Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability against chemical corrosion in dam structures exposed to acidic environments, while roller-compacted concrete provides high strength and rapid construction with lower water content. Selecting acid-resistant concrete enhances longevity in corrosive conditions, whereas roller-compacted concrete optimizes cost and construction speed for large dam projects.
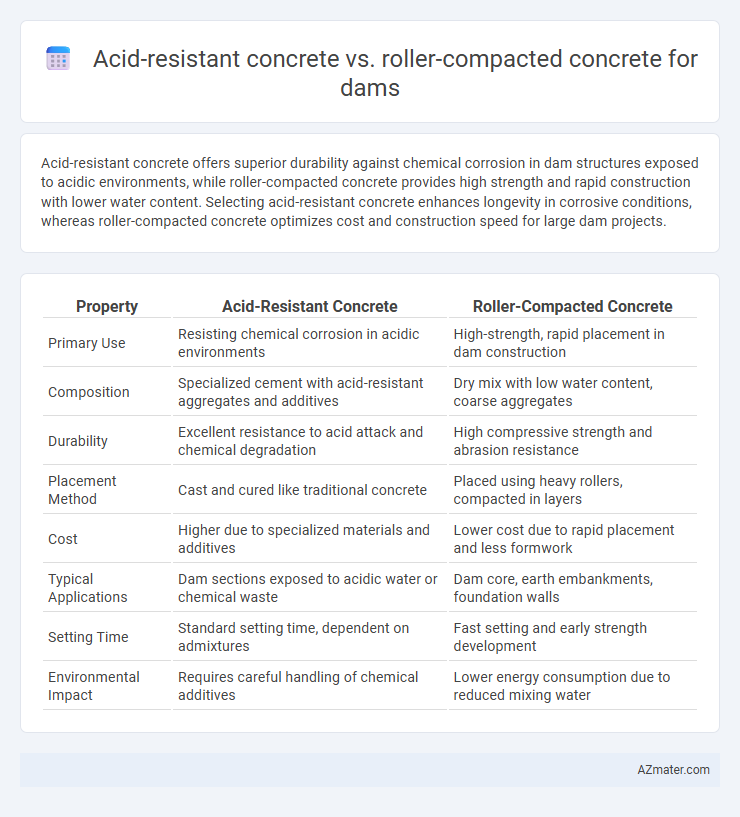
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Roller-Compacted Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Resisting chemical corrosion in acidic environments | High-strength, rapid placement in dam construction |
| Composition | Specialized cement with acid-resistant aggregates and additives | Dry mix with low water content, coarse aggregates |
| Durability | Excellent resistance to acid attack and chemical degradation | High compressive strength and abrasion resistance |
| Placement Method | Cast and cured like traditional concrete | Placed using heavy rollers, compacted in layers |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials and additives | Lower cost due to rapid placement and less formwork |
| Typical Applications | Dam sections exposed to acidic water or chemical waste | Dam core, earth embankments, foundation walls |
| Setting Time | Standard setting time, dependent on admixtures | Fast setting and early strength development |
| Environmental Impact | Requires careful handling of chemical additives | Lower energy consumption due to reduced mixing water |
Introduction to Dam Construction Materials
Acid-resistant concrete and roller-compacted concrete (RCC) are critical materials in dam construction, each offering distinct advantages based on environmental and structural demands. Acid-resistant concrete provides enhanced durability against chemical attack in acidic water reservoirs, extending the lifespan of dam structures exposed to harsh conditions. RCC, characterized by its high strength and rapid placement, enables efficient construction with reduced costs and accelerated project timelines, making it suitable for large-scale dam projects requiring robust performance.
Overview of Acid-Resistant Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is specifically engineered with specialized cementitious materials and chemical additives that enhance its durability against acidic environments commonly found in industrial and wastewater applications near dams. Its composition typically includes low-permeability aggregates and pozzolanic materials like silica fume or fly ash, which significantly reduce chemical attack and prolong structural integrity. This type of concrete is essential for maintaining dam safety and longevity when exposed to aggressive acids, unlike roller-compacted concrete, which prioritizes rapid placement and high strength but offers less chemical resistance.
