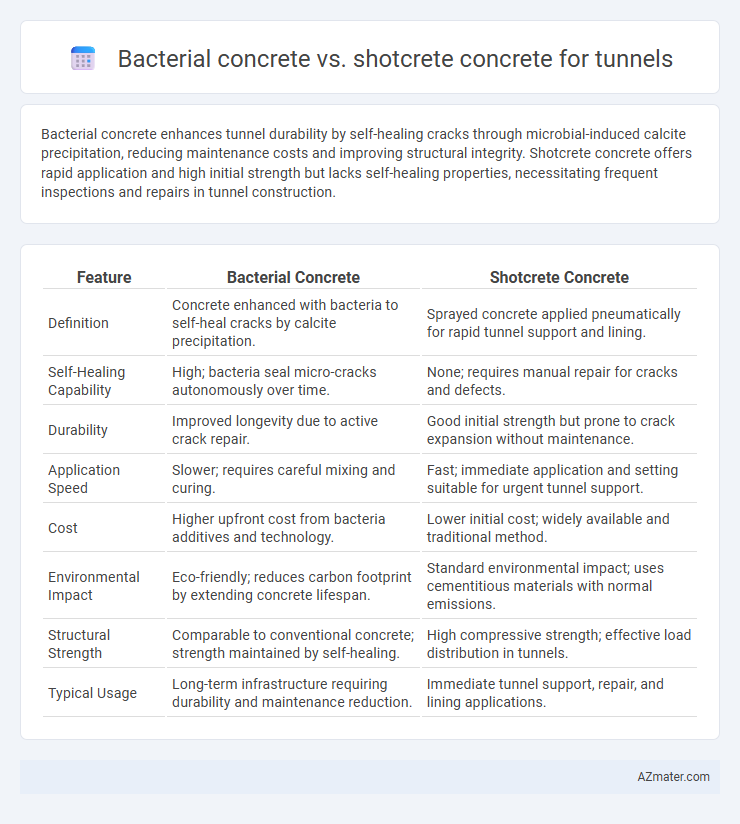
Bacterial concrete enhances tunnel durability by self-healing cracks through microbial-induced calcite precipitation, reducing maintenance costs and improving structural integrity. Shotcrete concrete offers rapid application and high initial strength but lacks self-healing properties, necessitating frequent inspections and repairs in tunnel construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bacterial Concrete | Shotcrete Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete enhanced with bacteria to self-heal cracks by calcite precipitation. | Sprayed concrete applied pneumatically for rapid tunnel support and lining. |
| Self-Healing Capability | High; bacteria seal micro-cracks autonomously over time. | None; requires manual repair for cracks and defects. |
| Durability | Improved longevity due to active crack repair. | Good initial strength but prone to crack expansion without maintenance. |
| Application Speed | Slower; requires careful mixing and curing. | Fast; immediate application and setting suitable for urgent tunnel support. |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost from bacteria additives and technology. | Lower initial cost; widely available and traditional method. |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; reduces carbon footprint by extending concrete lifespan. | Standard environmental impact; uses cementitious materials with normal emissions. |
| Structural Strength | Comparable to conventional concrete; strength maintained by self-healing. | High compressive strength; effective load distribution in tunnels. |
| Typical Usage | Long-term infrastructure requiring durability and maintenance reduction. | Immediate tunnel support, repair, and lining applications. |
Introduction to Tunnel Construction Techniques
Bacterial concrete enhances tunnel construction by self-healing microcracks through microbial-induced calcite precipitation, improving durability and reducing maintenance costs. Shotcrete concrete is widely used for immediate ground support in tunnels, sprayed onto surfaces to provide rapid setting and strong adhesion to complex geometries. Comparing their applications, bacterial concrete offers long-term structural integrity while shotcrete ensures quick stabilization during excavation phases.
Overview of Bacterial Concrete
Bacterial concrete incorporates specific bacteria that precipitate calcium carbonate to heal cracks autonomously, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance costs in tunnel construction. This self-healing property increases the lifespan of tunnel linings by preventing water ingress and chemical attacks. Compared to shotcrete concrete, bacterial concrete offers sustainable advantages by minimizing repair frequency and improving structural integrity in harsh underground environments.
