Nano-concrete enhances durability and reduces CO2 emissions through nanoparticle additives, improving structural lifespan in environment-friendly projects. Green concrete utilizes recycled materials and industrial by-products like fly ash, significantly lowering carbon footprint and conserving natural resources in sustainable construction.
Table of Comparison
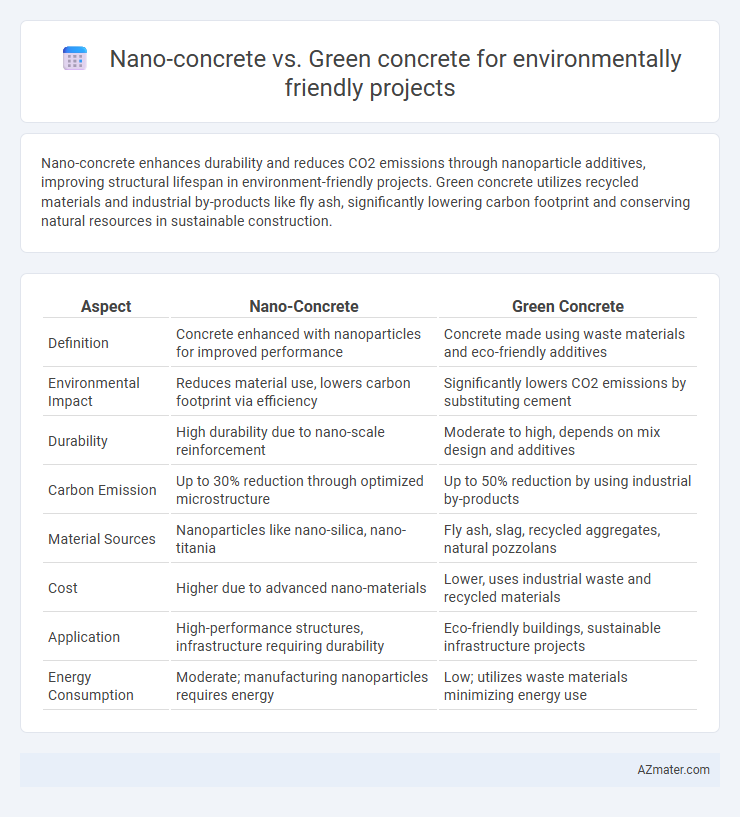
| Aspect | Nano-Concrete | Green Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete enhanced with nanoparticles for improved performance | Concrete made using waste materials and eco-friendly additives |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces material use, lowers carbon footprint via efficiency | Significantly lowers CO2 emissions by substituting cement |
| Durability | High durability due to nano-scale reinforcement | Moderate to high, depends on mix design and additives |
| Carbon Emission | Up to 30% reduction through optimized microstructure | Up to 50% reduction by using industrial by-products |
| Material Sources | Nanoparticles like nano-silica, nano-titania | Fly ash, slag, recycled aggregates, natural pozzolans |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced nano-materials | Lower, uses industrial waste and recycled materials |
| Application | High-performance structures, infrastructure requiring durability | Eco-friendly buildings, sustainable infrastructure projects |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate; manufacturing nanoparticles requires energy | Low; utilizes waste materials minimizing energy use |
Introduction to Nano-Concrete and Green Concrete
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles such as nano-silica and nano-titanium dioxide to enhance mechanical properties, durability, and self-cleaning capabilities, making it a cutting-edge material for sustainable construction. Green concrete utilizes industrial by-products like fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates to reduce carbon emissions and minimize environmental impact while maintaining structural integrity. Both materials support eco-friendly projects by improving resource efficiency and lowering the carbon footprint in modern infrastructure development.
Defining Key Properties of Nano-Concrete
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles such as nanosilica or titanium dioxide, enhancing its mechanical strength, durability, and resistance to chemical attacks. Its ultrafine particle distribution leads to a denser microstructure, reducing porosity and improving sustainability by extending the lifespan of structures. These key properties position nano-concrete as a highly resilient material for environment-friendly construction projects.
