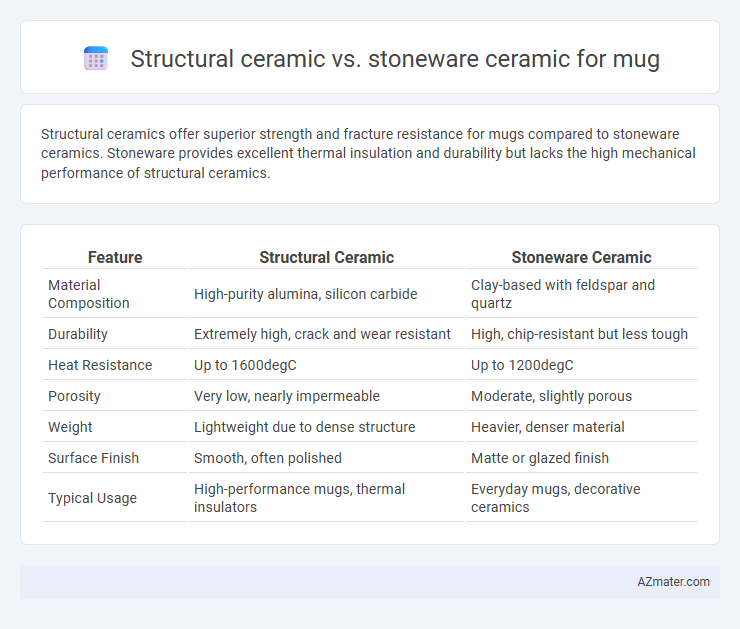
Structural ceramics offer superior strength and fracture resistance for mugs compared to stoneware ceramics. Stoneware provides excellent thermal insulation and durability but lacks the high mechanical performance of structural ceramics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Structural Ceramic | Stoneware Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity alumina, silicon carbide | Clay-based with feldspar and quartz |
| Durability | Extremely high, crack and wear resistant | High, chip-resistant but less tough |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1600degC | Up to 1200degC |
| Porosity | Very low, nearly impermeable | Moderate, slightly porous |
| Weight | Lightweight due to dense structure | Heavier, denser material |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, often polished | Matte or glazed finish |
| Typical Usage | High-performance mugs, thermal insulators | Everyday mugs, decorative ceramics |
Introduction to Structural Ceramic and Stoneware Ceramic
Structural ceramics, characterized by high strength and durability, are engineered materials ideal for functional uses such as mugs requiring resistance to thermal shock and mechanical wear. Stoneware ceramics, a subtype of structural ceramics, are fired at high temperatures between 1,100degC and 1,300degC, resulting in a dense, non-porous material that is both robust and suitable for everyday use. The inherent strength, thermal resistance, and low porosity of stoneware make it a popular choice for mugs intended for hot beverages, combining practical utility with aesthetic appeal.
Composition Differences: Structural vs. Stoneware Ceramic
Structural ceramics are primarily composed of alumina, zirconia, and silicon carbide, offering high strength and thermal shock resistance suitable for technical applications. Stoneware ceramics consist mainly of clay, feldspar, and quartz, providing a dense, non-porous structure ideal for everyday use and food-safe mugs. The key composition difference lies in structural ceramics' engineered inorganic compounds for durability versus stoneware's natural clay and mineral blend for usability and aesthetic appeal.
Manufacturing Processes and Techniques
Structural ceramics for mugs undergo advanced manufacturing processes like powder pressing and sintering, providing high mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance. Stoneware ceramic production employs traditional techniques such as slip casting or jiggering, followed by high-temperature firing, which results in a dense, vitrified, and durable product. Both methods influence the final mug's porosity, durability, and aesthetic, with structural ceramics emphasizing performance and stoneware focusing on classic appeal and robustness.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Structural ceramics exhibit superior durability and strength compared to stoneware ceramics, thanks to their advanced composite materials and high-temperature processing. Structural ceramic mugs resist chipping, cracking, and thermal shock more effectively than stoneware, making them ideal for long-term, heavy use. Stoneware offers good durability but generally falls short of the fracture toughness and impact resistance found in structural ceramics.
Thermal Properties and Heat Retention
Structural ceramics, often made from alumina or silicon carbide, exhibit superior thermal stability and resistance to thermal shock compared to stoneware ceramics, which are primarily composed of clay and fired at lower temperatures. Stoneware mugs offer good heat retention due to their dense, vitrified body but lack the high-temperature endurance and rapid heat dissipation control found in structural ceramics. For applications requiring prolonged thermal insulation and durability under extreme temperature fluctuations, structural ceramic mugs provide enhanced performance over traditional stoneware options.
Aesthetic Qualities and Finish
Structural ceramics used for mugs typically exhibit a sleek, modern aesthetic with smooth, uniform surfaces and high durability, offering a refined matte or glossy finish that resists chipping. Stoneware ceramics present a rustic, earthy appearance characterized by natural variations in color, texture, and glaze, providing a handcrafted feel with a typically heavier, textured finish. The finish of structural ceramics emphasizes precision and strength, while stoneware mugs highlight organic patterns and warmth, appealing to different stylistic preferences in kitchenware.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Structural ceramics used for mugs typically offer greater strength and durability with thinner walls, resulting in lighter weight designs compared to stoneware ceramics. Stoneware mugs generally have thicker walls and higher density, contributing to a heavier and more robust feel that retains heat longer. Weight and thickness considerations influence user comfort and thermal performance, making structural ceramics preferable for lightweight portability and stoneware ideal for heat retention and sturdiness.
Safety and Health Aspects in Everyday Use
Structural ceramics for mugs offer superior chemical inertness and high-temperature resistance, minimizing leaching of harmful substances during daily use, making them safer for hot beverages. Stoneware ceramics are often glazed to enhance durability but may pose risks if low-quality glazes contain lead or cadmium, potentially affecting health over time. Choosing structural ceramic mugs ensures greater safety and longevity by reducing exposure to toxic elements and maintaining structural integrity under repetitive heat stress.
Cost and Availability of Each Material
Structural ceramics, typically made from engineered materials like alumina or zirconia, offer superior strength and durability but come with higher production costs and limited availability due to specialized manufacturing processes. Stoneware ceramics, composed of natural clays fired at high temperatures, are more widely available and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for mass-produced mugs. The cost-efficiency and abundant supply of stoneware result in lower retail prices, whereas structural ceramic mugs are often priced higher due to premium material and fabrication expenses.
Choosing the Best Ceramic for Mugs: Final Recommendations
Structural ceramics offer superior strength and thermal resistance, making them ideal for durable, long-lasting mugs that withstand high temperatures and daily use. Stoneware ceramics provide excellent heat retention and a classic aesthetic, but they may be more prone to chipping and require careful handling. For choosing the best ceramic for mugs, prioritize structural ceramics when durability and heat resistance are essential, while stoneware suits those valuing traditional appearance and feel.
Infographic: Structural ceramic vs Stoneware ceramic for Mug
 azmater.com
azmater.com