays, where rapid curing and improved tensile strength contribute to enhanced performance and sustainability in pavement engineering.
Choosing the Right Concrete Type for Pavement Projects
Polymer-modified concrete enhances pavement durability by improving tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and reducing permeability compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for high-traffic and harsh environmental conditions. While conventional concrete remains cost-effective and sufficient for standard pavement projects with moderate loading, polymer-modified variants provide superior performance in terms of longevity and reduced maintenance. Selecting the right concrete type depends on project-specific factors such as traffic load, environmental exposure, budget constraints, and desired lifecycle costs.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Conventional concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com