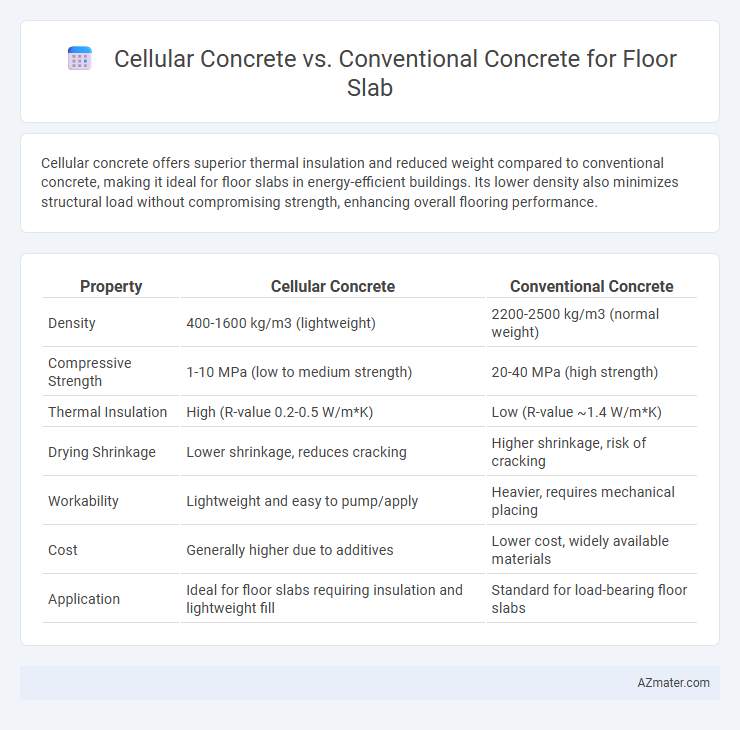
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced weight compared to conventional concrete, making it ideal for floor slabs in energy-efficient buildings. Its lower density also minimizes structural load without compromising strength, enhancing overall flooring performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Conventional Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 400-1600 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (normal weight) |
| Compressive Strength | 1-10 MPa (low to medium strength) | 20-40 MPa (high strength) |
| Thermal Insulation | High (R-value 0.2-0.5 W/m*K) | Low (R-value ~1.4 W/m*K) |
| Drying Shrinkage | Lower shrinkage, reduces cracking | Higher shrinkage, risk of cracking |
| Workability | Lightweight and easy to pump/apply | Heavier, requires mechanical placing |
| Cost | Generally higher due to additives | Lower cost, widely available materials |
| Application | Ideal for floor slabs requiring insulation and lightweight fill | Standard for load-bearing floor slabs |
Introduction to Cellular Concrete and Conventional Concrete
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, low-density material composed of cement, water, and stabilized foam, providing excellent thermal insulation and reduced self-weight for floor slabs. Conventional concrete consists of cement, water, sand, and aggregates, offering high compressive strength and durability for structural floor applications. The distinct composition of cellular concrete enables enhanced energy efficiency and ease of installation compared to the traditional density and load-bearing capacity of conventional concrete.
Composition Differences Between Cellular and Conventional Concrete
Cellular concrete contains a mixture of cement, water, fine aggregates, and a stable foam agent that introduces numerous air bubbles, resulting in lower density and improved insulation properties compared to conventional concrete. Conventional concrete primarily consists of cement, water, coarse aggregates, and fine aggregates, yielding a denser and stronger material suitable for high-load applications. The presence of foam in cellular concrete reduces material weight and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for floor slabs requiring lightweight and thermal efficiency.
Weight Comparison: Cellular vs Conventional Concrete Slabs
Cellular concrete floor slabs weigh approximately 25-40% less than conventional concrete slabs due to their air-entrained lightweight aggregate composition. This reduced weight significantly lessens structural load on foundations, enabling cost savings in substructure design and handling. Despite lower density, cellular concrete maintains adequate compressive strength for floor slab applications, offering an efficient balance between weight reduction and performance.
Thermal Insulation Properties of Each Concrete Type
Cellular concrete exhibits significantly better thermal insulation properties compared to conventional concrete due to its lightweight structure filled with air bubbles, which reduces heat transfer effectively. Its low thermal conductivity, typically ranging between 0.09 to 0.18 W/m*K, enhances energy efficiency in floor slabs by maintaining stable indoor temperatures. Conventional concrete, with a higher thermal conductivity of about 1.4 to 2.0 W/m*K, provides less insulation, resulting in greater heat loss and reduced energy performance in building floors.
Structural Performance in Floor Slab Applications
Cellular concrete offers superior thermal insulation and reduced dead load compared to conventional concrete, enhancing structural performance in floor slab applications by lowering stress on supporting elements. Its lower density, typically ranging from 400 to 1800 kg/m3, provides adequate compressive strength between 3 to 15 MPa, making it suitable for non-load-bearing and light-load floor slabs. Conventional concrete, with compressive strengths commonly exceeding 25 MPa, delivers higher structural capacity but at the cost of increased weight and reduced thermal efficiency, limiting design flexibility for some floor systems.
Installation Methods and Construction Time
Cellular concrete offers easier installation for floor slabs due to its lightweight and flowable nature, allowing faster placement and minimal labor compared to conventional concrete, which requires more complex formwork and vibration techniques. The reduced curing time of cellular concrete further accelerates construction schedules, minimizing downtime and enabling quicker project completion. Conventional concrete slabs demand extended curing periods and careful moisture control, resulting in longer overall construction times.
Cost Analysis for Floor Slabs: Material and Labor
Cellular concrete offers significant cost savings for floor slabs due to its lightweight nature, reducing material expenses by using aerated mixtures that require less cement and aggregate compared to conventional concrete. Labor costs are often lower with cellular concrete since its ease of placement and faster curing times decrease labor hours and equipment usage. In contrast, conventional concrete demands higher material quantities and longer curing periods, resulting in increased overall expenditures for both materials and labor.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Cellular concrete offers enhanced durability for floor slabs due to its lightweight and high thermal insulation properties, reducing the risk of cracking from temperature variations compared to conventional concrete. The material's porous structure allows for better moisture resistance, minimizing maintenance needs and extending the lifespan of the slab. Conventional concrete requires more frequent repairs and sealing to combat wear and environmental exposure, increasing long-term maintenance efforts.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellular concrete significantly reduces environmental impact compared to conventional concrete due to its lower raw material consumption and reduced carbon footprint from cement production. Its lightweight and insulating properties decrease energy use in heating and cooling buildings, enhancing sustainability in floor slab applications. Additionally, cellular concrete facilitates reuse and recycling, supporting circular economy goals in construction.
Best Use Cases: Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Floor Slab
Cellular concrete is ideal for floor slabs requiring lightweight properties, superior thermal insulation, and fire resistance, making it excellent for multi-story buildings and areas with poor soil conditions. Conventional concrete offers higher compressive strength and durability, suited for industrial floors, heavy load-bearing slabs, and exterior pavements exposed to harsh weather. Selecting the right concrete depends on project-specific factors such as load requirements, insulation needs, and site conditions to optimize performance and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Conventional concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com