Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide to reduce air pollutants by breaking down nitrogen oxides, enhancing urban air quality along roads. Air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw durability by introducing microscopic air bubbles, extending road lifespan in cold climates.
Table of Comparison
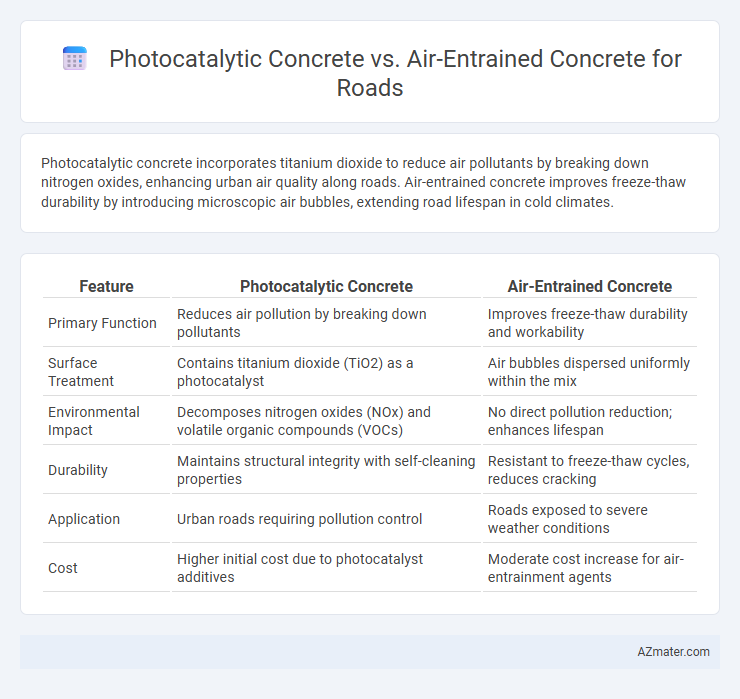
| Feature | Photocatalytic Concrete | Air-Entrained Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Reduces air pollution by breaking down pollutants | Improves freeze-thaw durability and workability |
| Surface Treatment | Contains titanium dioxide (TiO2) as a photocatalyst | Air bubbles dispersed uniformly within the mix |
| Environmental Impact | Decomposes nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) | No direct pollution reduction; enhances lifespan |
| Durability | Maintains structural integrity with self-cleaning properties | Resistant to freeze-thaw cycles, reduces cracking |
| Application | Urban roads requiring pollution control | Roads exposed to severe weather conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to photocatalyst additives | Moderate cost increase for air-entrainment agents |
Introduction to Road Concrete Technologies
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide to actively reduce air pollutants, enhancing urban air quality by breaking down harmful nitrogen oxides through sunlight exposure. Air-entrained concrete improves road durability by introducing microscopic air bubbles, which increase freeze-thaw resistance and reduce cracking in cold climates. Both technologies advance road concrete performance, with photocatalytic concrete targeting environmental benefits and air-entrained concrete focusing on structural longevity.
What is Photocatalytic Concrete?
Photocatalytic concrete is an innovative material embedded with titanium dioxide (TiO2) that activates under sunlight to break down air pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), thereby improving urban air quality. This concrete's photocatalytic properties enable it to reduce smog formation and harmful emissions directly on road surfaces, offering environmental benefits beyond traditional air-entrained concrete. Unlike air-entrained concrete, which mainly enhances freeze-thaw durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, photocatalytic concrete actively contributes to cleaner air in road environments.
Understanding Air-Entrained Concrete
Air-entrained concrete incorporates microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw durability, making it essential for road surfaces exposed to harsh weather conditions. These air voids increase resistance to cracking caused by water expansion during freezing cycles, enhancing pavement longevity. While photocatalytic concrete actively reduces pollution by breaking down airborne contaminants, air-entrained concrete primarily provides structural resilience and extends service life in cold climates.
Key Material Composition Differences
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles that exhibit photocatalytic properties, enabling the degradation of pollutants on the road surface, while air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles created by air-entraining agents to improve freeze-thaw durability. The key material difference lies in photocatalytic concrete's reactive TiO2 component versus the surfactant-based admixtures used in air-entrained concrete for entraining stable air voids. These variations impact functionality, with photocatalytic concrete targeting environmental pollutant reduction and air-entrained concrete enhancing resilience to weather-induced damage on roadways.
Performance in Urban Air Pollution Reduction
Photocatalytic concrete demonstrates superior performance in urban air pollution reduction by actively breaking down nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) through titanium dioxide (TiO2) embedded in its surface, enhancing air quality around roads. In contrast, air-entrained concrete primarily improves freeze-thaw durability but lacks significant capabilities in mitigating airborne pollutants. Urban deployments of photocatalytic concrete have shown measurable decreases in harmful emissions, making it a preferred material for sustainable infrastructure in polluted cities.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Photocatalytic concrete enhances durability by actively breaking down pollutants and organic matter on its surface, reducing surface wear and maintaining structural integrity over time, which significantly extends road lifespan. Air-entrained concrete improves resistance to freeze-thaw cycles by trapping microscopic air bubbles, thereby preventing internal cracking and spalling, crucial for roads in cold climates. While photocatalytic concrete offers self-cleaning properties that contribute to long-term maintenance cost reduction, air-entrained concrete remains the benchmark for freeze-thaw durability, making the choice climate-dependent for optimal road longevity.
Weather Resistance and Freeze-Thaw Performance
Photocatalytic concrete exhibits superior weather resistance due to its ability to self-clean and reduce surface pollutants, enhancing durability in harsh environmental conditions. Air-entrained concrete specifically improves freeze-thaw performance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles that relieve internal pressure from ice formation, preventing cracking and spalling. Combining the photocatalytic properties with optimized air-entrainment can significantly extend the lifespan of road pavements in cold climates with frequent freeze-thaw cycles.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Costs
Photocatalytic concrete significantly reduces maintenance costs by actively degrading pollutants and preventing surface dirt accumulation, extending the road's clean appearance and functional lifespan. Air-entrained concrete, while improving freeze-thaw resistance, often incurs higher maintenance expenses due to limited self-cleaning properties and susceptibility to surface wear. Lifecycle costs favor photocatalytic concrete in urban environments where pollution and dirt buildup drive frequent maintenance, resulting in lower overall expenditures over time.
Environmental and Sustainability Impacts
Photocatalytic concrete utilizes titanium dioxide to reduce airborne pollutants by breaking down nitrogen oxides, significantly improving urban air quality and contributing to environmental sustainability. Air-entrained concrete enhances durability through improved freeze-thaw resistance but has limited impact on air pollution mitigation. Selecting photocatalytic concrete for road construction supports sustainable urban development by actively reducing smog and harmful gases, while air-entrained concrete primarily extends pavement lifespan without direct environmental benefits.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Modern Roads
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide to actively reduce air pollutants, improving urban air quality and enhancing road durability by breaking down harmful substances. Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that improve freeze-thaw resistance and durability in cold climates, making it ideal for roads subjected to harsh weather conditions. Selecting the right concrete depends on environmental factors and maintenance priorities, with photocatalytic concrete excelling in pollution control and air-entrained concrete providing superior durability against freeze-thaw cycles.
Infographic: Photocatalytic concrete vs Air-entrained concrete for Road
 azmater.com
azmater.com