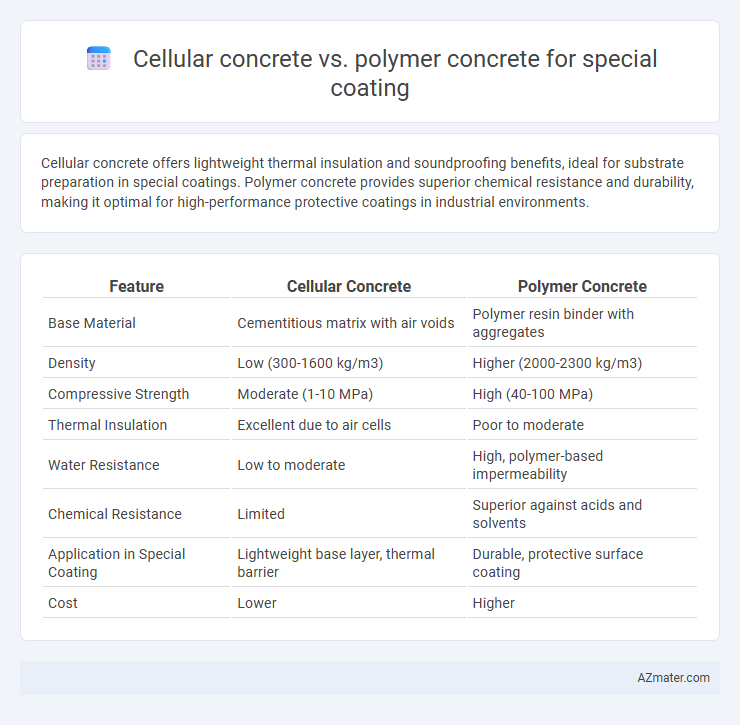
Cellular concrete offers lightweight thermal insulation and soundproofing benefits, ideal for substrate preparation in special coatings. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and durability, making it optimal for high-performance protective coatings in industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellular Concrete | Polymer Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Cementitious matrix with air voids | Polymer resin binder with aggregates |
| Density | Low (300-1600 kg/m3) | Higher (2000-2300 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (1-10 MPa) | High (40-100 MPa) |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent due to air cells | Poor to moderate |
| Water Resistance | Low to moderate | High, polymer-based impermeability |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited | Superior against acids and solvents |
| Application in Special Coating | Lightweight base layer, thermal barrier | Durable, protective surface coating |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Cellular Concrete and Polymer Concrete
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, aerated material composed of cement, water, and air bubbles, offering excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance properties ideal for special coatings. Polymer concrete incorporates polymer resins as a binder instead of cement, providing superior chemical resistance, durability, and adhesion for advanced protective coatings. Both materials are increasingly utilized in construction and industrial applications due to their enhanced performance characteristics tailored to specific environmental and structural requirements.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Cellular concrete exhibits lightweight characteristics, high thermal insulation, and good fire resistance, whereas polymer concrete offers superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and abrasion durability. The low density and porosity of cellular concrete make it ideal for insulation coatings, while polymer concrete's dense matrix ensures enhanced structural protection and longevity in harsh environments. Material selection depends on balancing thermal performance with mechanical robustness and chemical stability for specialized coating applications.
Strength and Durability Differences
Cellular concrete exhibits lower compressive strength and reduced durability compared to polymer concrete, making the latter more suitable for special coatings requiring enhanced mechanical performance. Polymer concrete offers superior chemical resistance, increased tensile strength, and excellent adhesion properties, which contribute to its longevity under harsh environmental conditions. The porous nature of cellular concrete limits its durability, while polymer concrete's dense matrix ensures prolonged structural integrity and resistance to wear and corrosion.
Application Methods in Special Coating
Cellular concrete and polymer concrete differ significantly in application methods for special coatings due to their material properties. Cellular concrete typically requires surface priming and curing steps before coating to ensure adhesion and prevent moisture entrapment, often applied using spray or trowel techniques. Polymer concrete leverages its inherent chemical resistance and lower porosity, allowing for direct application of specialized coatings via brush, roller, or spray, providing superior durability and chemical bond strength in protective layer formations.
Resistance to Chemicals and Environmental Stress
Cellular concrete offers moderate chemical resistance due to its porous structure but excels in thermal insulation and lightweight applications. Polymer concrete provides superior resistance to aggressive chemicals and environmental stress, making it ideal for special coatings in harsh industrial environments. Its dense, non-porous matrix prevents chemical penetration and withstands UV exposure, acids, alkalis, and solvents effectively.
Thermal and Acoustic Insulation Performance
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its porous structure, significantly reducing heat transfer compared to polymer concrete, which has denser molecular composition and higher thermal conductivity. In acoustic insulation, cellular concrete's air-filled cavities absorb sound waves effectively, making it ideal for noise reduction, whereas polymer concrete provides moderate sound dampening with better resistance to chemical and mechanical stresses. When selecting a special coating, cellular concrete is preferred for applications prioritizing energy efficiency and noise control, while polymer concrete suits environments demanding enhanced durability and chemical resistance.
Cost Analysis and Economic Value
Cellular concrete offers a cost-effective solution with lower raw material and production expenses, making it economically attractive for large-scale special coating projects. Polymer concrete, while more expensive due to specialized resins and curing processes, provides superior chemical resistance and durability, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs. Evaluating lifecycle expenses reveals cellular concrete's advantage in initial budget constraints, whereas polymer concrete delivers higher value in applications requiring enhanced performance and longevity.
Suitability for Specific Coating Scenarios
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it suitable for coatings requiring enhanced energy efficiency and fire resistance in building applications. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and mechanical strength, ideal for protective coatings exposed to harsh industrial environments or aggressive chemicals. Selecting between cellular and polymer concrete depends on the specific performance requirements of the coating scenario, such as load bearing, environmental exposure, and durability needs.
Maintenance Needs and Longevity
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties but requires regular maintenance due to its porous structure, which can be susceptible to moisture penetration and degradation over time. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance and durability, resulting in lower maintenance needs and longer service life, making it ideal for special coatings exposed to harsh environments. The choice between cellular and polymer concrete hinges on balancing maintenance frequency against longevity and environmental conditions.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Special Coating Applications
Cellular concrete offers excellent thermal insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for special coating applications requiring reduced structural load and enhanced fire resistance. Polymer concrete provides superior chemical resistance, high strength, and durability, suitable for environments exposed to aggressive chemicals or heavy mechanical stress. Selecting the right concrete depends on specific project needs, balancing factors like thermal performance, chemical exposure, mechanical load, and environmental conditions.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Polymer concrete for Special coating
 azmater.com
azmater.com