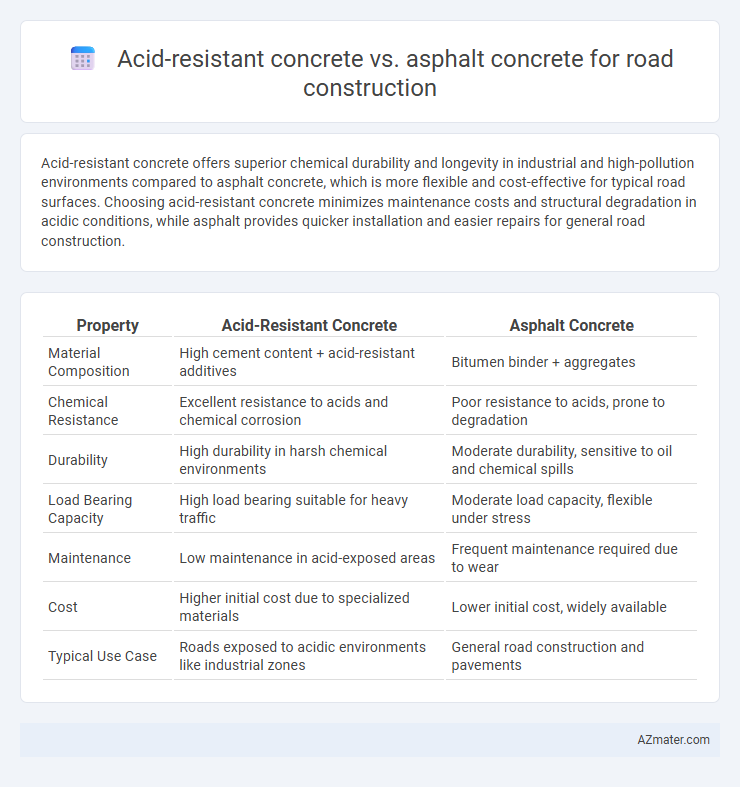
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical durability and longevity in industrial and high-pollution environments compared to asphalt concrete, which is more flexible and cost-effective for typical road surfaces. Choosing acid-resistant concrete minimizes maintenance costs and structural degradation in acidic conditions, while asphalt provides quicker installation and easier repairs for general road construction.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Asphalt Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High cement content + acid-resistant additives | Bitumen binder + aggregates |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids and chemical corrosion | Poor resistance to acids, prone to degradation |
| Durability | High durability in harsh chemical environments | Moderate durability, sensitive to oil and chemical spills |
| Load Bearing Capacity | High load bearing suitable for heavy traffic | Moderate load capacity, flexible under stress |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance in acid-exposed areas | Frequent maintenance required due to wear |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to specialized materials | Lower initial cost, widely available |
| Typical Use Case | Roads exposed to acidic environments like industrial zones | General road construction and pavements |
Introduction to Acid-Resistant and Asphalt Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is engineered with special cement and aggregates to withstand corrosive environments, making it ideal for roads exposed to acidic substances or chemical spills. Asphalt concrete, primarily composed of bitumen and aggregates, offers flexibility and durability for general road surfaces with high traffic loads. The choice between acid-resistant and asphalt concrete depends on environmental conditions, chemical exposure, and expected wear resistance.
Composition Differences Between Acid-Resistant and Asphalt Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete is primarily composed of specialized aggregates such as quartz, silica, and chemically inert materials combined with low-permeability cement matrices designed to withstand aggressive acidic environments. Asphalt concrete consists of a mixture of bitumen binder and mineral aggregates like sand, gravel, or crushed stone, optimized for flexibility and durability under traffic loads but lacks chemical resistance to acids. The key compositional difference lies in acid-resistant concrete incorporating chemically stable components to prevent degradation, whereas asphalt concrete focuses on binding aggregates for mechanical strength without specific treatments for chemical resistance.
Performance in Acidic Environments
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits superior durability and longevity in acidic environments due to its enhanced chemical composition, which includes additives like silica fume and acid-resistant aggregates that prevent deterioration caused by acidic rain or industrial pollutants. Asphalt concrete, while flexible and cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under acidic conditions, leading to surface erosion and potholes from chemical reactions with acids. Choosing acid-resistant concrete for road construction in areas exposed to high acidity ensures reduced maintenance costs and improved structural integrity over time.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical resistance and maintains structural integrity in corrosive environments, making it ideal for roads exposed to acidic pollutants or industrial runoff. Asphalt concrete provides flexibility and better fatigue resistance under dynamic loading but is more susceptible to chemical degradation and temperature variations. Strength-wise, acid-resistant concrete excels in compressive strength and long-term durability, whereas asphalt concrete performs better under tensile stresses and cyclic traffic loads.
Cost Analysis: Acid-Resistant vs Asphalt Concrete
Acid-resistant concrete generally incurs higher initial costs compared to asphalt concrete due to its specialized materials and manufacturing processes designed to withstand chemical corrosion. Maintenance expenses for acid-resistant concrete are often lower over time, as it resists degradation in acidic environments better than asphalt, which tends to require more frequent repairs and resurfacing. Life-cycle cost analysis commonly favors acid-resistant concrete in environments exposed to acidic substances despite its upfront cost premium, due to reduced long-term maintenance and replacement needs.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits superior durability in chemically aggressive environments, reducing the frequency of maintenance and extending the lifespan of road surfaces compared to asphalt concrete. Asphalt concrete, while cost-effective and flexible, often requires more frequent repairs due to susceptibility to chemical damage and weathering. The enhanced longevity and lower maintenance needs of acid-resistant concrete make it a preferable choice for roads exposed to industrial pollutants and acid rain.
Application Suitability for Various Road Types
Acid-resistant concrete excels in industrial areas and chemical plants due to its durability against acidic environments, making it highly suitable for roads exposed to corrosive substances. Asphalt concrete is preferred for highways and urban roads because of its flexibility, ease of repair, and cost-effectiveness in moderate traffic conditions. For heavy-duty or specialized roadways requiring chemical resistance, acid-resistant concrete outperforms asphalt by providing longer service life and reduced maintenance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior durability in chemically aggressive environments, significantly reducing maintenance frequency and resource consumption compared to asphalt concrete, which is prone to faster degradation and higher emissions from petroleum-based materials. Asphalt concrete production generates considerable greenhouse gases and requires frequent resurfacing, leading to increased material waste and environmental disturbance. Acid-resistant concrete's longevity and lower lifecycle emissions contribute to enhanced sustainability in road construction, promoting reduced ecological footprint and resource conservation.
Installation Process and Time Efficiency
Acid-resistant concrete requires specialized mixing and curing processes to enhance chemical durability, leading to longer curing times compared to asphalt concrete. Asphalt concrete features a relatively quick installation process due to its thermal setting properties, allowing roads to reopen faster and minimizing traffic disruption. The time efficiency of asphalt concrete makes it preferable for projects demanding rapid deployment, while acid-resistant concrete suits environments with high chemical exposure despite its extended curing period.
Final Recommendations for Road Construction Choices
Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical durability and longevity in environments exposed to acidic substances, making it ideal for industrial zones or areas with frequent acid rain. Asphalt concrete provides greater flexibility and faster installation, suitable for regions requiring rapid repairs and adaptability to temperature fluctuations. For long-term durability in chemically aggressive environments, acid-resistant concrete is recommended, whereas asphalt concrete remains preferable for cost-effective, flexible road surfaces in moderate conditions.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Asphalt concrete for Road construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com