Polymer clay offers flexibility and vibrant color options ideal for detailed ceramic crafts, while earthenware clay provides traditional porous texture and durability suitable for functional pottery. Choose polymer clay for lightweight, non-firing projects and earthenware clay for kiln-fired, heat-resistant creations.
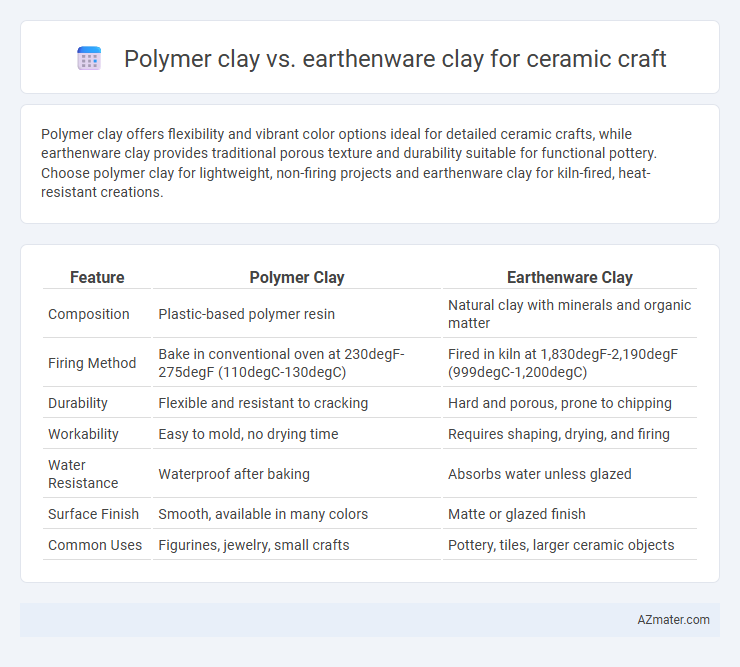
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polymer Clay | Earthenware Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Plastic-based polymer resin | Natural clay with minerals and organic matter |
| Firing Method | Bake in conventional oven at 230degF-275degF (110degC-130degC) | Fired in kiln at 1,830degF-2,190degF (999degC-1,200degC) |
| Durability | Flexible and resistant to cracking | Hard and porous, prone to chipping |
| Workability | Easy to mold, no drying time | Requires shaping, drying, and firing |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof after baking | Absorbs water unless glazed |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, available in many colors | Matte or glazed finish |
| Common Uses | Figurines, jewelry, small crafts | Pottery, tiles, larger ceramic objects |
Introduction to Polymer Clay and Earthenware Clay
Polymer clay is a synthetic modeling material made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) combined with plasticizers, known for its versatility, vibrant colors, and ability to harden at low temperatures in a home oven. Earthenware clay is a natural, porous clay fired at lower temperatures (typically 1000-1150degC), offering a traditional ceramic texture that is more fragile and absorbent compared to stoneware or porcelain. Both clays cater to different ceramic craft applications, with polymer clay ideal for detailed, lightweight items and earthenware clay suited for functional pottery and artistic sculptures.
Composition and Material Properties
Polymer clay consists of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) combined with plasticizers, giving it flexibility and ease of shaping at room temperature, unlike earthenware clay, which is primarily composed of natural clay minerals such as kaolinite, quartz, and feldspar that require high-temperature kiln firing for hardening. Polymer clay remains lightweight and does not require water to shape, making it less porous and more resistant to water absorption compared to earthenware clay, which is porous and more fragile after firing. The thermal stability of earthenware clay allows it to endure higher temperatures, whereas polymer clay softens above 130degC and is not suitable for traditional kiln firing, limiting its durability in heat-exposed applications.
Workability and Ease of Use
Polymer clay offers superior workability due to its pliable, non-drying nature, allowing intricate detailing and easy reshaping without the need for a kiln. Earthenware clay, while traditional and versatile, requires more skill to manage as it dries quickly, shrinks, and demands careful moisture control to prevent cracking. The ease of use in polymer clay makes it ideal for beginners and small projects, whereas earthenware clay is favored for larger, durable pieces needing firing.
Firing and Curing Requirements
Polymer clay cures at low temperatures, typically between 230degF and 275degF (110degC to 135degC) in a standard oven, making it accessible for home crafters without the need for a kiln. Earthenware clay requires firing in a kiln at much higher temperatures, usually between 1,000degC and 1,150degC (1,832degF to 2,102degF), to achieve proper hardness and durability. The low-temperature curing of polymer clay allows for quicker project completion, whereas earthenware firing produces more durable, functional ceramic pieces.
Color and Finish Options
Polymer clay offers a vibrant color palette with customizable hues that remain bright after baking, ideal for detailed ceramic craft projects requiring consistent color retention. Earthenware clay provides natural, earthy tones with a porous finish that can be altered through glazing techniques, resulting in a glossy or matte surface based on firing methods. The choice between polymer and earthenware clay hinges on desired color vibrancy and finish texture, as polymer yields a smooth, plastic-like finish, whereas earthenware delivers a traditional ceramic feel.
Durability and Longevity
Polymer clay offers excellent durability due to its synthetic composition, resisting cracks and chips under normal use, making it ideal for small, detailed ceramic crafts. Earthenware clay, while traditional and porous, requires glazing and proper firing to enhance its strength but remains more susceptible to chipping and wear over time compared to polymer clay. For projects demanding long-lasting durability and minimal maintenance, polymer clay outperforms earthenware in longevity and resistance to environmental factors.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Polymer clay is a synthetic material often made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and can release toxic fumes, such as hydrochloric acid, if overheated, necessitating careful baking at recommended temperatures. Earthenware clay, a natural ceramic material, generally contains non-toxic components but may include potentially harmful additives or glazing materials that require proper handling and firing to ensure safety. Both clays demand appropriate ventilation during use and curing to minimize exposure to harmful substances, making informed usage critical for ceramic craft safety.
Project Suitability and Versatility
Polymer clay offers exceptional versatility for detailed and small-scale ceramic crafts due to its pliability and low-temperature curing process, making it ideal for intricate jewelry and miniatures. Earthenware clay, fired at high temperatures, provides durability and strength suited for functional pottery and larger sculptural projects but requires specialized kiln access. Project suitability depends on the desired outcome: polymer clay excels in versatility and ease of use for decorative items, while earthenware clay is preferred for traditional ceramics demanding permanence and structural integrity.
Cost and Availability
Polymer clay typically costs more per pound than earthenware clay but is widely available in craft stores and online, making it accessible for hobbyists and small projects. Earthenware clay is generally more affordable, especially when purchased in bulk from pottery supply stores or local suppliers, but may require specialized equipment for firing. Availability of earthenware clay can vary regionally, while polymer clay offers consistent global distribution and ease of use without kiln firing.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Ceramic Craft
Choosing the right clay for your ceramic craft depends on your project's durability and finishing preferences. Polymer clay offers vibrant colors, flexibility, and air-drying convenience, ideal for detailed, small-scale pieces and mixed-media art. Earthenware clay requires kiln firing, providing more durability and a traditional ceramic feel, suitable for functional pottery and larger sculptural works.
Infographic: Polymer clay vs Earthenware clay for Ceramic craft
 azmater.com
azmater.com