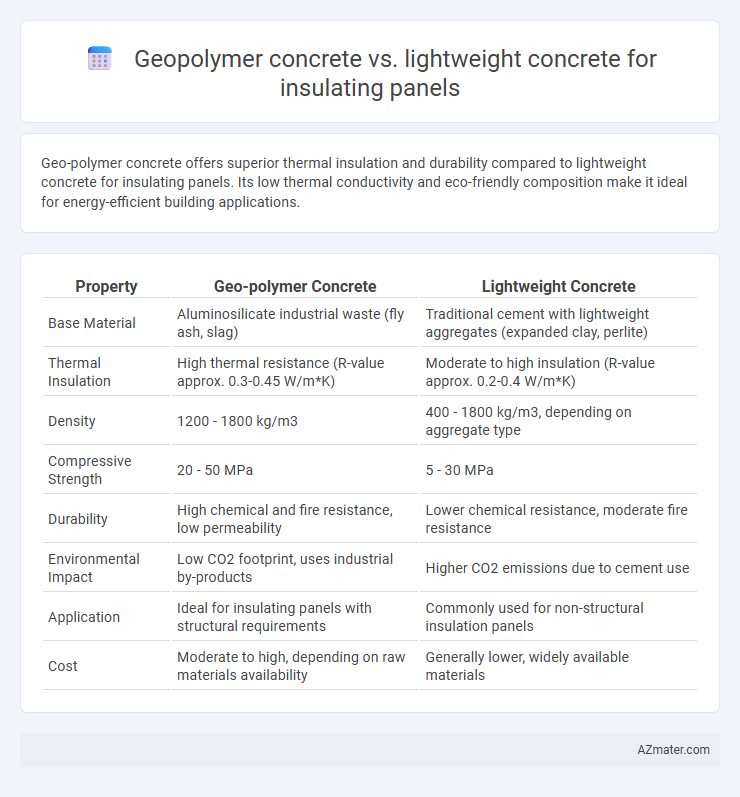
Geo-polymer concrete offers superior thermal insulation and durability compared to lightweight concrete for insulating panels. Its low thermal conductivity and eco-friendly composition make it ideal for energy-efficient building applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Geo-polymer Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Aluminosilicate industrial waste (fly ash, slag) | Traditional cement with lightweight aggregates (expanded clay, perlite) |
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance (R-value approx. 0.3-0.45 W/m*K) | Moderate to high insulation (R-value approx. 0.2-0.4 W/m*K) |
| Density | 1200 - 1800 kg/m3 | 400 - 1800 kg/m3, depending on aggregate type |
| Compressive Strength | 20 - 50 MPa | 5 - 30 MPa |
| Durability | High chemical and fire resistance, low permeability | Lower chemical resistance, moderate fire resistance |
| Environmental Impact | Low CO2 footprint, uses industrial by-products | Higher CO2 emissions due to cement use |
| Application | Ideal for insulating panels with structural requirements | Commonly used for non-structural insulation panels |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on raw materials availability | Generally lower, widely available materials |
Introduction to Insulating Panels
Insulating panels rely on materials that provide thermal resistance, structural integrity, and durability, where Geo-polymer concrete offers superior fire resistance and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional Lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete excels in thermal insulation due to its porous structure but may lack the environmental benefits and chemical stability of Geo-polymer formulations. Selecting the right concrete type impacts panel performance in energy efficiency and sustainability of building envelopes.
Overview of Geo-polymer Concrete
Geo-polymer concrete is an innovative construction material composed primarily of industrial by-products like fly ash or slag, activated by alkaline solutions to form a durable, chemically stable matrix. Its superior thermal insulation properties, low thermal conductivity, and fire resistance make it highly suitable for insulating panels in energy-efficient buildings. Compared to lightweight concrete, geo-polymer concrete offers enhanced environmental benefits due to lower carbon emissions and improved long-term durability.
Overview of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete is a versatile material characterized by lower density and enhanced thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for insulating panels. It typically incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, which significantly reduce heat transfer while maintaining adequate structural strength. This concrete variant offers improved energy efficiency, sound insulation, and fire resistance, positioning it as a popular choice in construction for thermal management applications.
Composition and Material Sourcing
Geo-polymer concrete for insulating panels primarily consists of industrial by-products like fly ash or slag combined with alkaline activators, enabling sustainable material sourcing through waste reutilization. Lightweight concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, sourced from natural mineral deposits or recycled materials, focusing on reducing panel density and thermal conductivity. Both materials emphasize eco-friendly inputs, but geo-polymer concrete relies more on chemical activators and industrial waste, while lightweight concrete depends on physically lightweight natural or manufactured aggregates.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Geopolymer concrete exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to lightweight concrete due to its low thermal conductivity, typically ranging between 0.2 to 0.4 W/m*K, which enhances energy efficiency in insulating panels. Lightweight concrete, composed mainly of expanded aggregates, generally has a higher thermal conductivity around 0.3 to 0.6 W/m*K, resulting in comparatively moderate insulation performance. The inorganic polymer binder in geopolymer concrete also provides better fire resistance and thermal stability, making it more suitable for high-performance insulating applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior mechanical strength with compressive values often exceeding 40 MPa, making it highly suitable for insulating panels requiring structural resilience. Lightweight concrete, while offering excellent thermal insulation due to its low density, typically shows lower mechanical strength, ranging between 10 to 25 MPa, which may limit its use in load-bearing applications. Geo-polymer concrete also demonstrates enhanced durability through resistance to chemical attack, high temperature, and freeze-thaw cycles, outperforming lightweight concrete in long-term insulation panel performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer concrete significantly reduces carbon emissions by utilizing industrial by-products like fly ash, compared to traditional lightweight concrete which often relies on energy-intensive materials such as expanded clay or shale. The production of geopolymer concrete consumes less energy and generates lower greenhouse gases, making it a more sustainable choice for insulating panels. Lightweight concrete, while offering good thermal insulation, typically involves higher embodied energy and resource depletion, whereas geopolymer concrete promotes circular economy principles through waste reutilization.
Cost-effectiveness and Economic Analysis
Geopolymer concrete offers significant cost savings over lightweight concrete due to its use of industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, reducing raw material expenses and energy consumption during production. Lightweight concrete typically incurs higher costs because of specialized aggregates and additional processing required for insulation properties. Economic analysis shows geopolymer insulating panels provide superior life-cycle cost benefits through enhanced durability and thermal performance, minimizing maintenance and energy expenses over time.
Application Suitability in Construction
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it highly suitable for insulating panels in energy-efficient building designs. Lightweight concrete offers enhanced workability and reduced structural load, ideal for non-load bearing partitions and facade insulation. Selection depends on project requirements, where geo-polymer suits high-performance insulation needs, while lightweight concrete benefits cost-effective, lightweight construction applications.
Future Trends and Innovations in Insulating Panels
Geo-polymer concrete exhibits superior thermal resistance and sustainability, making it a prime candidate for next-generation insulating panels. Lightweight concrete innovations emphasize enhanced porosity and fiber reinforcements, optimizing insulation while reducing structural weight. Emerging trends involve integrating nano-materials and phase-change additives in both types to boost energy efficiency and durability in building envelopes.
Infographic: Geo-polymer concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Insulating panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com