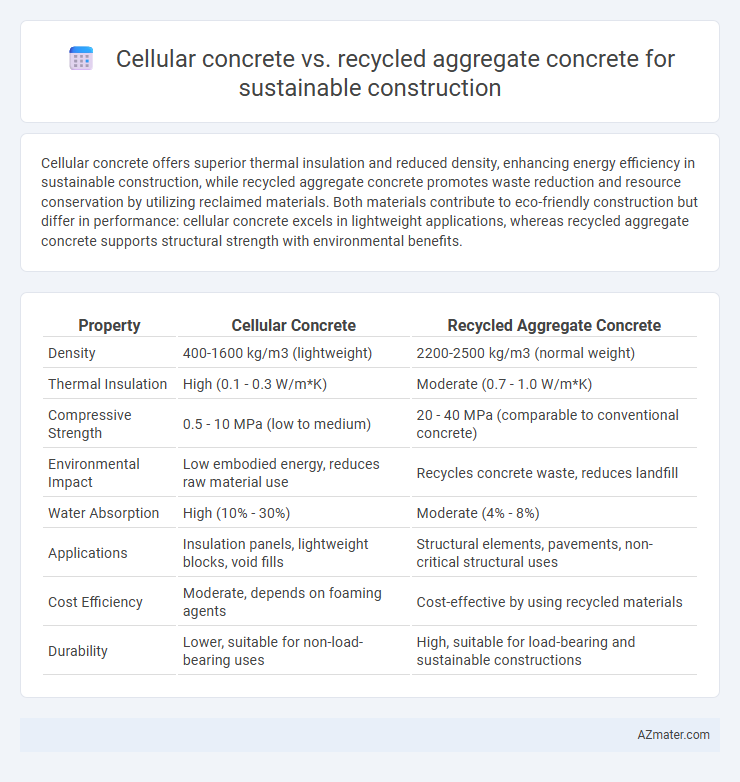
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced density, enhancing energy efficiency in sustainable construction, while recycled aggregate concrete promotes waste reduction and resource conservation by utilizing reclaimed materials. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly construction but differ in performance: cellular concrete excels in lightweight applications, whereas recycled aggregate concrete supports structural strength with environmental benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Recycled Aggregate Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 400-1600 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (normal weight) |
| Thermal Insulation | High (0.1 - 0.3 W/m*K) | Moderate (0.7 - 1.0 W/m*K) |
| Compressive Strength | 0.5 - 10 MPa (low to medium) | 20 - 40 MPa (comparable to conventional concrete) |
| Environmental Impact | Low embodied energy, reduces raw material use | Recycles concrete waste, reduces landfill |
| Water Absorption | High (10% - 30%) | Moderate (4% - 8%) |
| Applications | Insulation panels, lightweight blocks, void fills | Structural elements, pavements, non-critical structural uses |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate, depends on foaming agents | Cost-effective by using recycled materials |
| Durability | Lower, suitable for non-load-bearing uses | High, suitable for load-bearing and sustainable constructions |
Introduction to Sustainable Concrete Solutions
Cellular concrete and recycled aggregate concrete represent innovative materials driving sustainable construction by reducing environmental impact and promoting resource efficiency. Cellular concrete offers lightweight properties and excellent insulation, minimizing energy consumption in buildings, while recycled aggregate concrete utilizes waste materials to decrease landfill use and conserve natural aggregates. Both solutions contribute to eco-friendly infrastructure through enhanced durability, lower carbon footprints, and waste valorization in sustainable concrete technologies.
Overview of Cellular Concrete
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, low-density material composed of cement, water, and pre-formed foam, creating air-filled voids that reduce its weight and thermal conductivity. Its high insulation properties, excellent fire resistance, and ease of workability make it ideal for sustainable construction, enabling energy-efficient buildings with reduced environmental impact. Compared to recycled aggregate concrete, cellular concrete provides superior insulation and weight reduction, contributing to lower structural loads and enhanced sustainability in construction projects.
Defining Recycled Aggregate Concrete
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) is a sustainable construction material produced by incorporating crushed concrete debris, reclaimed asphalt, and other recycled concrete elements as aggregates, reducing the need for virgin materials. RAC enhances resource efficiency, lowers environmental impact by diverting construction waste from landfills, and supports circular economy principles in the construction sector. Its performance characteristics, such as compressive strength and durability, can be optimized by controlling the quality and proportion of recycled aggregates used in the concrete mix.
Material Properties Comparison
Cellular concrete exhibits superior thermal insulation, lightweight properties, and enhanced fire resistance compared to recycled aggregate concrete, which offers higher compressive strength and better durability due to the use of crushed concrete and masonry. The porosity of cellular concrete reduces density and improves energy efficiency but compromises load-bearing capacity, whereas recycled aggregate concrete maintains structural integrity while promoting resource conservation by incorporating waste materials. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction, with cellular concrete ideal for non-structural insulation applications and recycled aggregate concrete suitable for structural elements requiring mechanical strength.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation but generally exhibits lower mechanical strength compared to recycled aggregate concrete, which provides enhanced load-bearing capacity due to the inclusion of crushed concrete and masonry aggregates. Recycled aggregate concrete demonstrates improved durability through better resistance to freeze-thaw cycles and abrasion, while cellular concrete's porous structure may reduce long-term durability under harsh environmental conditions. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction, but selecting between them depends on balancing strength requirements and insulation performance for specific structural applications.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its high porosity and lightweight structure, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to recycled aggregate concrete. Recycled aggregate concrete provides moderate acoustic insulation but typically underperforms cellular concrete in both sound absorption and thermal resistance. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction by reusing waste and lowering environmental impact, yet cellular concrete is preferred for projects prioritizing enhanced energy efficiency and noise reduction.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Cellular concrete significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing air voids to lower material consumption, resulting in decreased CO2 emissions and energy use during production. Recycled aggregate concrete promotes sustainability by reusing construction waste, reducing landfill volume, and conserving natural resources, although its energy footprint depends on recycling processes. Life cycle assessments show that cellular concrete excels in thermal insulation and carbon footprint reduction, whereas recycled aggregate concrete supports circular economy objectives through material reuse.
Application Areas in Sustainable Construction
Cellular concrete excels in thermal insulation and lightweight applications, making it ideal for non-load-bearing walls, void filling, and soundproofing in sustainable construction projects. Recycled aggregate concrete offers high structural performance suitable for roads, foundations, and structural elements while significantly reducing environmental impact by reusing construction waste. Both materials contribute to green building by enhancing resource efficiency and minimizing carbon footprints across diverse construction applications.
Cost Efficiency and Lifecycle Analysis
Cellular concrete offers significant cost savings through reduced material usage and lower transportation expenses due to its lightweight nature, while recycled aggregate concrete decreases costs by utilizing waste materials and minimizing landfill fees. Lifecycle analysis reveals cellular concrete's superior thermal insulation properties, resulting in lower energy consumption and long-term operational costs, whereas recycled aggregate concrete enhances sustainability by reducing the environmental impact of raw material extraction and promoting circular economy principles. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction by balancing upfront cost efficiency with extended lifecycle environmental benefits, depending on project-specific requirements and resource availability.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Cellular concrete offers promising future prospects in sustainable construction due to its lightweight properties, thermal insulation, and reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional materials. Innovations in recycled aggregate concrete focus on enhancing the strength and durability of concrete by optimizing the processing of recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste, supporting circular economy principles. Integrating advanced nanomaterials and additive manufacturing techniques with both cellular and recycled aggregate concrete can further improve performance, reduce environmental impact, and expand their applications in green building projects.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Recycled aggregate concrete for Sustainable construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com