Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and thermal shock durability compared to ball clay, making it ideal for cooking vessels exposed to direct flames. Ball clay provides excellent plasticity and workability but lacks the high-temperature strength necessary for flame-exposed cookware.
Table of Comparison
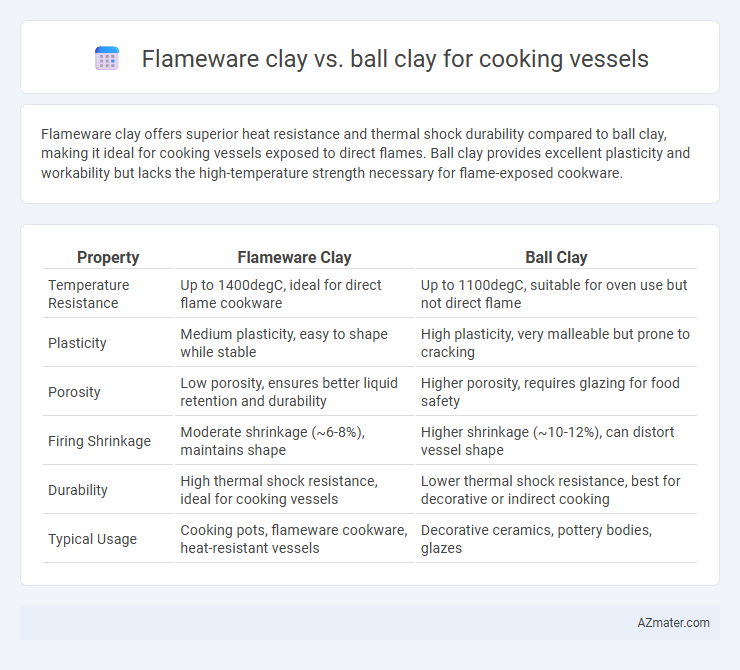
| Property | Flameware Clay | Ball Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1400degC, ideal for direct flame cookware | Up to 1100degC, suitable for oven use but not direct flame |
| Plasticity | Medium plasticity, easy to shape while stable | High plasticity, very malleable but prone to cracking |
| Porosity | Low porosity, ensures better liquid retention and durability | Higher porosity, requires glazing for food safety |
| Firing Shrinkage | Moderate shrinkage (~6-8%), maintains shape | Higher shrinkage (~10-12%), can distort vessel shape |
| Durability | High thermal shock resistance, ideal for cooking vessels | Lower thermal shock resistance, best for decorative or indirect cooking |
| Typical Usage | Cooking pots, flameware cookware, heat-resistant vessels | Decorative ceramics, pottery bodies, glazes |
Introduction to Cooking Vessels: Flameware Clay vs Ball Clay
Flameware clay, known for its high thermal shock resistance and durability, is ideal for cooking vessels subjected to direct flame and rapid temperature changes. Ball clay offers excellent plasticity and smooth texture but lacks the thermal resilience required for flame-exposed cookware. Choosing flameware clay enhances heat distribution and longevity in cooking pots and pans compared to ball clay's primary use in ceramics requiring fine detail rather than functional heat exposure.
What is Flameware Clay?
Flameware clay is a specialized type of ceramic material designed to withstand direct exposure to open flames and high heat, making it ideal for cooking vessels such as grills, fire pits, and stovetop cookware. Unlike ball clay, which is highly plastic and used mainly for shaping and refining ceramics, flameware clay possesses enhanced thermal shock resistance and durability to endure rapid temperature changes without cracking. Its unique mineral composition and high refractory properties allow flameware clay to maintain structural integrity and heat distribution, providing superior performance in cooking applications exposed to intense flame conditions.
What is Ball Clay?
Ball clay is a highly plastic, fine-grained sedimentary clay composed mainly of kaolinite, mica, and quartz, valued for its exceptional plasticity and strength in ceramic production. Compared to Flameware clay, which is designed for thermal shock resistance and durability in cooking vessels, ball clay improves workability and adds bonding strength but lacks inherent heat resistance. The incorporation of ball clay in cooking vessels enhances formability and firing shrinkage control, yet it requires blending with other clays like Flameware to achieve optimal heat tolerance.
Key Differences Between Flameware and Ball Clay
Flameware clay is specifically designed for high-temperature applications, offering excellent thermal shock resistance and durability in cooking vessels, whereas ball clay is fine-grained and highly plastic but lacks the heat resistance needed for direct flame exposure. Flameware's composition includes materials like kaolin and feldspar that enhance its strength and thermal stability, while ball clay primarily contributes to plasticity and workability in ceramic mixtures. The key difference lies in flameware's superior ability to withstand rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for cookware subjected to direct heat, unlike ball clay which is better suited as a blending agent in ceramic production.
Thermal Shock Resistance in Cooking Applications
Flameware clay exhibits superior thermal shock resistance compared to ball clay, making it ideal for cooking vessels exposed to rapid temperature changes. Its dense microstructure minimizes cracking when transitioning from stovetop heat to cooler environments. Ball clay, while plastic and flexible, tends to have lower thermal shock resistance, increasing the risk of damage under fluctuating cooking temperatures.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns in Food Use
Flameware clay, often composed of high-fire stoneware materials, exhibits excellent durability and low porosity, reducing the risk of chemical leaching and making it safer for cooking vessels. Ball clay, while offering plasticity and workability, may contain higher levels of impurities like kaolinite and mica that can potentially introduce toxic elements when exposed to high temperatures. Prioritizing flameware clay in cookware manufacturing ensures enhanced food safety by minimizing toxic contamination and enhancing thermal resistance.
Durability and Longevity of Clay Cooking Vessels
Flameware clay offers superior durability compared to ball clay, as it is specifically formulated to withstand high temperatures and direct flame exposure without cracking. Ball clay, though smooth and workable, typically lacks the heat resistance necessary for long-term use in cooking vessels, leading to a shorter lifespan. Consequently, cooking vessels made from flameware clay exhibit enhanced longevity and maintain structural integrity under repeated heating cycles.
Heat Retention and Cooking Performance
Flameware clay, composed of heat-resistant minerals, offers superior heat retention, ensuring even cooking temperatures and consistent heat distribution for optimal culinary results. Ball clay, known for its plasticity but higher porosity, absorbs more moisture and retains less heat, which can lead to uneven cooking and longer cooking times. Choosing Flameware clay enhances durability and thermal efficiency, making it more suitable for cooking vessels that require steady, prolonged heat exposure.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and durability, requiring less frequent seasoning and easier cleaning compared to ball clay, which is more porous and prone to cracking under thermal stress. Maintenance of flameware cooking vessels typically involves simple hand washing and occasional oiling, while ball clay cookware demands more careful drying and regular reseasoning to prevent moisture absorption and structural damage. Choosing flameware clay reduces the risk of bacterial buildup and extends the lifespan of cooking vessels due to its dense, non-porous composition and resilience to thermal shock.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Culinary Needs
Flameware clay offers superior thermal shock resistance and durability, making it ideal for cooking vessels exposed to direct flame and rapid temperature changes. Ball clay provides excellent plasticity and workability but lacks the heat resilience required for flame-exposed cookware, limiting its functionality for high-heat applications. Selecting Flameware clay ensures long-lasting performance and safety in cookware, while Ball clay suits decorative or low-heat ceramic uses.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Ball clay for Cooking vessel
 azmater.com
azmater.com