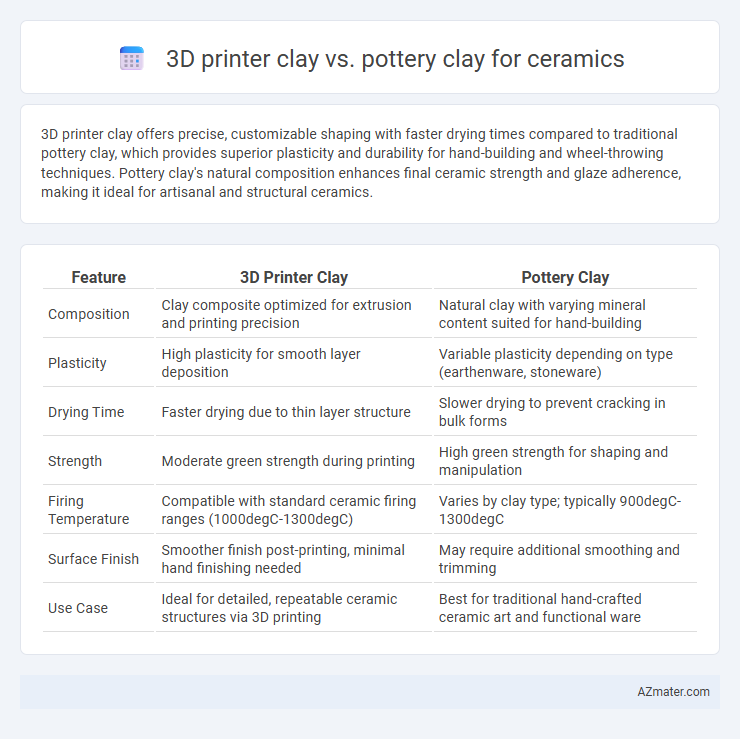
3D printer clay offers precise, customizable shaping with faster drying times compared to traditional pottery clay, which provides superior plasticity and durability for hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques. Pottery clay's natural composition enhances final ceramic strength and glaze adherence, making it ideal for artisanal and structural ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3D Printer Clay | Pottery Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Clay composite optimized for extrusion and printing precision | Natural clay with varying mineral content suited for hand-building |
| Plasticity | High plasticity for smooth layer deposition | Variable plasticity depending on type (earthenware, stoneware) |
| Drying Time | Faster drying due to thin layer structure | Slower drying to prevent cracking in bulk forms |
| Strength | Moderate green strength during printing | High green strength for shaping and manipulation |
| Firing Temperature | Compatible with standard ceramic firing ranges (1000degC-1300degC) | Varies by clay type; typically 900degC-1300degC |
| Surface Finish | Smoother finish post-printing, minimal hand finishing needed | May require additional smoothing and trimming |
| Use Case | Ideal for detailed, repeatable ceramic structures via 3D printing | Best for traditional hand-crafted ceramic art and functional ware |
Introduction to 3D Printer Clay and Pottery Clay
3D printer clay is a specially formulated material designed for additive manufacturing, allowing precise, layer-by-layer construction of ceramic objects with complex geometries that traditional pottery methods struggle to achieve. Pottery clay, typically composed of natural minerals like kaolin and ball clay, offers plasticity and moisture retention crucial for hand-building and wheel-throwing techniques in ceramic art. While 3D printer clay focuses on digital precision and customization, pottery clay remains preferred for tactile manipulation and firing traditions in ceramics.
Material Composition: 3D Printer Clay vs Pottery Clay
3D printer clay typically consists of fine particulate matter mixed with binders designed for extrusion and layer adhesion during the printing process, often incorporating polymers that enhance flexibility and drying control. Pottery clay, on the other hand, is primarily composed of natural minerals like kaolin, ball clay, and silica, providing plasticity and structural integrity essential for hand shaping and wheel throwing. The inorganic and organic composition differences directly impact workability, firing temperatures, and final ceramic strength between 3D printed and traditionally crafted pottery items.
