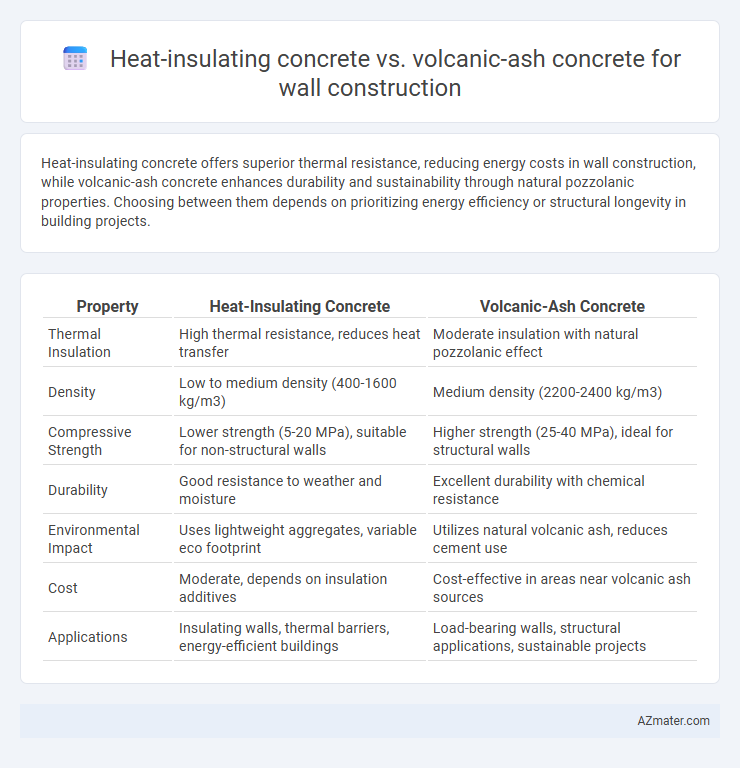
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance, reducing energy costs in wall construction, while volcanic-ash concrete enhances durability and sustainability through natural pozzolanic properties. Choosing between them depends on prioritizing energy efficiency or structural longevity in building projects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Heat-Insulating Concrete | Volcanic-Ash Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance, reduces heat transfer | Moderate insulation with natural pozzolanic effect |
| Density | Low to medium density (400-1600 kg/m3) | Medium density (2200-2400 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Lower strength (5-20 MPa), suitable for non-structural walls | Higher strength (25-40 MPa), ideal for structural walls |
| Durability | Good resistance to weather and moisture | Excellent durability with chemical resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Uses lightweight aggregates, variable eco footprint | Utilizes natural volcanic ash, reduces cement use |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on insulation additives | Cost-effective in areas near volcanic ash sources |
| Applications | Insulating walls, thermal barriers, energy-efficient buildings | Load-bearing walls, structural applications, sustainable projects |
Introduction to Concrete Types for Wall Construction
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance by incorporating materials with low thermal conductivity, reducing heat transfer through walls and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Volcanic-ash concrete, containing natural pozzolanic materials, improves durability and resistance to chemical attack while maintaining adequate thermal insulation properties. Both concrete types provide specialized benefits for wall construction, with heat-insulating concrete focusing on energy savings and volcanic-ash concrete emphasizing strength and environmental sustainability.
Overview of Heat-Insulating Concrete
Heat-insulating concrete is engineered with aerated or lightweight aggregates to enhance thermal resistance, reducing heat transfer through walls significantly. This type of concrete offers lower thermal conductivity compared to volcanic-ash concrete, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. Its porous structure not only improves insulation but also contributes to sound absorption and fire resistance in wall construction.
Characteristics of Volcanic-Ash Concrete
Volcanic-ash concrete, known for its pozzolanic properties, enhances durability and reduces permeability by reacting with calcium hydroxide to form additional cementitious compounds. Its fine particles improve workability and contribute to long-term strength gain, making it suitable for wall construction in diverse climates. The natural insulating ability and resistance to chemical attack provide advantages over traditional heat-insulating concrete, combining structural integrity with thermal efficiency.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat-insulating concrete typically features lightweight aggregates and air-entraining materials, achieving thermal conductivity values as low as 0.1 to 0.3 W/m*K, significantly reducing heat transfer through walls. Volcanic-ash concrete, utilizing natural pozzolanic ash, offers moderate thermal performance with conductivity ranging from 0.3 to 0.6 W/m*K, benefiting from its dense microstructure and improved fire resistance. Walls constructed with heat-insulating concrete provide superior energy efficiency and enhanced interior temperature regulation compared to volcanic-ash concrete, making it more effective for thermal insulation in building envelopes.
Structural Strength and Durability Analysis
Heat-insulating concrete offers enhanced thermal resistance with moderate compressive strength typically ranging between 12-25 MPa, making it suitable for non-load-bearing wall applications. Volcanic-ash concrete exhibits higher structural strength, often exceeding 30 MPa due to the pozzolanic properties of volcanic ash that improve durability, resistance to chemical attack, and reduced permeability. Durability analysis reveals volcanic-ash concrete provides superior long-term performance in aggressive environments, while heat-insulating concrete prioritizes energy efficiency with acceptable structural reliability in less demanding conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Heat-insulating concrete reduces energy consumption in buildings by enhancing thermal efficiency, thereby lowering carbon emissions over the structure's lifespan. Volcanic-ash concrete utilizes natural pozzolanic materials, which decreases reliance on Portland cement and reduces overall CO2 emissions during production. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction, with volcanic-ash concrete offering the added benefit of repurposing industrial by-products and promoting circular economy principles.
Cost Implications and Availability
Heat-insulating concrete generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized additives and manufacturing processes, but it offers long-term energy savings by enhancing thermal efficiency. Volcanic-ash concrete tends to be more cost-effective in regions abundant with volcanic ash, leveraging locally sourced, sustainable materials that lower material expenses and reduce transportation costs. Availability of volcanic ash significantly impacts project budgeting and feasibility, while heat-insulating concrete materials remain more consistently accessible in commercial markets worldwide.
Construction & Application Techniques
Heat-insulating concrete for wall construction incorporates lightweight aggregates and air-entraining agents to enhance thermal resistance, requiring precise mixing ratios to ensure uniform insulation performance. Volcanic-ash concrete utilizes pozzolanic properties of volcanic ash to improve durability and thermal stability, often applied using standard casting or shotcrete methods tailored to optimize material bonding and curing. Both concretes demand specific curing techniques to maximize thermal efficiency and structural integrity, with heat-insulating concrete focusing on minimizing thermal bridging, while volcanic-ash concrete emphasizes long-term strength and resistance to environmental factors.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Heat-insulating concrete offers superior thermal resistance, reducing energy costs and requiring minimal maintenance due to its dense, moisture-resistant structure. Volcanic-ash concrete, known for its exceptional durability and natural resistance to chemical attacks, tends to increase longevity with lower susceptibility to cracking and weathering over time. Both materials extend wall lifespan, but volcanic-ash concrete often demands less frequent repairs and maintenance under harsh environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Project
Heat-insulating concrete enhances energy efficiency by significantly reducing thermal conductivity, making it ideal for climates with extreme temperature variations. Volcanic-ash concrete offers superior durability and natural resistance to chemical attack due to pozzolanic properties, which improve long-term strength and sustainability. Selecting the right concrete depends on prioritizing insulation performance for energy savings versus structural longevity and environmental resilience in wall construction.
Infographic: Heat-insulating concrete vs Volcanic-ash concrete for Wall construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com