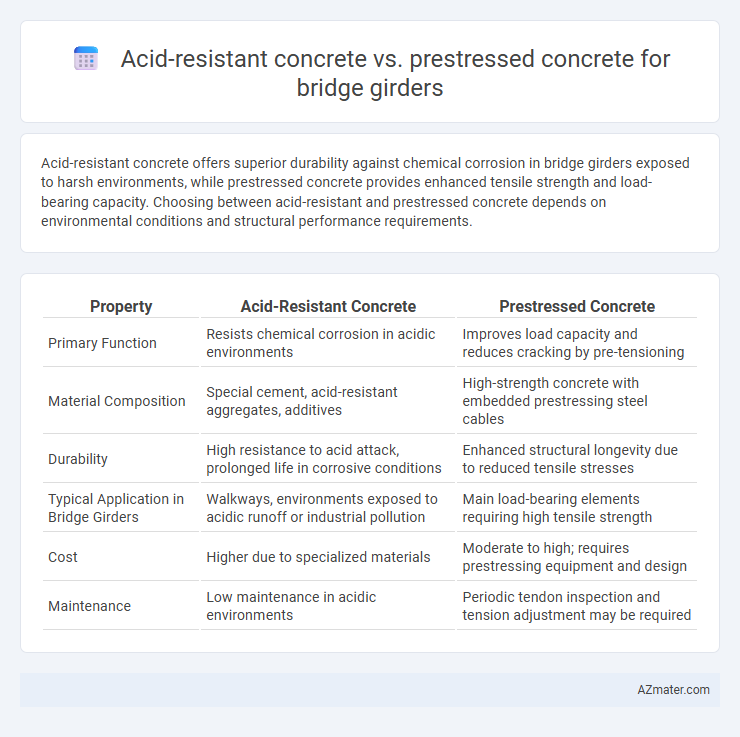
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability against chemical corrosion in bridge girders exposed to harsh environments, while prestressed concrete provides enhanced tensile strength and load-bearing capacity. Choosing between acid-resistant and prestressed concrete depends on environmental conditions and structural performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Prestressed Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Resists chemical corrosion in acidic environments | Improves load capacity and reduces cracking by pre-tensioning |
| Material Composition | Special cement, acid-resistant aggregates, additives | High-strength concrete with embedded prestressing steel cables |
| Durability | High resistance to acid attack, prolonged life in corrosive conditions | Enhanced structural longevity due to reduced tensile stresses |
| Typical Application in Bridge Girders | Walkways, environments exposed to acidic runoff or industrial pollution | Main load-bearing elements requiring high tensile strength |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials | Moderate to high; requires prestressing equipment and design |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance in acidic environments | Periodic tendon inspection and tension adjustment may be required |
Introduction to Bridge Girder Materials
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge girders offers enhanced durability against chemical attacks, making it ideal for structures exposed to acidic environments or industrial pollutants. Prestressed concrete girders provide superior load-carrying capacity and reduced cracking by introducing internal compressive stresses, which improve performance under tensile forces. Selecting between acid-resistant and prestressed concrete depends on environmental exposure and structural demands, with material properties directly influencing the longevity and safety of bridge girders.
Understanding Acid-Resistant Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is specifically formulated with chemical additives and low-permeability binders to withstand corrosive environments, making it ideal for bridge girders exposed to acidic conditions such as industrial pollution or acid rain. Its enhanced durability against chemical attack helps prevent structural deterioration, extending the lifespan of bridge components without extensive maintenance. Compared to prestressed concrete, which emphasizes load-bearing capacity through internal tensioning, acid-resistant concrete prioritizes chemical resistance to maintain structural integrity in harsh environments.
Overview of Prestressed Concrete
Prestressed concrete is engineered by applying compressive stresses to counteract tensile forces, enhancing its load-bearing capacity and durability in bridge girders. This method reduces cracking and deflection, enabling longer spans and thinner sections compared to conventional or acid-resistant concrete. Its superior performance in handling dynamic loads and environmental stresses makes it a preferred choice in modern bridge construction.
Chemical Resistance: Durability in Harsh Environments
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for bridge girders exposed to aggressive environments with high acid concentrations, such as industrial or coastal areas, ensuring enhanced durability. Prestressed concrete offers high tensile strength and load-bearing capacity but may require protective coatings or admixtures to improve resistance against chemical attacks. Selecting acid-resistant concrete significantly extends the lifespan of bridge girders in corrosive settings by minimizing surface degradation and structural weakening.
Load-Bearing Capacity and Structural Performance
Acid-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability and chemical resistance in harsh environments, ensuring long-term structural integrity for bridge girders exposed to acidic conditions, though its load-bearing capacity may be comparable to conventional concrete. Prestressed concrete significantly improves load-bearing capacity by introducing compressive stresses, effectively counteracting tensile forces and reducing crack development, resulting in superior structural performance under service loads. The choice between acid-resistant and prestressed concrete depends on balancing environmental durability with the required structural strength and service life demands of the bridge girder.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Lifecycle Expenses
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge girders typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes, while prestressed concrete offers lower upfront expenses with standard materials but may require additional maintenance. Lifecycle expenses of acid-resistant concrete tend to be lower as its durability minimizes repair frequency and extends service life, contrasting with prestressed concrete which might incur increased maintenance costs over time due to prestress loss and potential corrosion. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights acid-resistant concrete's economic advantage in aggressive environments despite higher installation cost, whereas prestressed concrete remains cost-effective in less corrosive settings.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in chemically aggressive environments, significantly reducing maintenance needs by preventing corrosion and surface degradation in bridge girders. Prestressed concrete enhances structural performance under tensile stresses, extending longevity through crack minimization but may require more frequent inspections to monitor tendon integrity and potential corrosion. Combining acid-resistant materials with prestressing techniques can optimize maintenance efficiency and lifespan for bridge girders in harsh conditions.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Acid-resistant concrete for bridge girders offers enhanced durability against corrosive environments, reducing maintenance frequency and minimizing environmental impact from repair activities. Prestressed concrete improves load-bearing capacity and extends service life, indirectly supporting sustainability by optimizing material use and reducing structural replacements. Selecting between the two materials depends on exposure conditions and lifecycle environmental assessments to ensure long-term ecological benefits.
Suitability for Different Bridge Types
Acid-resistant concrete is ideal for bridges exposed to aggressive chemical environments, such as industrial areas or sewage treatment plants, due to its high durability against acidic corrosion. Prestressed concrete offers superior load-bearing capacity and is suitable for long-span bridges requiring enhanced tensile strength and reduced girder depth. Choosing between these materials depends on the bridge's environmental exposure and structural demands, with acid-resistant concrete favored for durability in corrosive settings and prestressed concrete preferred for strength in heavy traffic or long-span designs.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Concrete for Girders
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability against chemical corrosion, making it ideal for bridge girders exposed to harsh environments with acidic substances. Prestressed concrete provides enhanced strength and load-bearing capacity through pre-tensioned reinforcement, optimizing structural performance under heavy loads. Selecting the optimal concrete depends on environmental exposure and structural requirements, with acid-resistant concrete preferred for chemical resilience and prestressed concrete favored for high structural demands.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Prestressed concrete for Bridge girder
 azmater.com
azmater.com