Workability and Handling Differences
3D printer clay offers enhanced workability through its uniform consistency and ability to be precisely extruded, enabling intricate designs and smoother layering compared to traditional pottery clay. Pottery clay provides a more tactile and flexible handling experience, allowing artisans to shape and manipulate the material easily by hand, with variable moisture content affecting its plasticity and drying time. While 3D printer clay excels in automated, detailed production, pottery clay remains preferred for manual craftsmanship due to its responsiveness and traditional textural qualities.
Design Precision and Complexity
3D printer clay offers superior design precision and complexity compared to traditional pottery clay, enabling the creation of intricate shapes and fine details through computer-aided modeling. Pottery clay relies on manual shaping techniques, which can limit the achievable complexity and consistency in design. Digital control in 3D printing allows for repeatable, highly detailed ceramic pieces that are difficult to replicate by hand.
Firing and Sintering Considerations
3D printer clay for ceramics typically involves fine, homogenous particles designed for precise layering and controlled shrinkage during firing, optimizing sintering to achieve strength without excessive warping. Pottery clay, traditionally used in wheel-throwing or hand-building, contains organic materials and impurities that affect firing temperature ranges and sintering behavior, often requiring slower heating rates to avoid cracks or deformation. Understanding the thermal properties and particle size distribution of each clay type is crucial for successful kiln firing, as 3D printed clay benefits from tailored sintering protocols, while pottery clay demands more flexible, experience-based firing schedules.
Surface Finish and Texture Quality
3D printer clay offers precise control over surface finish with smooth, consistent layers ideal for intricate details, while traditional pottery clay provides a more organic texture with natural variations due to hand shaping. The surface finish of 3D-printed ceramics tends to be uniform and can be easily customized through digital modeling, whereas pottery clay results in unique textures influenced by manual techniques. Texture quality in 3D printing often exhibits fine resolution but may require additional smoothing processes, contrasting with the tactile, rougher feel of hand-crafted pottery clay.
Durability and End-product Performance
3D printer clay often exhibits lower durability compared to traditional pottery clay due to its synthetic composition and faster drying rates, which can lead to increased brittleness and cracking. Pottery clay, especially stoneware or porcelain, provides superior end-product performance with enhanced strength, thermal resistance, and long-lasting durability after firing. For ceramic artisans prioritizing functional strength and longevity, pottery clay remains the preferred choice, while 3D printer clay suits prototyping and intricate design work with less mechanical stress.
Creative Flexibility and Artistic Expression
3D printer clay offers unparalleled creative flexibility by enabling intricate and precise designs through digital modeling, allowing artists to experiment with complex geometries unachievable by hand. Pottery clay provides tactile artistic expression, where the hands-on process fosters spontaneity and organic textures unique to traditional craftsmanship. Combining digital precision and manual techniques enhances the scope of ceramic artistry, making each medium valuable for different stages of the creative process.
Cost Analysis: 3D Printer Clay vs Pottery Clay
3D printer clay typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized equipment and filament expenses, while pottery clay remains more affordable with bulk purchasing options and minimal tooling requirements. Operational costs for 3D printer clay include maintenance of printers and frequent filament replacement, contrasting with the relatively low-cost kiln firing and shaping tools used for pottery clay. Over time, pottery clay offers better cost efficiency for large-scale or traditional ceramics production, whereas 3D printer clay suits precision and customized designs despite higher price points.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
3D printer clay offers a sustainable alternative to traditional pottery clay by reducing material waste through precise digital extrusion, minimizing excess use and scrap. Pottery clay often requires energy-intensive processes, such as mining and extensive water consumption, which contribute to environmental degradation. Using 3D printer clay supports eco-friendly ceramics production with lower energy demands, reduced water usage, and less reliance on chemical additives, enhancing overall environmental impact.
Infographic: 3D printer clay vs Pottery clay for Ceramics
 azmater.com
azmater.com