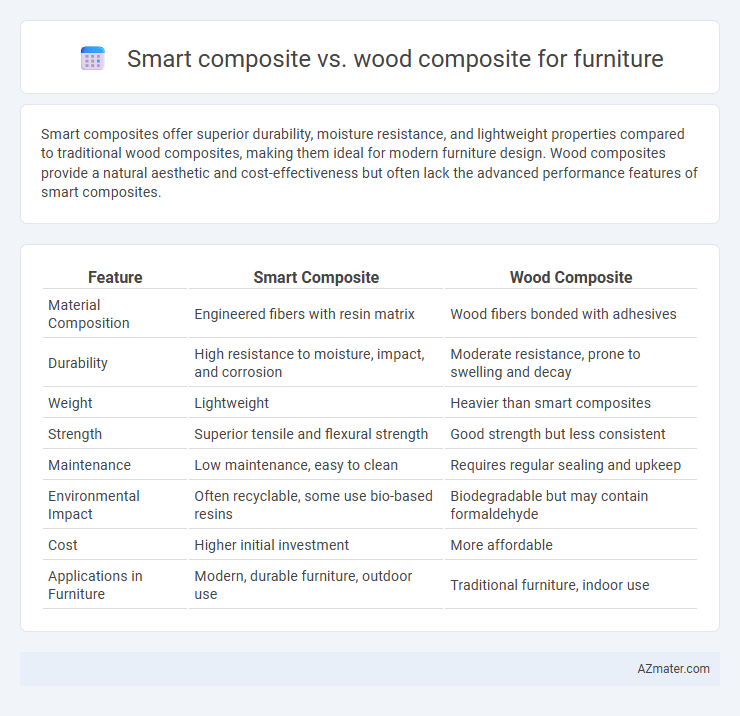
Smart composites offer superior durability, moisture resistance, and lightweight properties compared to traditional wood composites, making them ideal for modern furniture design. Wood composites provide a natural aesthetic and cost-effectiveness but often lack the advanced performance features of smart composites.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Composite | Wood Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Engineered fibers with resin matrix | Wood fibers bonded with adhesives |
| Durability | High resistance to moisture, impact, and corrosion | Moderate resistance, prone to swelling and decay |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than smart composites |
| Strength | Superior tensile and flexural strength | Good strength but less consistent |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to clean | Requires regular sealing and upkeep |
| Environmental Impact | Often recyclable, some use bio-based resins | Biodegradable but may contain formaldehyde |
| Cost | Higher initial investment | More affordable |
| Applications in Furniture | Modern, durable furniture, outdoor use | Traditional furniture, indoor use |
Introduction to Smart Composites and Wood Composites
Smart composites incorporate advanced materials such as carbon fiber, glass fiber, and resin matrices, offering superior strength, lightweight properties, and enhanced durability ideal for modern furniture design. Wood composites, made from wood fibers bound with adhesives, provide cost-effective, sustainable options with good structural integrity and aesthetic versatility. Both materials serve distinct roles in furniture manufacturing, balancing performance, environmental impact, and design flexibility.
Material Composition and Structure Comparison
Smart composites for furniture typically combine advanced polymers, resins, and reinforcing fibers like carbon or glass, resulting in lightweight yet high-strength materials with enhanced durability and resistance to moisture and pests. Wood composites, such as particleboard and MDF, are primarily composed of wood fibers or particles bonded together with adhesives, offering a more traditional texture but generally lower structural integrity and susceptibility to swelling in humid conditions. The engineered layering and molecular bonding in smart composites provide superior mechanical performance and longevity compared to the more homogenous and porous structure of wood composites.
Strength and Durability: Smart vs Wood Composite
Smart composite materials exhibit superior strength and durability compared to traditional wood composites, offering enhanced resistance to bending, impact, and environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations. Wood composites, while more affordable, tend to absorb moisture, leading to swelling and reduced structural integrity over time. Selecting smart composites for furniture ensures longer-lasting performance and maintains aesthetic appeal under heavy use and diverse conditions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart composite furniture combines recycled plastics and wood fibers, offering high durability and resistance to moisture while reducing deforestation. Wood composite furniture, primarily made from wood waste and adhesives, promotes resource efficiency but may involve formaldehyde-based resins with environmental concerns. Both materials contribute to sustainability by utilizing recycled content, but smart composites typically have a lower carbon footprint due to extended lifespan and reduced natural resource extraction.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Smart composite materials offer superior design flexibility compared to wood composites, allowing for intricate shapes and seamless finishes that traditional wood composites cannot easily achieve. These materials provide a broader palette of aesthetic options, including customizable textures, colors, and surface treatments suited for modern furniture styles. Wood composites, while more limited in formability, retain a natural wood appearance but often require additional finishing to match the versatile visual appeal of smart composites.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Smart composites typically offer higher durability and moisture resistance than wood composites, often resulting in a higher initial cost but lower long-term maintenance expenses for furniture. Wood composites are generally more affordable upfront, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects, but they may incur additional costs over time due to potential warping, swelling, or damage. When balancing cost and budget considerations, smart composites provide a cost-effective investment for furniture requiring longevity and minimal upkeep, while wood composites remain a viable option for short-term or lower-budget applications.
Manufacturing Techniques and Scalability
Smart composites for furniture manufacturing utilize advanced layering and bonding techniques integrating synthetic fibers and resins, offering precise control over material properties and enhanced durability. Wood composites rely on traditional hot-pressing methods combining wood fibers, adhesives, and fillers, enabling mass production but often with less customization flexibility. Scalability favors wood composites due to established industrial processes and abundant raw materials, while smart composites require specialized equipment and skilled labor, limiting large-scale adoption but delivering superior performance for high-end applications.
Maintenance and Longevity
Smart composite furniture offers superior resistance to moisture, scratches, and termites compared to traditional wood composites, resulting in lower maintenance requirements. Wood composites often require regular sealing, sanding, or refinishing to prevent warping and decay, especially in humid environments. The advanced materials in smart composites enhance durability and extend furniture lifespan, making them an ideal choice for long-term use with minimal upkeep.
Applications in Modern Furniture Design
Smart composites in modern furniture design offer enhanced durability, lightweight structure, and adaptability with embedded sensors, making them ideal for ergonomic chairs and modular systems. Wood composites provide natural aesthetics and sustainability, widely used in cabinetry, flooring, and decorative panels due to their strength and cost-effectiveness. Integrating smart composites allows for innovative functionalities like adjustable seating, while wood composites maintain classic design elements in contemporary interiors.
Future Trends in Furniture Composites
Smart composites in furniture are increasingly favored for their adaptability, integrating sensors and responsive materials that enhance durability and user interaction. Wood composites continue evolving with eco-friendly resins and advanced manufacturing techniques, improving sustainability and aesthetic appeal. Future trends emphasize hybrid composites combining smart technology with natural fibers to create lightweight, strong, and multifunctional furniture solutions.
Infographic: Smart composite vs Wood composite for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com