What Makes Concrete Green? Core Features
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles like silica or titanium dioxide to enhance durability, reduce permeability, and improve carbon dioxide absorption, leading to a longer lifespan and lower environmental impact. Green concrete typically uses recycled materials, waste by-products like fly ash or slag, and low-carbon cement alternatives to minimize carbon emissions and conserve natural resources. Both types emphasize reduced CO2 footprint, resource efficiency, and improved mechanical properties, making them core features for sustainable, environment-friendly construction projects.
Environmental Impact: Nano-Concrete vs Green Concrete
Nano-concrete enhances material strength and durability by incorporating nanoparticles, reducing the overall cement required and lowering CO2 emissions compared to traditional concrete. Green concrete utilizes industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, significantly minimizing natural resource extraction and carbon footprint during production. Both materials contribute to sustainability, but green concrete offers a more substantial reduction in environmental impact due to its reliance on recycled content and less energy-intensive manufacturing processes.
Raw Materials and Resource Efficiency
Nano-concrete utilizes nano-sized particles such as nano-silica and nano-alumina to enhance concrete properties, reducing the amount of cement required and thus lowering CO2 emissions during production. Green concrete incorporates industrial byproducts like fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates, maximizing resource efficiency by diverting waste from landfills and minimizing natural resource depletion. Both materials focus on sustainable raw material use, but green concrete emphasizes waste valorization while nano-concrete targets performance improvement at the molecular level.
Energy Consumption During Production
Nano-concrete significantly reduces energy consumption during production by requiring lower cement content and enhancing mechanical properties through nano-materials like nano-silica, which promotes faster curing and less energy-intensive processes. Green concrete utilizes industrial by-products such as fly ash and slag, decreasing the need for energy-heavy Portland cement production and reducing overall carbon emissions. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction by minimizing energy use and environmental impact during manufacturing, but nano-concrete offers advanced performance benefits with potentially greater energy savings.
Strength, Durability, and Lifespan Comparison
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles like nanosilica, significantly enhancing compressive strength and reducing permeability, which leads to superior durability compared to traditional concretes. Green concrete utilizes recycled materials and industrial byproducts, offering moderate strength but excels in environmental sustainability by lowering carbon footprints and improving lifecycle performance. While nano-concrete extends lifespan through enhanced microstructure and resistance to cracking, green concrete emphasizes ecological benefits with reasonably durable characteristics suitable for sustainable construction projects.
Application Suitability in Environment-Friendly Projects
Nano-concrete enhances durability and strength through nanomaterials, making it suitable for high-performance infrastructure requiring extended lifespan and reduced maintenance in environment-friendly projects. Green concrete utilizes industrial byproducts like fly ash and slag, significantly lowering carbon emissions and promoting sustainable construction practices ideal for projects prioritizing carbon footprint reduction. Selection depends on project goals: nano-concrete best serves structural longevity and resilience, while green concrete excels in minimizing environmental impact through recycled materials.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Adoption
Nano-concrete offers enhanced durability and strength at a higher initial cost, which limits its widespread market adoption despite long-term savings on maintenance and repairs. Green concrete, made from recycled materials and industrial byproducts, provides a cost-effective solution with growing acceptance due to its lower production costs and positive environmental impact. Market trends indicate greater scalability for green concrete in sustainable construction projects driven by regulatory incentives and consumer demand for eco-friendly options.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Sustainable Concrete
Nano-concrete incorporates nanoparticles like nano-silica and titanium dioxide to enhance strength and durability, reducing resource consumption and carbon footprint in construction. Green concrete leverages industrial by-products such as fly ash and slag, promoting waste recycling and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Future prospects in sustainable concrete emphasize integrating nanotechnology with eco-friendly materials, enabling self-healing properties, improved energy efficiency, and longer-lasting infrastructure for environment-friendly projects.
Infographic: Nano-concrete vs Green concrete for Environment-friendly project
 azmater.com
azmater.com