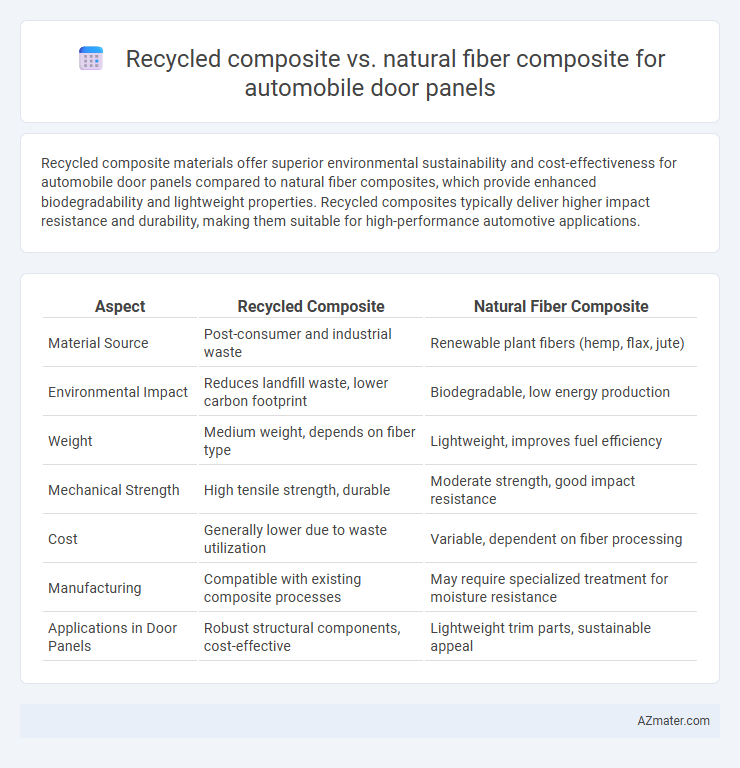
Recycled composite materials offer superior environmental sustainability and cost-effectiveness for automobile door panels compared to natural fiber composites, which provide enhanced biodegradability and lightweight properties. Recycled composites typically deliver higher impact resistance and durability, making them suitable for high-performance automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Recycled Composite | Natural Fiber Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer and industrial waste | Renewable plant fibers (hemp, flax, jute) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lower carbon footprint | Biodegradable, low energy production |
| Weight | Medium weight, depends on fiber type | Lightweight, improves fuel efficiency |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, good impact resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower due to waste utilization | Variable, dependent on fiber processing |
| Manufacturing | Compatible with existing composite processes | May require specialized treatment for moisture resistance |
| Applications in Door Panels | Robust structural components, cost-effective | Lightweight trim parts, sustainable appeal |
Introduction to Automobile Door Panel Materials
Automobile door panels predominantly utilize materials like recycled composites and natural fiber composites to balance durability, weight, and sustainability. Recycled composites offer enhanced mechanical strength and environmental benefits by repurposing waste materials, reducing carbon footprint in automotive manufacturing. Natural fiber composites provide lightweight alternatives with excellent insulation properties, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle emissions.
Overview of Recycled Composite Materials
Recycled composite materials for automobile door panels are primarily derived from post-consumer plastics and industrial waste, offering significant environmental benefits through reduced landfill use and lower carbon footprints. These composites combine recycled fibers, such as glass or carbon fibers reclaimed from manufacturing scraps, with polymer matrices like recycled thermoplastics, ensuring adequate mechanical performance and durability for automotive applications. The integration of recycled composites in door panels enhances sustainability while maintaining essential properties like impact resistance and weight reduction critical for vehicle efficiency.
Natural Fiber Composite: Composition and Properties
Natural fiber composites for automobile door panels primarily consist of fibers like flax, hemp, jute, or sisal embedded in a polymer matrix, usually polypropylene or epoxy, which enhances biodegradability and reduces environmental impact. These composites exhibit impressive mechanical properties such as high specific strength and stiffness, low density, and excellent vibration damping, contributing to noise reduction and lightweight vehicle design. Their natural origin offers improved sustainability, lower production energy consumption, and enhanced recyclability compared to traditional synthetic or recycled composites.
Comparative Mechanical Performance
Recycled composites for automobile door panels typically offer lower tensile strength and impact resistance compared to natural fiber composites, which benefit from higher stiffness and improved energy absorption due to lignocellulosic fiber content. Natural fiber composites also demonstrate better fatigue resistance and vibration damping, crucial for passenger comfort and durability in automotive applications. However, recycled composites excel in environmental sustainability and cost efficiency, presenting a trade-off between mechanical performance and ecological benefits.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled composite materials for automobile door panels significantly reduce landfill waste by repurposing plastic and metal scraps, lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin composites. Natural fiber composites, derived from renewable sources like flax or hemp, offer biodegradability and reduced fossil fuel dependence, enhancing sustainability in automotive manufacturing. Both materials contribute to lightweight vehicle design, improving fuel efficiency and decreasing overall environmental impact during the vehicle lifecycle.
Cost Analysis and Economic Viability
Recycled composite materials for automobile door panels offer significant cost advantages due to lower raw material expenses and reduced waste management fees compared to natural fiber composites, which often involve higher cultivation and processing costs. Economic viability of recycled composites improves with increasing demand for sustainable automotive parts and potential subsidies for recycled content usage, while natural fiber composites may face fluctuations in supply chain sustainability and price volatility. Lifecycle cost analysis indicates that recycled composites provide more consistent long-term savings and better alignment with circular economy principles in the automotive industry.
Manufacturing Process and Scalability
Recycled composite materials for automobile door panels utilize processed waste fibers and polymers, reducing raw material costs and environmental impact while enabling the use of existing manufacturing techniques like compression molding and injection molding. Natural fiber composites, often made from flax, hemp, or kenaf fibers combined with bio-based or synthetic resins, require more precise fiber treatment and moisture control during processing to ensure consistent quality and performance. Scalability favors recycled composites due to the abundant availability of waste feedstock and compatibility with high-throughput manufacturing systems, whereas natural fiber composites face challenges related to fiber variability and supply chain limitations, impacting mass production efficiency.
Weight Reduction and Fuel Efficiency
Recycled composite materials for automobile door panels offer significant weight reduction compared to traditional natural fiber composites, enhancing overall vehicle efficiency. The lower density of recycled composites directly contributes to decreased vehicle mass, which correlates with improved fuel economy and reduced CO2 emissions. Utilizing recycled composites supports sustainable manufacturing while maintaining structural integrity essential for automotive safety standards.
Challenges and Limitations
Recycled composites for automobile door panels face challenges related to inconsistent material properties and potential contamination, which can affect structural integrity and durability. Natural fiber composites encounter limitations such as moisture absorption, leading to reduced mechanical strength and increased susceptibility to fungal degradation. Both materials require advanced processing techniques to enhance performance and ensure long-term reliability in automotive applications.
Future Trends in Automotive Door Panel Materials
Recycled composite materials for automobile door panels demonstrate increasing adoption due to their environmental benefits and comparable performance metrics, such as impact resistance and weight reduction, relative to natural fiber composites. Future trends emphasize enhanced recyclability, lifecycle sustainability, and integration of bio-based resins to improve mechanical properties while minimizing carbon footprint. Advances in hybrid composites combining recycled content with natural fibers are projected to optimize structural integrity and cost-effectiveness in automotive door panel manufacturing.
Infographic: Recycled composite vs Natural fiber composite for Automobile door panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com