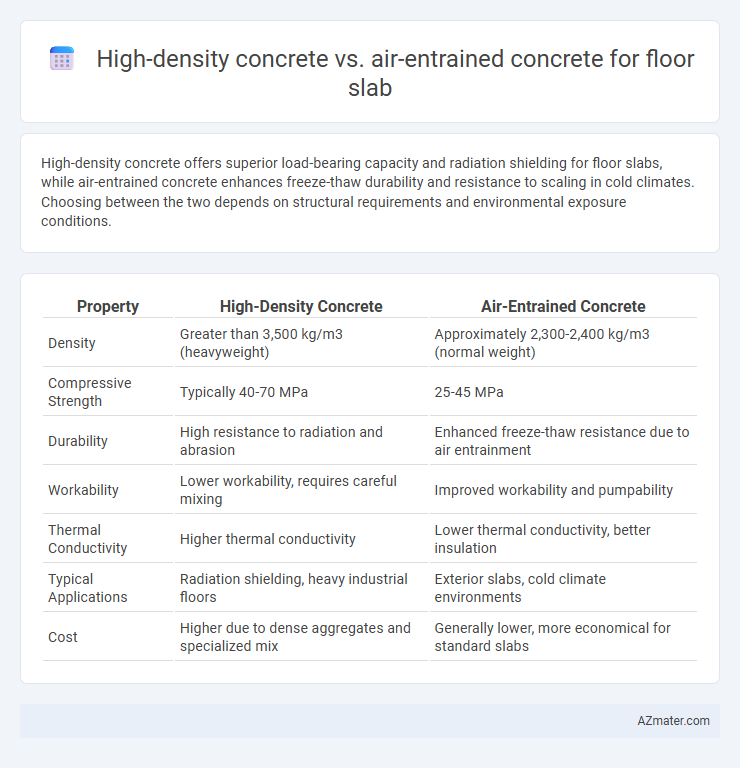
High-density concrete offers superior load-bearing capacity and radiation shielding for floor slabs, while air-entrained concrete enhances freeze-thaw durability and resistance to scaling in cold climates. Choosing between the two depends on structural requirements and environmental exposure conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Density Concrete | Air-Entrained Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Greater than 3,500 kg/m3 (heavyweight) | Approximately 2,300-2,400 kg/m3 (normal weight) |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 40-70 MPa | 25-45 MPa |
| Durability | High resistance to radiation and abrasion | Enhanced freeze-thaw resistance due to air entrainment |
| Workability | Lower workability, requires careful mixing | Improved workability and pumpability |
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher thermal conductivity | Lower thermal conductivity, better insulation |
| Typical Applications | Radiation shielding, heavy industrial floors | Exterior slabs, cold climate environments |
| Cost | Higher due to dense aggregates and specialized mix | Generally lower, more economical for standard slabs |
Introduction to High-Density and Air-Entrained Concrete
High-density concrete features a high specific gravity typically ranging from 3.5 to 4.0, achieved by incorporating heavy aggregates such as magnetite or barite, enhancing radiation shielding and structural mass. Air-entrained concrete contains millions of tiny air bubbles introduced through an air-entraining agent, improving freeze-thaw durability and workability by increasing resistance to moisture damage. Both types serve specialized purposes in floor slabs, with high-density concrete preferred for heavy load-bearing and radiation protection, while air-entrained concrete optimizes performance in freeze-thaw environments.
Key Properties of High-Density Concrete
High-density concrete used in floor slabs offers exceptional radiation shielding and increased compressive strength, making it ideal for industrial and nuclear applications. Its enhanced mass density, typically achieved by incorporating heavy aggregates like barite or magnetite, provides superior durability and reduced permeability compared to standard or air-entrained concrete. Unlike air-entrained concrete, which improves freeze-thaw resistance through microscopic air bubbles, high-density concrete prioritizes high weight and structural integrity over freeze-thaw durability.
Characteristics of Air-Entrained Concrete
Air-entrained concrete contains microscopic air bubbles that improve workability, reduce water permeability, and enhance freeze-thaw resistance, making it ideal for floor slabs in cold climates. The intentional entrainment of air increases durability by minimizing cracking due to freezing cycles and improving resistance to scaling from de-icing salts. While it has lower density compared to high-density concrete, air-entrained concrete offers superior durability and longevity for floor slabs exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Structural Performance in Floor Slab Applications
High-density concrete enhances structural performance in floor slabs by increasing load-bearing capacity and providing superior radiation shielding, making it ideal for applications requiring high strength and durability. Air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw resistance and durability by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, which reduce internal stress and prevent cracking under environmental exposure. Selecting between high-density and air-entrained concrete depends on specific floor slab requirements, such as structural load demands versus environmental resilience.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
High-density concrete exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to air-entrained concrete for floor slabs due to its enhanced compressive strength and reduced permeability, which effectively resist chemical attack and abrasion. Air-entrained concrete primarily improves freeze-thaw resistance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, but its lower density generally results in reduced load-bearing capacity and potential vulnerability to wear over time. For floor slabs subjected to heavy loads and aggressive environments, high-density concrete ensures prolonged service life and reduced maintenance requirements.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
High-density concrete offers superior resistance to radiation and chemical attacks due to its dense matrix and heavy aggregates, making it ideal for environments with high exposure to hazardous substances. Air-entrained concrete enhances resistance to freeze-thaw cycles by trapping microscopic air bubbles that relieve internal pressure during water expansion. For floor slabs exposed to harsh weather and deicing salts, air-entrained concrete significantly improves durability against cracking and scaling compared to high-density concrete.
Impact on Load-Bearing Capacity
High-density concrete significantly increases the load-bearing capacity of floor slabs due to its higher density and compressive strength, making it ideal for heavy structural applications. In contrast, air-entrained concrete, while improving freeze-thaw durability and reducing permeability, typically has lower compressive strength, which may reduce maximum load capacity. Selecting high-density concrete enhances structural support especially in industrial floors or areas subjected to heavy loads, whereas air-entrained concrete benefits environments requiring resistance to environmental degradation.
Workability and Construction Considerations
High-density concrete offers superior load-bearing capacity and radiation shielding for floor slabs but typically exhibits reduced workability due to its heavy aggregates, requiring careful mix design and mechanical compaction methods. Air-entrained concrete enhances workability and freeze-thaw resistance by incorporating microscopic air bubbles, which improve durability in cold climates but may slightly reduce compressive strength. Construction considerations prioritize the choice of mix based on structural demands, environmental exposure, and the trade-off between ease of placement and long-term performance in floor slab applications.
Cost Implications for Floor Slab Projects
High-density concrete typically incurs higher material and placement costs compared to air-entrained concrete due to the use of heavy aggregates such as barite or magnetite. Air-entrained concrete offers cost savings in floor slab projects by enhancing freeze-thaw durability and reducing the need for frequent repairs, lowering long-term maintenance expenses. Budget decisions should weigh upfront costs against lifecycle performance, especially in environments exposed to severe weather conditions or heavy loads.
Choosing the Right Concrete Type for Floor Slabs
High-density concrete offers enhanced durability and radiation shielding, making it suitable for specialized industrial floor slabs requiring high strength and resistance to heavy loads or radiation exposure. Air-entrained concrete improves freeze-thaw resistance and reduces surface scaling, ideal for exterior floor slabs exposed to harsh weather conditions. Selecting the right concrete type depends on environmental exposure, load requirements, and specific performance needs to ensure long-term slab integrity and functionality.
Infographic: High-density concrete vs Air-entrained concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com