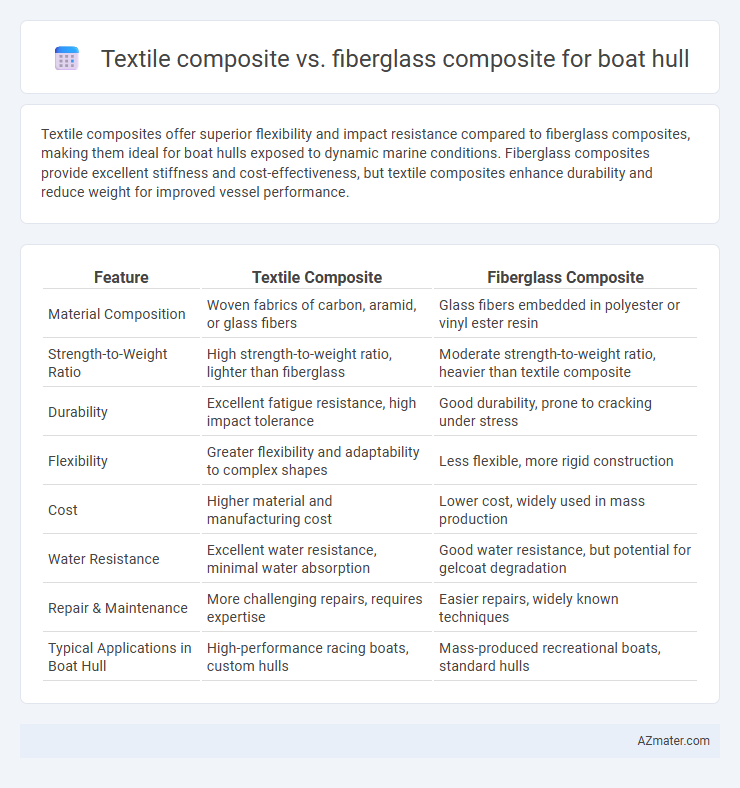
Textile composites offer superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to fiberglass composites, making them ideal for boat hulls exposed to dynamic marine conditions. Fiberglass composites provide excellent stiffness and cost-effectiveness, but textile composites enhance durability and reduce weight for improved vessel performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Textile Composite | Fiberglass Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Woven fabrics of carbon, aramid, or glass fibers | Glass fibers embedded in polyester or vinyl ester resin |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | High strength-to-weight ratio, lighter than fiberglass | Moderate strength-to-weight ratio, heavier than textile composite |
| Durability | Excellent fatigue resistance, high impact tolerance | Good durability, prone to cracking under stress |
| Flexibility | Greater flexibility and adaptability to complex shapes | Less flexible, more rigid construction |
| Cost | Higher material and manufacturing cost | Lower cost, widely used in mass production |
| Water Resistance | Excellent water resistance, minimal water absorption | Good water resistance, but potential for gelcoat degradation |
| Repair & Maintenance | More challenging repairs, requires expertise | Easier repairs, widely known techniques |
| Typical Applications in Boat Hull | High-performance racing boats, custom hulls | Mass-produced recreational boats, standard hulls |
Introduction to Marine Composite Materials
Marine composite materials such as textile composites and fiberglass composites are widely used in boat hull construction due to their strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. Textile composites feature woven fibers that improve impact resistance and flexibility, while fiberglass composites offer excellent tensile strength and durability. Choosing the right composite depends on factors such as vessel size, performance requirements, and environmental exposure.
Overview of Textile Composites
Textile composites for boat hulls consist of woven fibers such as carbon, aramid, or flax embedded in a resin matrix, offering enhanced flexibility, impact resistance, and weight reduction compared to traditional fiberglass composites. These materials provide superior fatigue strength and improved vibration damping, which contribute to increased durability and comfort in marine environments. The customizable fiber architecture in textile composites allows for optimized mechanical properties tailored to specific hull design requirements, making them a preferred choice in advanced boat manufacturing.
Understanding Fiberglass Composites
Fiberglass composites for boat hulls consist of woven glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, offering high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. These composites provide superior impact resistance and durability compared to traditional textile composites, making them ideal for marine environments. Understanding the fiber orientation, resin type, and layering techniques is crucial for optimizing the structural performance and longevity of fiberglass boat hulls.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Textile composites offer superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to fiberglass composites, enhancing durability under dynamic marine conditions. Fiberglass composites exhibit higher stiffness and better resistance to compressive forces, making them ideal for structural stability in boat hulls. The choice between textile and fiberglass composites depends on the specific mechanical demands such as flexibility versus rigidity required for optimal hull performance.
Weight and Performance Considerations
Textile composites, such as carbon fiber or aramid fiber reinforced polymers, offer superior strength-to-weight ratios compared to traditional fiberglass composites, making them ideal for lightweight and high-performance boat hulls. Fiberglass composites provide excellent durability and impact resistance but tend to be heavier, which can reduce speed and fuel efficiency in marine vessels. Choosing textile composites enhances acceleration, agility, and overall hull stiffness, crucial for competitive or high-end boating applications seeking optimal weight reduction and performance.
Durability and Longevity in Marine Environments
Textile composites exhibit superior resistance to fatigue and impact damage in marine environments compared to traditional fiberglass composites, enhancing boat hull durability. Fiberglass composites, while cost-effective and widely used, tend to absorb moisture over time, leading to potential degradation and reduced longevity. Advanced textile composites utilize high-performance fibers like carbon or aramid, which significantly improve hull strength and corrosion resistance, extending service life in harsh saltwater conditions.
Cost Analysis: Textile vs Fiberglass Composites
Textile composites generally offer a lower initial material cost compared to fiberglass composites, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious boat hull construction. While fiberglass composites incur higher expenses due to resin and fiber costs, their superior strength-to-weight ratio can reduce long-term maintenance and repair costs. The total cost analysis must consider lifecycle expenses, with textile composites benefiting from easier manufacturing processes and fiberglass composites excelling in performance longevity and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Textile composites for boat hulls often incorporate natural fibers such as flax or hemp, which reduce carbon footprint and enhance biodegradability compared to traditional fiberglass composites made from glass fibers and resin. Fiberglass composites pose environmental challenges due to their energy-intensive production and difficulty in recycling, leading to significant landfill waste. Sustainable textile composites promote circular economy principles by enabling easier recycling and minimizing toxic emissions throughout the lifecycle of the boat hull.
Ease of Manufacturing and Repair
Textile composites offer greater ease of manufacturing for boat hulls due to their flexibility and ability to conform to complex shapes, reducing labor time and costs compared to fiberglass composites. Repairing textile composites is typically more straightforward, as damaged areas can be patched seamlessly with similar materials and standard resin systems, enhancing vessel longevity. In contrast, fiberglass composites often require more extensive surface preparation and specialized skill sets for effective repairs, increasing downtime and maintenance expenses.
Future Trends in Boat Hull Composite Technology
Textile composites are emerging as a preferred material for boat hulls due to their superior flexibility, weight reduction, and enhanced impact resistance compared to traditional fiberglass composites. Innovations in hybrid textile-fiberglass composites and bio-based resins are driving sustainability and performance improvements, aligning with industry goals for eco-friendly and high-strength hull construction. Future trends emphasize additive manufacturing and smart textile integration, enabling real-time damage detection and adaptive response capabilities in advanced boat hull composites.
Infographic: Textile composite vs Fiberglass composite for Boat hull
 azmater.com
azmater.com