Overview of Shotcrete Concrete
Shotcrete concrete, also known as sprayed concrete, is pneumatically projected at high velocity onto tunnel surfaces, providing rapid application and strong adhesion essential for tunnel reinforcement and excavation support. It typically consists of a mixture of cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures, with fiber reinforcements often added to improve tensile strength and durability. Compared to bacterial concrete, shotcrete offers immediate structural support, making it a preferred choice in tunnel construction for stabilizing rock faces and minimizing excavation time.
Mechanisms of Self-Healing in Bacterial Concrete
Bacterial concrete incorporates specific strains of bacteria that precipitate calcium carbonate within microcracks, effectively sealing them and preventing water ingress, which significantly enhances durability compared to conventional shotcrete. The self-healing mechanism relies on dormant bacterial spores activated by moisture and oxygen exposure, triggering biomineralization processes that fill cracks autonomously without external intervention. This bio-mediated healing not only restores structural integrity but also reduces maintenance costs and extends the lifespan of tunnel linings subjected to harsh underground environments.
Application Methods of Shotcrete Concrete in Tunnels
Shotcrete concrete is applied in tunnels primarily through wet-mix and dry-mix spraying techniques, where the concrete is pneumatically projected onto the tunnel surface to provide immediate support and stabilization. The wet-mix method delivers pre-mixed concrete through a hose with compressed air, ensuring better control over material quality and reduced rebound, while the dry-mix process conveys dry ingredients with water added at the nozzle, allowing for precise application in confined or inclined areas. These application methods enable rapid placement, adaptability to complex tunnel geometries, and enhanced bonding to rock surfaces, making shotcrete a versatile and efficient choice for tunnel lining and reinforcement compared to bacterial concrete.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Bacterial concrete enhances tunnel durability by utilizing microorganisms to precipitate calcium carbonate, filling micro-cracks and reducing permeability, which significantly extends the service life compared to traditional shotcrete. Shotcrete concrete provides immediate structural support with fast application but tends to exhibit higher susceptibility to cracking and water ingress over time, compromising long-term durability. Studies indicate bacterial concrete can increase tunnel lifespan by up to 30% through self-healing properties, making it a superior choice for longevity in tunnel infrastructure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bacterial concrete integrates microbial-induced calcite precipitation to self-heal cracks, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and extending tunnel lifespan, thereby minimizing environmental impact through lower resource consumption and waste generation. Shotcrete concrete, commonly used for tunnel linings, involves high energy consumption during production and frequent repairs due to susceptibility to cracking, contributing to a larger carbon footprint and increased material usage. The sustainable advantage of bacterial concrete lies in its eco-friendly bio-repair mechanisms, which enhance durability and reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional shotcrete applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Bacterial concrete reduces long-term maintenance costs in tunnel construction by self-healing microcracks, potentially lowering lifecycle expenses compared to Shotcrete concrete, which often requires frequent repairs and material replacement. Initial costs for bacterial concrete are higher due to specialized bio-additives and production processes, but economic feasibility improves with extended service life and reduced downtime. Shotcrete concrete remains cost-effective for short-term projects with limited maintenance budgets, yet bacterial concrete offers superior value in large-scale or critical tunnel infrastructure requiring durability and sustainability.
Maintenance Requirements and Life-Cycle Performance
Bacterial concrete enhances tunnel durability by autonomously repairing micro-cracks through microbial-induced calcite precipitation, significantly reducing maintenance frequency compared to shotcrete. Shotcrete, while providing immediate structural support, requires more frequent inspection and repair due to susceptibility to cracking and deterioration under environmental stress. Over the life cycle, bacterial concrete offers superior performance with self-healing properties that extend service intervals and lower overall maintenance costs in tunnel applications.
Conclusion: Optimal Concrete Choice for Tunnel Projects
Bacterial concrete offers enhanced self-healing properties and improved durability, making it an excellent choice for long-term tunnel projects exposed to moisture and cracks. Shotcrete concrete provides rapid application and high initial strength, ideal for immediate structural support during tunnel excavation and reinforcement. For optimal tunnel construction, combining bacterial concrete's longevity with shotcrete's quick installation can deliver superior performance and cost efficiency.
Infographic: Bacterial concrete vs Shotcrete concrete for Tunnel
 azmater.com
azmater.com