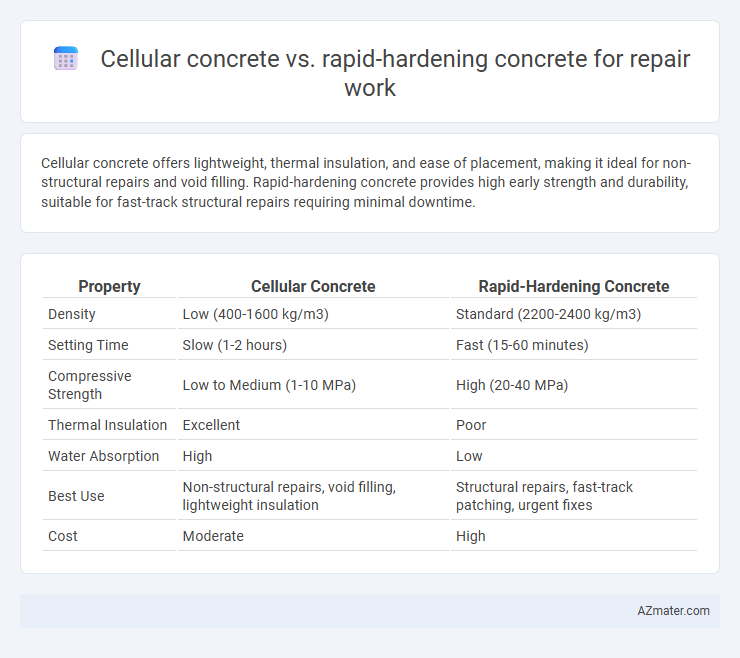
Cellular concrete offers lightweight, thermal insulation, and ease of placement, making it ideal for non-structural repairs and void filling. Rapid-hardening concrete provides high early strength and durability, suitable for fast-track structural repairs requiring minimal downtime.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Rapid-Hardening Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (400-1600 kg/m3) | Standard (2200-2400 kg/m3) |
| Setting Time | Slow (1-2 hours) | Fast (15-60 minutes) |
| Compressive Strength | Low to Medium (1-10 MPa) | High (20-40 MPa) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent | Poor |
| Water Absorption | High | Low |
| Best Use | Non-structural repairs, void filling, lightweight insulation | Structural repairs, fast-track patching, urgent fixes |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Overview of Cellular Concrete and Rapid-Hardening Concrete
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, foam-based material known for its excellent thermal insulation and soundproofing properties, making it suitable for non-structural repair work and void filling. Rapid-hardening concrete, formulated with special cementitious materials, achieves high early strength within hours, allowing quick reopening of repaired structures and minimizing downtime. Both materials serve distinct purposes: cellular concrete improves energy efficiency and ease of application, while rapid-hardening concrete ensures fast load-bearing capacity in urgent repair scenarios.
Composition and Material Properties
Cellular concrete consists of cement, water, and pre-formed foam, creating a lightweight, porous structure with excellent thermal insulation and low density, making it ideal for void filling and non-structural repairs. Rapid-hardening concrete, made with high-early-strength cement and fine aggregates, achieves impressive compressive strength within hours, suitable for quick structural repairs requiring fast load-bearing capacity. The cellular concrete's low density reduces shrinkage and thermal conductivity, while rapid-hardening concrete offers superior durability and mechanical strength for critical repair applications.
Setting and Curing Times
Cellular concrete typically has slower setting and curing times due to its lightweight composition and air-entrained structure, which can extend the time before it gains full strength. Rapid-hardening concrete is formulated to achieve high early strength with significantly faster setting and curing times, often within a few hours, making it ideal for urgent repair work. Choosing between these materials depends on the balance between project time constraints and the desired thermal or insulating properties provided by cellular concrete.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Cellular concrete exhibits lower density and enhanced thermal insulation but generally offers reduced compressive strength and load-bearing capacity compared to rapid-hardening concrete, making it less suitable for structural repairs requiring high strength. Rapid-hardening concrete attains high early strength, enabling efficient restoration of structural performance and load transfer in load-bearing elements under rehabilitative conditions. Selecting rapid-hardening concrete is optimal for applications demanding expedited structural stability and superior mechanical properties in repair works.
Workability and Ease of Application
Cellular concrete offers superior workability due to its lightweight, flowable consistency, making it easy to pump and place in complex repair areas without excessive compaction. Rapid-hardening concrete provides quick strength gain, enabling faster return to service, but its stiff mix can be more challenging to finish and requires skilled handling for proper application. Selecting cellular concrete improves ease of application in intricate repairs, while rapid-hardening concrete is preferred where time-sensitive strength development is critical.
Durability and Crack Resistance
Cellular concrete offers superior crack resistance due to its lightweight, flexible structure, which effectively absorbs stress and reduces shrinkage-related damage in repair work. Rapid-hardening concrete provides enhanced durability by achieving early strength gain, enabling quicker load application and faster repair completion, especially in time-sensitive projects. Comparing both, cellular concrete excels in mitigating long-term cracking while rapid-hardening concrete ensures structural resilience under accelerated curing conditions.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Benefits
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its lightweight, porous structure, which traps air and reduces heat transfer, making it ideal for repair work in temperature-sensitive environments. Rapid-hardening concrete, while providing faster strength gain essential for quick repairs, generally has lower thermal insulation properties but can be enhanced with additives to improve acoustic dampening. For acoustic insulation, cellular concrete's voids absorb sound waves more effectively than the dense matrix of rapid-hardening concrete, contributing to noise reduction in repaired structures.
Suitability for Different Repair Scenarios
Cellular concrete offers lightweight, insulating properties ideal for void filling and non-structural repairs, especially in areas requiring thermal resistance and reduced load. Rapid-hardening concrete excels in structural repairs demanding quick strength gain, such as highway patching or emergency restoration, enabling faster reopening of facilities. Selecting between these materials depends on repair urgency, load-bearing needs, and environmental conditions to ensure durability and performance.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Efficiency
Cellular concrete offers superior cost-effectiveness for repair work due to its lightweight nature, which reduces transportation and labor expenses. Rapid-hardening concrete minimizes downtime by achieving early strength gain, enhancing resource efficiency through quicker project completion and less equipment idle time. Selecting between these materials depends on balancing initial material costs and the value of accelerated repair timelines.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellular concrete offers superior environmental benefits due to its lightweight, low-density composition, which reduces material usage and heat absorption, contributing to energy-efficient buildings and lower carbon footprints. Rapid-hardening concrete, while allowing quicker project turnover and minimizing construction emissions, generally requires higher cement content, increasing CO2 emissions and environmental impact. Prioritizing cellular concrete in repair work enhances sustainability by promoting recyclability and minimizing resource consumption compared to traditional rapid-hardening alternatives.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Rapid-hardening concrete for Repair work
 azmater.com
azmater.com