Key Properties of Roller-Compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is characterized by its zero-slump consistency, high density, and rapid placement using asphalt paving equipment, making it ideal for dam construction due to its enhanced durability and cost-effectiveness. RCC exhibits excellent compressive strength and abrasion resistance, key for withstanding hydraulic pressures and erosive forces commonly encountered in dam structures. Its low cement content reduces heat of hydration, minimizing thermal cracking and improving long-term structural integrity compared to traditional acid-resistant concrete.
Durability in Aggressive Environments
Acid-resistant concrete demonstrates superior durability in aggressive environments due to its enhanced chemical composition incorporating silica fume and specialized admixtures that prevent acid penetration and degradation. Roller-compacted concrete, while offering high compressive strength and rapid constructability for dams, may require additional protective coatings or additives to withstand acidic conditions effectively. For long-term durability in acid-exposed dam applications, acid-resistant concrete provides a more reliable barrier against chemical attack, ensuring structural integrity and longevity.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Acid-resistant concrete enhances dam durability by resisting chemical corrosion, maintaining structural integrity under harsh acidic environments, and extending service life. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior load-bearing capacity through dense compaction and rapid placement, enabling efficient construction of large-scale dams with high compressive strength. Structural performance in acidic or high-load conditions favors acid-resistant concrete for chemical stability, while RCC excels in accommodating heavy static and dynamic loads due to its optimized mechanical properties.
Construction Techniques and Installation Time
Acid-resistant concrete employs specialized chemical admixtures and dense aggregate mixtures to enhance durability against chemical attacks, requiring meticulous mixing and curing processes that extend installation time. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for dams utilizes a dry, stiff mix placed with heavy rollers, enabling rapid layering and compaction, significantly reducing construction time compared to traditional concrete methods. RCC's mechanized placement and lower water content streamline the installation, making it preferable for large-scale dam projects demanding fast completion without compromising structural integrity.
Cost-Effectiveness and Lifecycle Analysis
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in chemically aggressive environments, reducing maintenance costs and extending service life, which enhances overall lifecycle cost-effectiveness for dam structures. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides rapid placement and lower initial construction costs but may require more frequent maintenance in acidic conditions, potentially increasing long-term expenses. Lifecycle analysis reveals that acid-resistant concrete, despite higher upfront costs, delivers better cost efficiency and longevity in dams exposed to acidic water or industrial effluents compared to RCC.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acid-resistant concrete for dams offers enhanced durability by resisting chemical degradation, reducing the frequency of repairs and material replacements, which lowers long-term environmental impact. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes less cement and energy-intensive processes, resulting in a smaller carbon footprint and promoting sustainability through efficient resource use. The choice between acid-resistant concrete and RCC depends on balancing chemical resilience with ecological footprint, where RCC often provides a more sustainable option due to its reduced emissions during production.
Case Studies: Acid-Resistant vs Roller-Compacted Concrete
Case studies reveal that acid-resistant concrete excels in environments with high sulfuric acid exposure, such as wastewater treatment dams, showcasing superior chemical durability and extended service life compared to roller-compacted concrete. Roller-compacted concrete, favored for its rapid placement and high early strength, is widely used in large-scale dam projects like the Hoover Dam, demonstrating cost efficiency and structural integrity under heavy load conditions. Comparative analyses highlight acid-resistant concrete's enhanced longevity in corrosive settings, while roller-compacted concrete remains optimal for projects prioritizing construction speed and mechanical strength.
Recommendations for Material Selection in Dams
Acid-resistant concrete is recommended for dams exposed to aggressive chemical environments, ensuring long-term durability and protection against acid attack. Roller-compacted concrete offers high compressive strength and rapid construction benefits, ideal for large-scale dam projects requiring efficient placement and reduced costs. Selecting the most suitable material depends on environmental conditions, expected chemical exposure, and structural performance requirements of the dam.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Dam
 azmater.com
azmater.com